8.3 KiB
Frontend Testing
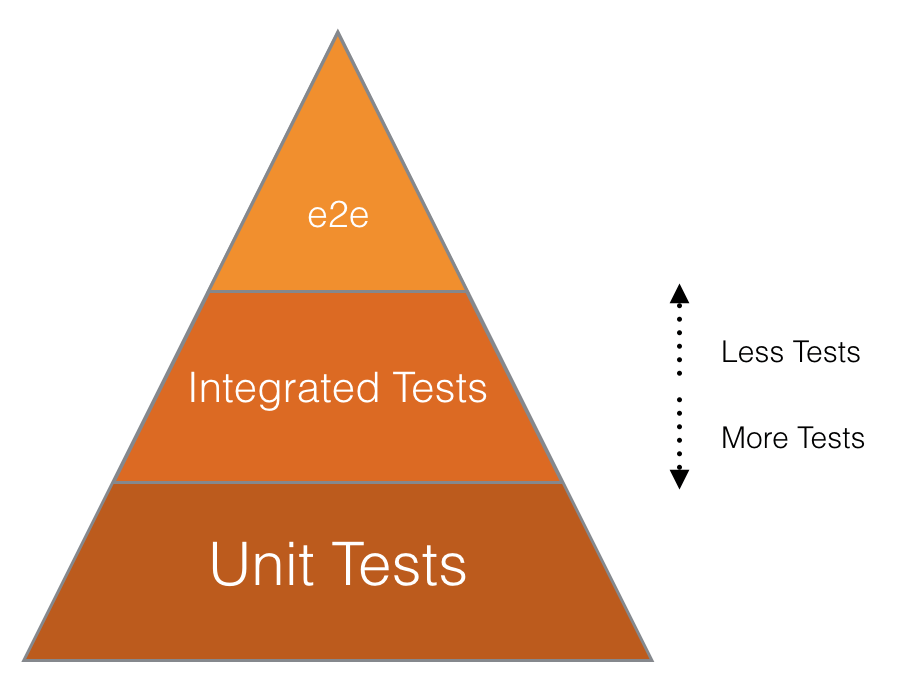
There are two types of test suites you'll encounter while developing frontend code at GitLab. We use Karma and Jasmine for JavaScript unit and integration testing, and RSpec feature tests with Capybara for e2e (end-to-end) integration testing.
Unit and feature tests need to be written for all new features. Most of the time, you should use rspec for your feature tests. There are cases where the behaviour you are testing is not worth the time spent running the full application, for example, if you are testing styling, animation, edge cases or small actions that don't involve the backend, you should write an integration test using Jasmine.
This diagram demonstrates the relative priority of each test type we use
Regression tests should be written for bug fixes to prevent them from recurring in the future.
See the Testing Standards and Style Guidelines for more information on general testing practices at GitLab.
Karma test suite
GitLab uses the Karma test runner with Jasmine as its test
framework for our JavaScript unit and integration tests. For integration tests,
we generate HTML files using RSpec (see spec/javascripts/fixtures/*.rb for examples).
Some fixtures are still HAML templates that are translated to HTML files using the same mechanism (see static_fixtures.rb).
Adding these static fixtures should be avoided as they are harder to keep up to date with real views.
The existing static fixtures will be migrated over time.
Please see gitlab-org/gitlab-ce#24753 to track our progress.
Fixtures are served during testing by the jasmine-jquery plugin.
JavaScript tests live in spec/javascripts/, matching the folder structure
of app/assets/javascripts/: app/assets/javascripts/behaviors/autosize.js
has a corresponding spec/javascripts/behaviors/autosize_spec.js file.
Keep in mind that in a CI environment, these tests are run in a headless
browser and you will not have access to certain APIs, such as
Notification,
which will have to be stubbed.
Best practice
Naming unit tests
When writing describe test blocks to test specific functions/methods, please use the method name as the describe block name.
// Good
describe('methodName', () => {
it('passes', () => {
expect(true).toEqual(true);
});
});
// Bad
describe('#methodName', () => {
it('passes', () => {
expect(true).toEqual(true);
});
});
// Bad
describe('.methodName', () => {
it('passes', () => {
expect(true).toEqual(true);
});
});
Testing Promises
When testing Promises you should always make sure that the test is asynchronous and rejections are handled.
