2.2 KiB
| stage | group | info |
|---|---|---|
| Create | Ecosystem | To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/engineering/ux/technical-writing/#assignments |
Redmine Service (FREE)
-
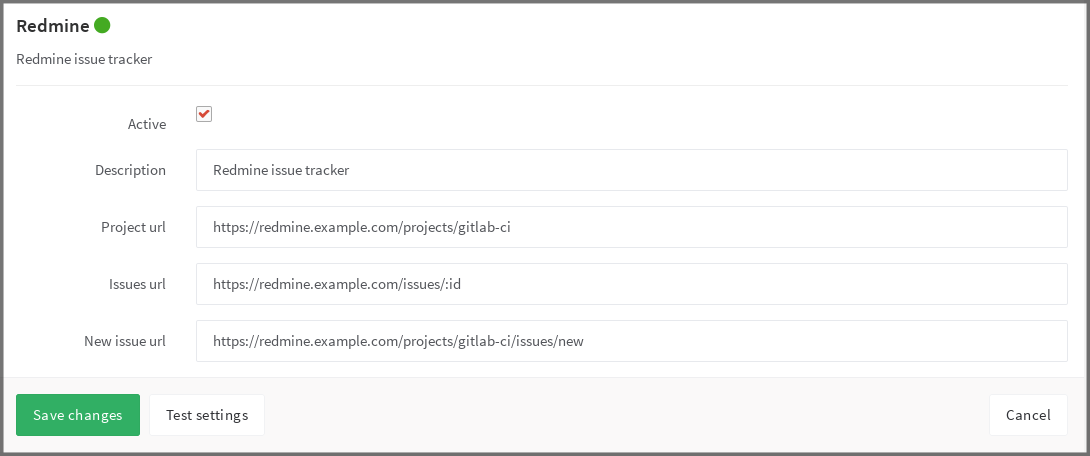
To enable the Redmine integration in a project, navigate to the Integrations page, click the Redmine service, and fill in the required details on the page as described in the table below.
Field Description project_urlThe URL to the project in Redmine which is being linked to this GitLab project issues_urlThe URL to the issue in Redmine project that is linked to this GitLab project. Note that the issues_urlrequires:idin the URL. This ID is used by GitLab as a placeholder to replace the issue number.new_issue_urlThis is the URL to create a new issue in Redmine for the project linked to this GitLab project. This is currently not being used and is planned be removed in a future release. Once you have configured and enabled Redmine, you see the Redmine link on the GitLab project pages that takes you to the appropriate Redmine project.
As an example, below is a configuration for a project named
gitlab-ci. -
To disable the internal issue tracking system in a project, navigate to the General page, expand the permissions section and switch the Issues toggle to disabled.
Referencing issues in Redmine
Issues in Redmine can be referenced in two alternative ways:
#<ID>where<ID>is a number (example#143).<PROJECT>-<ID>where<PROJECT>starts with a capital letter which is then followed by capital letters, numbers or underscores, and<ID>is a number (exampleAPI_32-143).
We suggest using the longer format if you have both internal and external issue trackers enabled. If you use the shorter format and an issue with the same ID exists in the internal issue tracker, the internal issue is linked.
Please note that <PROJECT> part is ignored and links always point to the
address specified in issues_url.