10 KiB
Extra Sidekiq processes (STARTER ONLY)
NOTE: Note: The information in this page applies only to Omnibus GitLab.
GitLab Starter allows one to start an extra set of Sidekiq processes besides the default one. These processes can be used to consume a dedicated set of queues. This can be used to ensure certain queues always have dedicated workers, no matter the number of jobs that need to be processed.
Available Sidekiq queues
For a list of the existing Sidekiq queues, check the following files:
Each entry in the above files represents a queue on which extra Sidekiq processes can be started.
Starting extra processes
To start extra Sidekiq processes, you must enable sidekiq-cluster:
-
Edit
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband add:sidekiq_cluster['enable'] = true -
You will then need to specify how many additional processes to create via
sidekiq-clusterand which queue they should handle via thesidekiq_cluster['queue_groups']array setting. Each item in the array equates to one additional Sidekiq process, and values in each item determine the queues it works on.For example, the following setting adds additional Sidekiq processes to two queues, one to
elastic_indexerand one tomailers:sidekiq_cluster['queue_groups'] = [ "elastic_indexer", "mailers" ]To have an additional Sidekiq process handle multiple queues, add multiple queue names to its item delimited by commas. For example:
sidekiq_cluster['queue_groups'] = [ "elastic_indexer, elastic_commit_indexer", "mailers" ] -
Save the file and reconfigure GitLab for the changes to take effect:
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
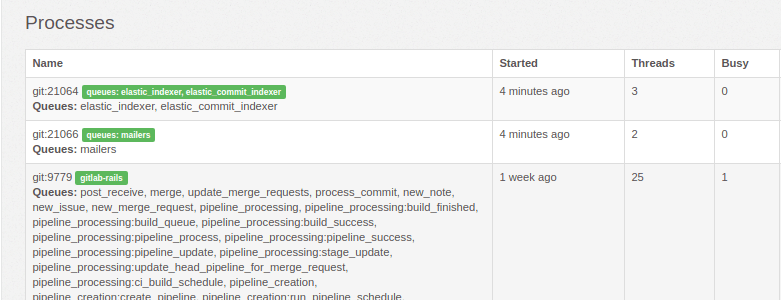
Once the extra Sidekiq processes are added, you can visit the "Background Jobs"
section under the admin area in GitLab (/admin/background_jobs).
Negating settings
To have the additional Sidekiq processes work on every queue except the ones you list:
-
After you follow the steps for starting extra processes, edit
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband add:sidekiq_cluster['negate'] = true -
Save the file and reconfigure GitLab for the changes to take effect:
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
Ignore all GitHub import queues
When importing from GitHub, Sidekiq might
use all of its resources to perform those operations. To set up a separate
sidekiq-cluster process to ignore all GitHub import-related queues:
-
Edit
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband add:sidekiq_cluster['enable'] = true sidekiq_cluster['negate'] = true sidekiq_cluster['queue_groups'] = [ "github_import_advance_stage", "github_importer:github_import_import_diff_note", "github_importer:github_import_import_issue", "github_importer:github_import_import_note", "github_importer:github_import_import_lfs_object", "github_importer:github_import_import_pull_request", "github_importer:github_import_refresh_import_jid", "github_importer:github_import_stage_finish_import", "github_importer:github_import_stage_import_base_data", "github_importer:github_import_stage_import_issues_and_diff_notes", "github_importer:github_import_stage_import_notes", "github_importer:github_import_stage_import_lfs_objects", "github_importer:github_import_stage_import_pull_requests", "github_importer:github_import_stage_import_repository" ] -
Save the file and reconfigure GitLab for the changes to take effect:
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
Number of threads
Each process defined under sidekiq_cluster starts with a
number of threads that equals the number of queues, plus one spare thread.
For example, a process that handles the process_commit and post_receive
queues will use three threads in total.
Limiting concurrency
To limit the concurrency of the Sidekiq process:
-
Edit
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband add:sidekiq['concurrency'] = 25 -
Save the file and reconfigure GitLab for the changes to take effect:
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
To limit the max concurrency of the Sidekiq cluster processes:
-
Edit
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband add:sidekiq_cluster['max_concurrency'] = 25 -
Save the file and reconfigure GitLab for the changes to take effect:
sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure
For each queue group, the concurrency factor will be set to min(number of queues, N).