Your Promise chain should therefore end with a call of the done callback and done.fail in case an error occurred.
// Good
it('tests a promise', (done) => {
promise
.then((data) => {
expect(data).toBe(asExpected);
})
.then(done)
.catch(done.fail);
});
// Good
it('tests a promise rejection', (done) => {
promise
.then(done.fail)
.catch((error) => {
expect(error).toBe(expectedError);
})
.then(done)
.catch(done.fail);
});
// Bad (missing done callback)
it('tests a promise', () => {
promise
.then((data) => {
expect(data).toBe(asExpected);
})
});
// Bad (missing catch)
it('tests a promise', (done) => {
promise
.then((data) => {
expect(data).toBe(asExpected);
})
.then(done)
});
// Bad (use done.fail in asynchronous tests)
it('tests a promise', (done) => {
promise
.then((data) => {
expect(data).toBe(asExpected);
})
.then(done)
.catch(fail)
});
// Bad (missing catch)
it('tests a promise rejection', (done) => {
promise
.catch((error) => {
expect(error).toBe(expectedError);
})
.then(done)
});
Stubbing
For unit tests, you should stub methods that are unrelated to the current unit you are testing. If you need to use a prototype method, instantiate an instance of the class and call it there instead of mocking the instance completely.
For integration tests, you should stub methods that will effect the stability of the test if they execute their original behaviour. i.e. Network requests.
Vue.js unit tests
See this section.
Running frontend tests
rake karma runs the frontend-only (JavaScript) tests.
It consists of two subtasks:
rake karma:fixtures(re-)generates fixturesrake karma:testsactually executes the tests
As long as the fixtures don't change, rake karma:tests (or yarn karma)
is sufficient (and saves you some time).
Live testing and focused testing
While developing locally, it may be helpful to keep karma running so that you
can get instant feedback on as you write tests and modify code. To do this
you can start karma with npm run karma-start. It will compile the javascript
assets and run a server at http://localhost:9876/ where it will automatically
run the tests on any browser which connects to it. You can enter that url on
multiple browsers at once to have it run the tests on each in parallel.
While karma is running, any changes you make will instantly trigger a recompile
and retest of the entire test suite, so you can see instantly if you've broken
a test with your changes. You can use jasmine focused or
excluded tests (with fdescribe or xdescribe) to get karma to run only the
tests you want while you're working on a specific feature, but make sure to
remove these directives when you commit your code.
RSpec Feature Integration Tests
Information on setting up and running RSpec integration tests with Capybara can be found in the general testing guide.
Gotchas
Errors due to use of unsupported JavaScript features
Similar errors will be thrown if you're using JavaScript features not yet supported by the PhantomJS test runner which is used for both Karma and RSpec tests. We polyfill some JavaScript objects for older browsers, but some features are still unavailable:
- Array.from
- Array.first
- Async functions
- Generators
- Array destructuring
- For..Of
- Symbol/Symbol.iterator
- Spread
Until these are polyfilled appropriately, they should not be used. Please update this list with additional unsupported features.
RSpec errors due to JavaScript
By default RSpec unit tests will not run JavaScript in the headless browser and will simply rely on inspecting the HTML generated by rails.
If an integration test depends on JavaScript to run correctly, you need to make sure the spec is configured to enable JavaScript when the tests are run. If you don't do this you'll see vague error messages from the spec runner.
To enable a JavaScript driver in an rspec test, add :js to the
individual spec or the context block containing multiple specs that need
JavaScript enabled:
# For one spec
it 'presents information about abuse report', :js do
# assertions...
end
describe "Admin::AbuseReports", :js do
it 'presents information about abuse report' do
# assertions...
end
it 'shows buttons for adding to abuse report' do
# assertions...
end
end
Spinach errors due to missing JavaScript
Note: Since we are discouraging the use of Spinach when writing new feature tests, you shouldn't ever need to use this. This information is kept available for legacy purposes only.
In Spinach, the JavaScript driver is enabled differently. In the *.feature
file for the failing spec, add the @javascript flag above the Scenario:
@javascript
Scenario: Developer can approve merge request
Given I am a "Shop" developer
And I visit project "Shop" merge requests page
And merge request 'Bug NS-04' must be approved
And I click link "Bug NS-04"
When I click link "Approve"
Then I should see approved merge request "Bug NS-04"