5.4 KiB
| type |
|---|
| howto |
Cloud deployment
Interacting with a major cloud provider such as Amazon AWS may have become a much needed task that's part of your delivery process. GitLab is making this process less painful by providing Docker images that come with the needed libraries and tools pre-installed. By referencing them in your CI/CD pipeline, you'll be able to interact with your chosen cloud provider more easily.
AWS
Introduced in GitLab 12.6.
GitLab's AWS Docker image provides the AWS Command Line Interface,
which enables you to run aws commands. As part of your deployment strategy, you can run aws commands directly from
.gitlab-ci.yml by specifying GitLab's AWS Docker image.
Some credentials are required to be able to run aws commands:
-
Sign up for an AWS account if you don't have one yet.
-
Log in onto the console and create a new IAM user.
-
Select your newly created user to access its details. Navigate to Security credentials > Create a new access key.
NOTE: Note: A new Access key ID and Secret access key pair will be generated. Please take a note of them right away.
-
In your GitLab project, go to Settings > CI / CD. Set the Access key ID and Secret access key as environment variables, using the following variable names:
Env. variable name Value AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDYour "Access key ID" AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYYour "Secret access key" -
You can now use
awscommands in the.gitlab-ci.ymlfile of this project:deploy: stage: deploy image: registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/cloud-deploy:latest # see the note below script: - aws s3 ... - aws create-deployment ...NOTE: Note: Please note that the image used in the example above (
registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/cloud-deploy:latest) is hosted on the GitLab Container Registry and is ready to use. Alternatively, replace the image with another one hosted on AWS ECR.
AWS ECR
Instead of referencing an image hosted on the GitLab Registry, you are free to reference any other image hosted on any third-party registry, such as Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR).
To do so, please make sure to push your image into your ECR
repository
before referencing it in your .gitlab-ci.yml file and replace the image
path to point to your ECR.
Deploy your application to AWS Elastic Container Service (ECS)
Introduced in GitLab 12.9.
GitLab provides a series of CI templates that you can include in your project.
To automate deployments of your application to your Amazon Elastic Container Service (AWS ECS)
cluster, you can include the Deploy-ECS.gitlab-ci.yml template in your .gitlab-ci.yml file.
Before getting started with this process, you need a cluster on AWS ECS, as well as related components, like an ECS service, ECS task definition, a database on AWS RDS, etc. Read more about AWS ECS.
After you're all set up on AWS ECS, follow these steps:
-
Make sure your AWS credentials are set up as environment variables for your project. You can follow the steps above to complete this setup.
-
Add these variables to your project's
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile:variables: CI_AWS_ECS_CLUSTER: my-cluster CI_AWS_ECS_SERVICE: my-service CI_AWS_ECS_TASK_DEFINITION: my-task-definitionThree variables are defined in this snippet:
CI_AWS_ECS_CLUSTER: The name of your AWS ECS cluster that you're targeting for your deployments.CI_AWS_ECS_SERVICE: The name of the targeted service tied to your AWS ECS cluster.CI_AWS_ECS_TASK_DEFINITION: The name of the task definition tied to the service mentioned above.
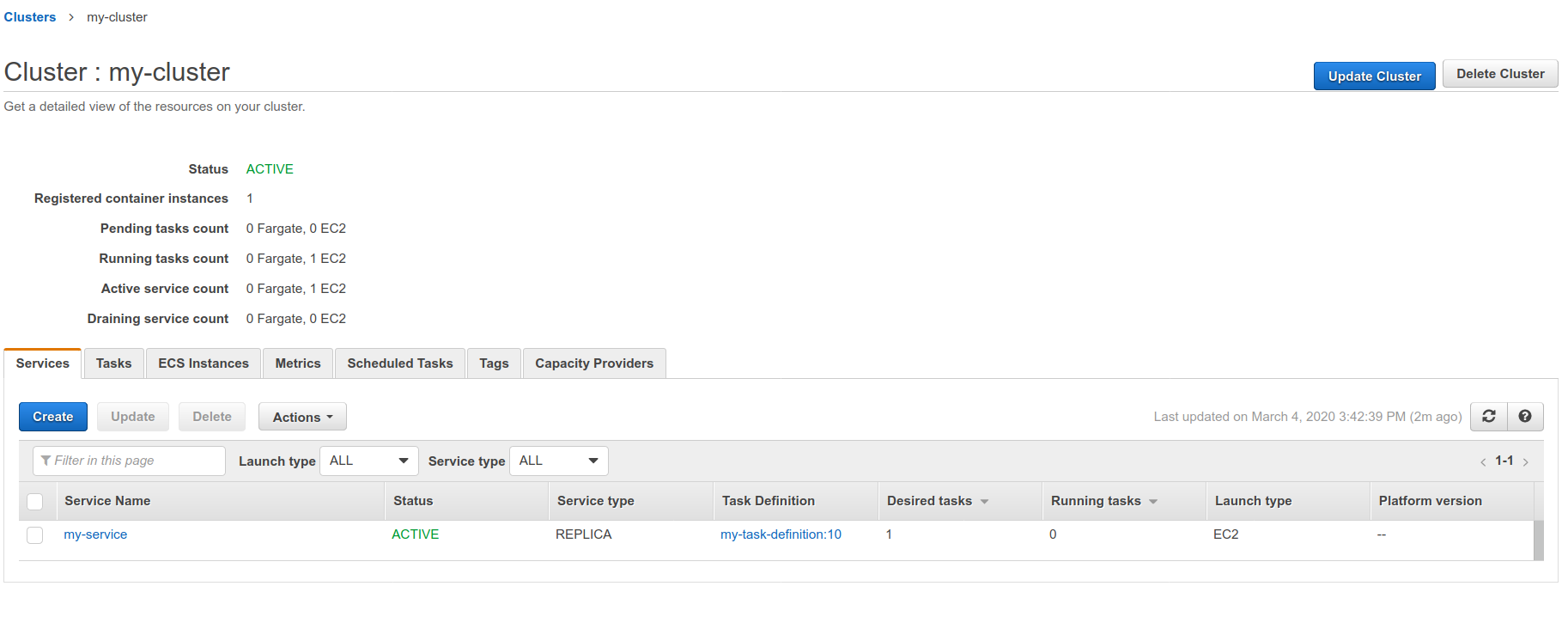
You can find these names after selecting the targeted cluster on your AWS ECS dashboard:
-
Include this template in
.gitlab-ci.yml:include: - template: Deploy-ECS.gitlab-ci.ymlThe
Deploy-ECStemplate ships with GitLab and is available on GitLab.com. -
Commit and push your updated
.gitlab-ci.ymlto your project's repository, and you're done!Your application Docker image will be rebuilt and pushed to the GitLab registry. Then the targeted task definition will be updated with the location of the new Docker image, and a new revision will be created in ECS as result.
Finally, your AWS ECS service will be updated with the new revision of the task definition, making the cluster pull the newest version of your application.