5.7 KiB
Integrate your GitLab instance with GitHub
You can integrate your GitLab instance with GitHub.com as well as GitHub Enterprise to enable users to import projects from GitHub and/or to login to your GitLab instance with your GitHub account.
Enabling GitHub OAuth
To enable GitHub OmniAuth provider, you must use GitHub's credentials for your GitLab instance. To get the credentials (a pair of Client ID and Client Secret), you must register an application as an OAuth App on GitHub.
-
Sign in to GitHub.
-
Navigate to your individual user or organization settings, depending on how you want the application registered. It does not matter if the application is registered as an individual or an organization - that is entirely up to you.
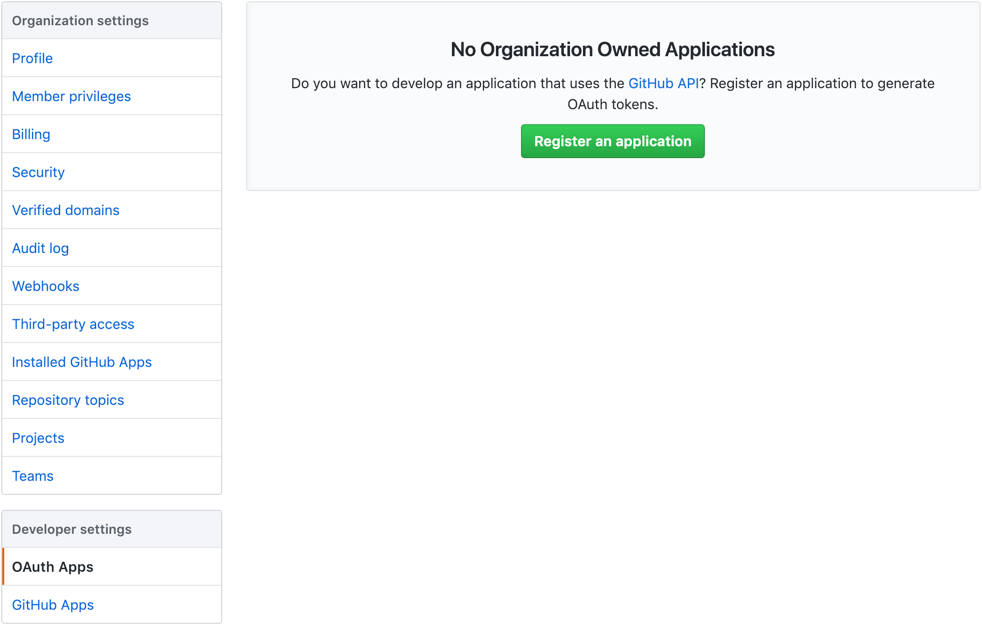
- For individual accounts, select Developer settings from the left menu, then select OAuth Apps.
- For organization accounts, directly select OAuth Apps from the left menu.
-
Select Register an application (if you don't have any OAuth App) or New OAuth App (if you already have OAuth Apps).
-
Provide the required details.
- Application name: This can be anything. Consider something like
<Organization>'s GitLabor<Your Name>'s GitLabor something else descriptive. - Homepage URL: the URL to your GitLab installation. e.g.,
https://gitlab.company.com - Application description: Fill this in if you wish.
