12 KiB
| stage | group | info |
|---|---|---|
| Verify | Pipeline Execution | To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/engineering/ux/technical-writing/#assignments |
Merge trains (PREMIUM)
- Introduced in GitLab 12.0.
- Squash and merge support introduced in GitLab 12.6.
For more information about why you might want to use merge trains, read How starting merge trains improve efficiency for DevOps.
When merged results pipelines are enabled, the pipeline jobs run as if the changes from your source branch have already been merged into the target branch.
However, the target branch may be changing rapidly. When you're ready to merge, if you haven't run the pipeline in a while, the target branch may have already changed. Merging now could introduce breaking changes.
Merge trains can prevent this from happening. A merge train is a queued list of merge requests, each waiting to be merged into the target branch.
Many merge requests can be added to the train. Each merge request runs its own merged results pipeline, which includes the changes from all of the other merge requests in front of it on the train. All the pipelines run in parallel, to save time. The author of the internal merged result commit is always the user that initiated the merge.
If the pipeline for a merge request fails, the breaking changes are not merged, and the target branch is unaffected. The merge request is removed from the train, and all pipelines behind it restart.
If the pipeline for the merge request at the front of the train completes successfully, the changes are merged into the target branch, and the other pipelines continue to run.
To add a merge request to a merge train, you need permissions to merge or push to the target branch.
Each merge train can run a maximum of twenty pipelines in parallel. If more than twenty merge requests are added to the merge train, the merge requests are queued until a slot in the merge train is free. There is no limit to the number of merge requests that can be queued.
Merge train example
Three merge requests (A, B and C) are added to a merge train in order, which
creates three merged results pipelines that run in parallel:
- The first pipeline runs on the changes from
Acombined with the target branch. - The second pipeline runs on the changes from
AandBcombined with the target branch. - The third pipeline runs on the changes from
A,B, andCcombined with the target branch.
If the pipeline for B fails, it is removed from the train. The pipeline for
C restarts with the A and C changes, but without the B changes.
If A then completes successfully, it merges into the target branch, and C continues
to run. If more merge requests are added to the train, they now include the A
changes that are included in the target branch, and the C changes that are from
the merge request already in the train.
Watch this video for a demonstration on how parallel execution of merge trains can prevent commits from breaking the default branch.
Prerequisites
To enable merge trains:
- You must have the Maintainer role.
- You must be using GitLab Runner 11.9 or later.
- In GitLab 13.0 and later, you need Redis 5.0 or later.
- Your repository must be a GitLab repository, not an external repository.
Merge trains do not work with Semi-linear history merge requests or fast-forward merge requests.
Enable merge trains
To enable merge trains for your project:
- If you are on a self-managed GitLab instance, ensure the feature flag is set correctly.
- Configure your CI/CD configuration file so that the pipeline or individual jobs run for merge requests.
- On the top bar, select Menu > Projects and find your project.
- On the left sidebar, select Settings > General.
- Expand Merge requests.
- In the Merge method section, verify that Merge commit is selected.
- In the Merge options section, select Enable merged results pipelines (if not already selected) and Enable merge trains.
- Select Save changes.
In GitLab 13.5 and earlier, there is only one checkbox, named Enable merge trains and pipelines for merged results.
WARNING: If you select the check box but don't configure your CI/CD to use merge request pipelines, your merge requests may become stuck in an unresolved state or your pipelines may be dropped.
Start a merge train
To start a merge train:
- Visit a merge request.
- Select Start merge train.
Other merge requests can now be added to the train.
Add a merge request to a merge train
To add a merge request to a merge train:
- Visit a merge request.
- Select Add to merge train.
If pipelines are already running for the merge request, you cannot add the merge request to the train. Instead, you can schedule to add the merge request to a merge train when the latest pipeline succeeds.
Remove a merge request from a merge train
- Visit a merge request.
- Select Remove from merge train.
If you want to add the merge request to a merge train again later, you can.
View a merge request's current position on the merge train
After a merge request has been added to the merge train, the merge request's current position is displayed under the pipeline widget:
Immediately merge a merge request with a merge train
If you have a high-priority merge request (for example, a critical patch) that must be merged urgently, you can bypass the merge train by using the Merge Immediately option. This is the fastest option to get the change merged into the target branch.
WARNING: Each time you merge a merge request immediately, the current merge train is recreated, all pipelines restart, and redundant pipelines are cancelled.
Automatic pipeline cancellation
Introduced in GitLab 12.3.
GitLab CI/CD can detect the presence of redundant pipelines, and cancels them to conserve CI resources.
