4.8 KiB
Repository mirroring
Repository Mirroring is a way to mirror repositories from external sources. It can be used to mirror all branches, tags, and commits that you have in your repository.
Your mirror at GitLab will be updated automatically. You can also manually trigger an update at most once every 5 minutes.
Overview
Repository mirroring is very useful when, for some reason, you must use a project from another source.
There are two kinds of repository mirroring features supported by GitLab: push and pull, the latter being only available in GitLab Enterprise Edition. The push method mirrors the repository in GitLab to another location.
Once the mirror repository is updated, all new branches, tags, and commits will be visible in the project's activity feed. Users with at least developer access to the project can also force an immediate update with the click of a button. This button will not be available if the mirror is already being updated or 5 minutes still haven't passed since its last update.
A few things/limitations to consider:
- The repository must be accessible over
http://,https://,ssh://orgit://. - If your HTTP repository is not publicly accessible, add authentication
information to the URL, like:
https://username@gitlab.company.com/group/project.git. In some cases, you might need to use a personal access token instead of a password, e.g., you want to mirror to GitHub and have 2FA enabled. - The import will time out after 15 minutes. For repositories that take longer use a clone/push combination.
- The Git LFS objects will not be synced. You'll need to push/pull them manually.
Use-case
- You have old projects in another source that you don't use actively anymore, but don't want to remove for archiving purposes. In that case, you can create a push mirror so that your active GitLab repository can push its changes to the old location.
Pushing to a remote repository [STARTER]
Introduced in GitLab Enterprise Edition 8.7. Moved to GitLab Community Edition in 10.8.
For an existing project, you can set up push mirror from your project's Settings ➔ Repository and searching for the "Push to a remote repository" section. Check the "Remote mirror repository" box and fill in the Git URL of the repository to push to. Click Save changes for the changes to take effect.
When push mirroring is enabled, you are advised not to push commits directly to the mirrored repository to prevent the mirror diverging. All changes will end up in the mirrored repository whenever commits are pushed to GitLab, or when a forced update is initiated.
Pushes into GitLab are automatically pushed to the remote mirror at least once every 5 minutes after they are received or once every minute if push only protected branches is enabled.
In case of a diverged branch, you will see an error indicated at the Mirror repository settings.
Push only protected branches
Introduced in GitLab Enterprise Edition 10.3. Moved to GitLab Community Edition in 10.8.
You can choose to only push your protected branches from GitLab to your remote repository.
To use this option go to your project's repository settings page under push mirror.
Setting up a push mirror from GitLab to GitHub
To set up a mirror from GitLab to GitHub, you need to follow these steps:
-
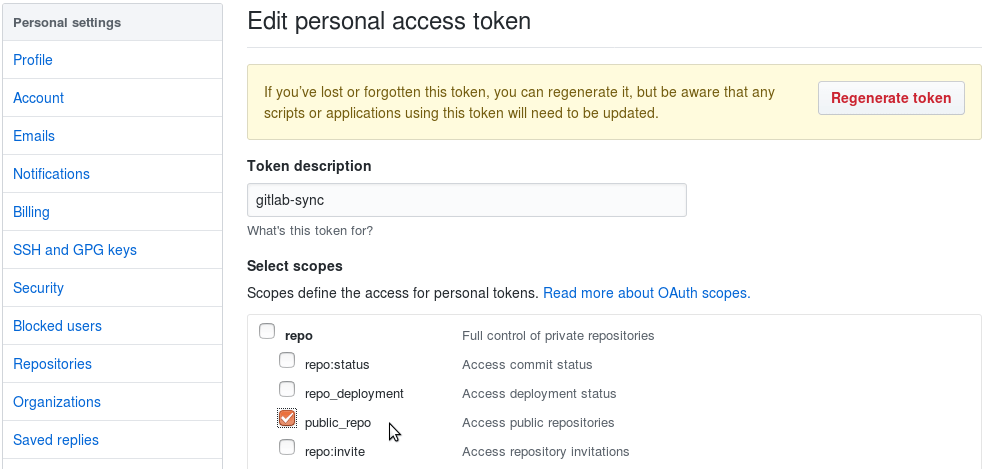
Create a GitHub personal access token with the "public_repo" box checked:
-
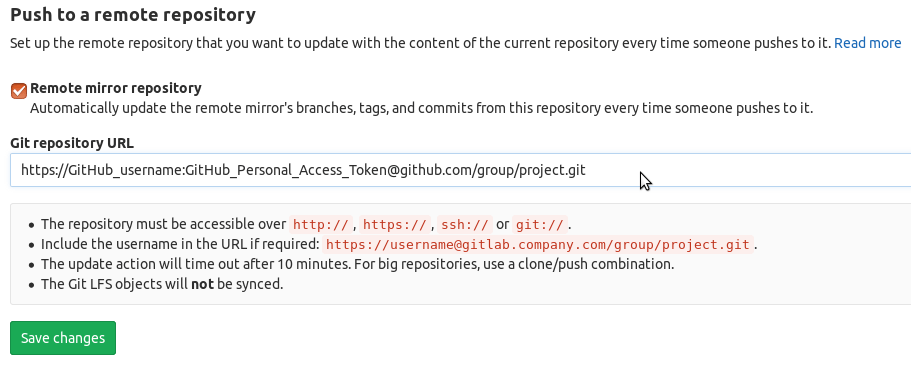
Fill in the "Git repository URL" with the personal access token replacing the password
https://GitHubUsername:GitHubPersonalAccessToken@github.com/group/project.git: -
Save
-
And either wait or trigger the "Update Now" button:
Forcing an update
While mirrors are scheduled to update automatically, you can always force an update by using the Update now button which is exposed in various places:
- in the commits page
- in the branches page
- in the tags page
- in the Mirror repository settings page