- Authorization callback URL:
http(s)://${YOUR_DOMAIN}/users/auth. Please make sure the port is included if your GitLab instance is not configured on default port.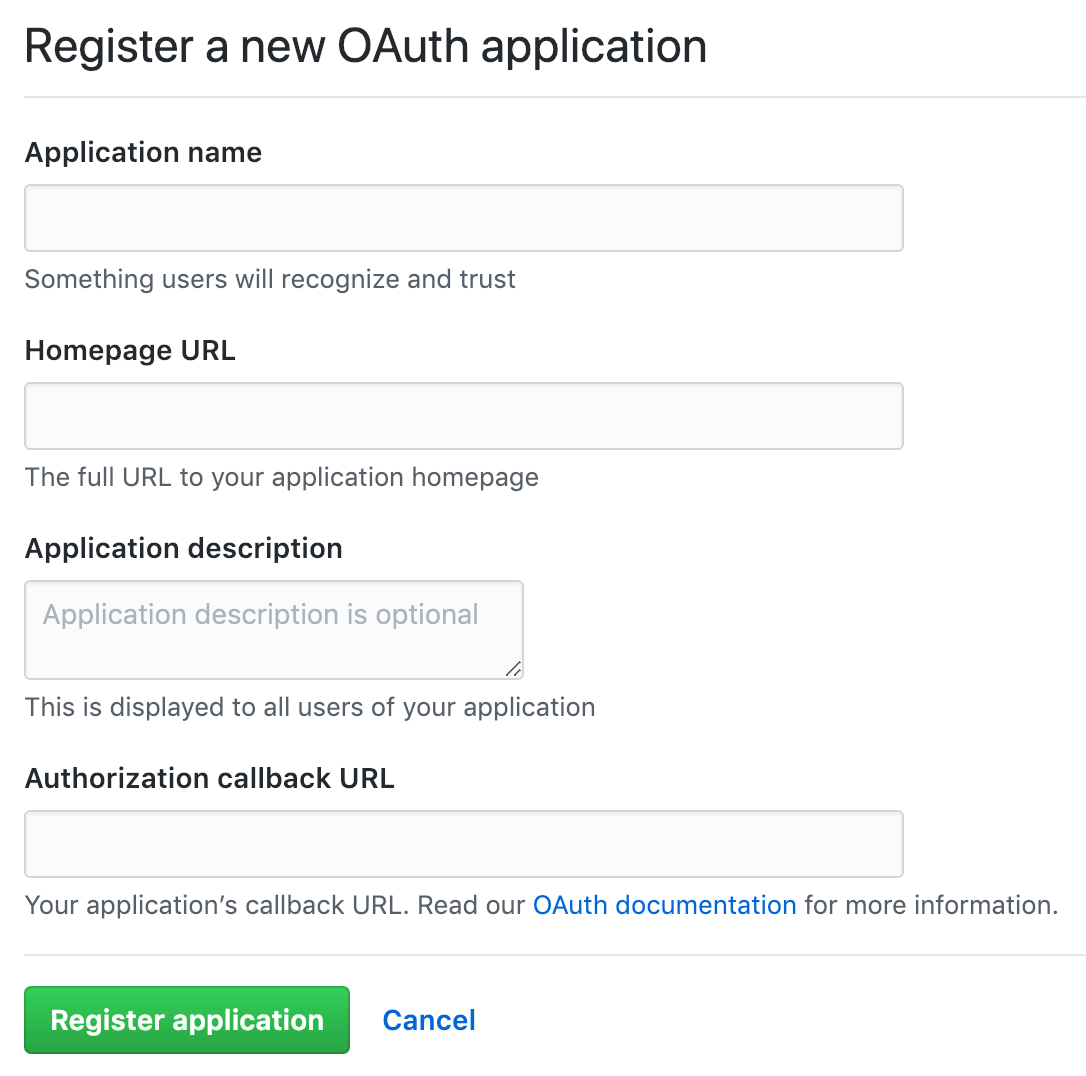
NOTE: Be sure to append
/users/authto the end of the callback URL to prevent a OAuth2 convert redirect vulnerability. - Application name: This can be anything. Consider something like
-
Select Register application.