When a user merges a merge request immediately in an ongoing merge train, the train is reconstructed, because it recreates the expected post-merge commit and pipeline. In this case, the merge train may already have pipelines running against the previous expected post-merge commit. These pipelines are considered redundant and are automatically canceled.
Troubleshooting
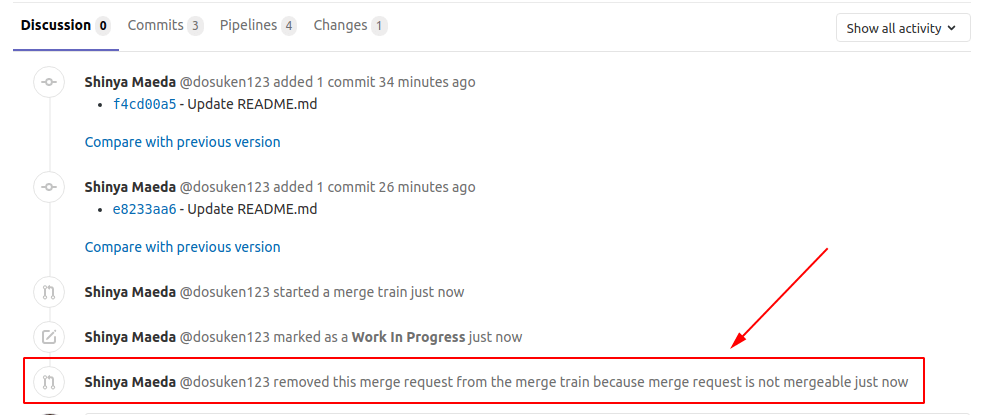
Merge request dropped from the merge train immediately
If a merge request is not mergeable (for example, it's a draft merge request or it has a merge conflict), the merge train drops your merge request automatically.
In these cases, the reason for dropping the merge request is in the system notes.
To check the reason:
- Open the merge request that was dropped from the merge train.
- Select the Discussion tab.
- Find a system note that includes either:
- ... removed this merge request from the merge train because ...
- ... aborted this merge request from the merge train because ...
The reason is given in the text after the because ... phrase.
Merge When Pipeline Succeeds cannot be chosen
Merge When Pipeline Succeeds is currently unavailable when merge trains are enabled.
See the related issue for more information.
Merge train pipeline cannot be retried
When a merge train pipeline fails, the merge request is dropped from the train and the pipeline can't be retried. Merge train pipelines run on the merged result of the changes in the merge request and the changes from other merge requests already on the train. If the merge request is dropped from the train, the merged result is out of date and the pipeline can't be retried.
Instead, you should add the merge request to the train again, which triggers a new pipeline.
If a job only fails intermittently, you can try using the retry
keyword in the .gitlab-ci.yml file to have the job retried before the pipeline completes.
If it succeeds after a retry, the merge request is not removed from the merge train.
Unable to add to merge train with message "The pipeline for this merge request failed."
Sometimes the Start/Add to merge train button is not available and the merge request says, "The pipeline for this merge request failed. Please retry the job or push a new commit to fix the failure."
This issue occurs when Pipelines must succeed is enabled in Settings > General > Merge requests. This option requires that you run a new successful pipeline before you can re-add a merge request to a merge train.
Merge trains ensure that each pipeline has succeeded before a merge happens, so you can:
-
Clear the Pipelines must succeed checkbox.
-
Select the Enable merged results pipelines and Enable merge trains checkboxes.
In GitLab 13.5 and earlier, there is only one checkbox, named Enable merge trains and pipelines for merged results.
If you want to keep the Pipelines must succeed option selected along with merge trains, create a new merged results pipeline when this error occurs:
- On the Pipelines tab, select Run pipeline.
- Select Start/Add to merge train when pipeline succeeds.
See the related issue for more information.
Merge trains feature flag (PREMIUM SELF)
In GitLab 13.6 and later, you can enable or disable merge trains in the project settings.
In GitLab 13.5 and earlier, merge trains are automatically enabled when merged results pipelines are enabled. To use merged results pipelines without using merge trains, you can enable a feature flag that blocks the merge trains feature.
GitLab administrators with access to the GitLab Rails console can enable the feature flag to disable merge trains:
Feature.enable(:disable_merge_trains)
After you enable this feature flag, all existing merge trains are cancelled and the Start/Add to merge train button no longer appears in merge requests.
To disable the feature flag, and enable merge trains again:
Feature.disable(:disable_merge_trains)