Setting the value to 0 will disable the limit. Keep in mind this normally would
not exceed the number of CPU cores available.
Each thread requires a Redis connection, so adding threads may increase Redis latency and potentially cause client timeouts. See the Sidekiq documentation about Redis for more details.
Modifying the check interval
To modify the check interval for the additional Sidekiq processes:
-
Edit
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband add:sidekiq_cluster['interval'] = 5 -
Save the file and reconfigure GitLab for the changes to take effect.
This tells the additional processes how often to check for enqueued jobs.
Troubleshooting using the CLI
CAUTION: Warning:
It's recommended to use /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb to configure the Sidekiq processes.
If you experience a problem, you should contact GitLab support. Use the command
line at your own risk.
For debugging purposes, you can start extra Sidekiq processes by using the command
/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/ee/bin/sidekiq-cluster. This command
takes arguments using the following syntax:
/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/ee/bin/sidekiq-cluster [QUEUE,QUEUE,...] [QUEUE, ...]
Each separate argument denotes a group of queues that have to be processed by a Sidekiq process. Multiple queues can be processed by the same process by separating them with a comma instead of a space.
Instead of a queue, a queue namespace can also be provided, to have the process automatically listen on all queues in that namespace without needing to explicitly list all the queue names. For more information about queue namespaces, see the relevant section in the Sidekiq style guide.
For example, say you want to start 2 extra processes: one to process the
process_commit queue, and one to process the post_receive queue. This can be
done as follows:
/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/ee/bin/sidekiq-cluster process_commit post_receive
If you instead want to start one process processing both queues, you'd use the following syntax:
/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/ee/bin/sidekiq-cluster process_commit,post_receive
If you want to have one Sidekiq process dealing with the process_commit and
post_receive queues, and one process to process the gitlab_shell queue,
you'd use the following:
/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/ee/bin/sidekiq-cluster process_commit,post_receive gitlab_shell
Monitoring the sidekiq-cluster command
The sidekiq-cluster command will not terminate once it has started the desired
amount of Sidekiq processes. Instead, the process will continue running and
forward any signals to the child processes. This makes it easy to stop all
Sidekiq processes as you simply send a signal to the sidekiq-cluster process,
instead of having to send it to the individual processes.
If the sidekiq-cluster process crashes or receives a SIGKILL, the child
processes will terminate themselves after a few seconds. This ensures you don't
end up with zombie Sidekiq processes.
All of this makes monitoring the processes fairly easy. Simply hook up
sidekiq-cluster to your supervisor of choice (e.g. runit) and you're good to
go.
If a child process died the sidekiq-cluster command will signal all remaining
process to terminate, then terminate itself. This removes the need for
sidekiq-cluster to re-implement complex process monitoring/restarting code.
Instead you should make sure your supervisor restarts the sidekiq-cluster
process whenever necessary.
PID files
The sidekiq-cluster command can store its PID in a file. By default no PID
file is written, but this can be changed by passing the --pidfile option to
sidekiq-cluster. For example:
/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/ee/bin/sidekiq-cluster --pidfile /var/run/gitlab/sidekiq_cluster.pid process_commit
Keep in mind that the PID file will contain the PID of the sidekiq-cluster
command and not the PID(s) of the started Sidekiq processes.
Environment
The Rails environment can be set by passing the --environment flag to the
sidekiq-cluster command, or by setting RAILS_ENV to a non-empty value. The
default value can be found in /opt/gitlab/etc/gitlab-rails/env/RAILS_ENV.
Using negation
You're able to run all queues in sidekiq_queues.yml file on a single or
multiple processes with exceptions using the --negate flag.
For example, say you want to run a single process for all queues,
except process_commit and post_receive:
/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/ee/bin/sidekiq-cluster process_commit,post_receive --negate
For multiple processes of all queues (except process_commit and post_receive):
/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/ee/bin/sidekiq-cluster process_commit,post_receive process_commit,post_receive --negate
Limiting concurrency
By default, sidekiq-cluster will spin up extra Sidekiq processes that use
one thread per queue up to a maximum of 50. If you wish to change the cap, use
the -m N option. For example, this would cap the maximum number of threads to 1:
/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/ee/bin/sidekiq-cluster process_commit,post_receive -m 1