-
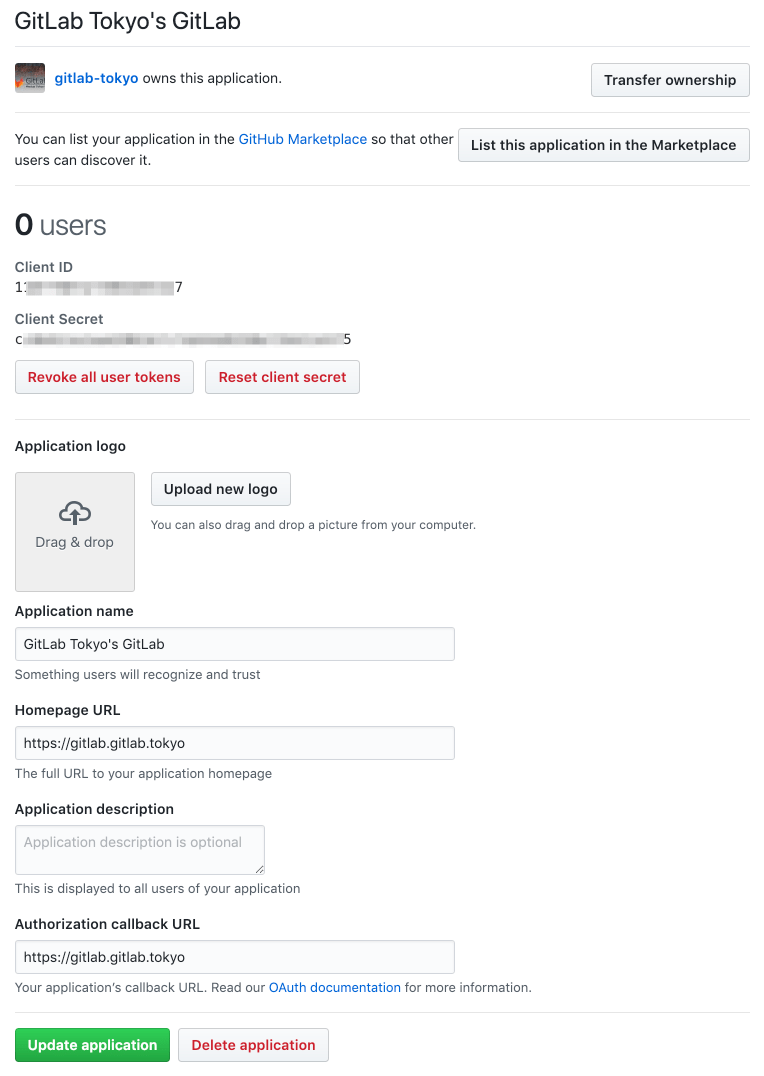
You should now see a pair of Client ID and Client Secret near the top right of the page (see screenshot). Keep this page open as you continue configuration.
-
On your GitLab server, open the configuration file.
For omnibus package:
sudo editor /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rbFor installations from source:
cd /home/git/gitlab sudo -u git -H editor config/gitlab.yml -
See Initial OmniAuth Configuration for initial settings.
-
Add the provider configuration:
For omnibus package:
For GitHub.com:
gitlab_rails['omniauth_providers'] = [ { "name" => "github", "app_id" => "YOUR_APP_ID", "app_secret" => "YOUR_APP_SECRET", "args" => { "scope" => "user:email" } } ]For GitHub Enterprise:
gitlab_rails['omniauth_providers'] = [ { "name" => "github", "app_id" => "YOUR_APP_ID", "app_secret" => "YOUR_APP_SECRET", "url" => "https://github.example.com/", "args" => { "scope" => "user:email" } } ]For installation from source:
For GitHub.com:
- { name: 'github', app_id: 'YOUR_APP_ID', app_secret: 'YOUR_APP_SECRET', args: { scope: 'user:email' } }For GitHub Enterprise:
- { name: 'github', app_id: 'YOUR_APP_ID', app_secret: 'YOUR_APP_SECRET', url: "https://github.example.com/", args: { scope: 'user:email' } }Replace
https://github.example.com/with your GitHub URL. -
Change
YOUR_APP_IDto the Client ID from the GitHub application page from step 6. -
Change
YOUR_APP_SECRETto the Client Secret from the GitHub application page from step 6. -
Save the configuration file.
-
Reconfigure GitLab or restart GitLab for the changes to take effect if you installed GitLab via Omnibus or from source respectively.
On the sign in page there should now be a GitHub icon below the regular sign in form. Click the icon to begin the authentication process. GitHub will ask the user to sign in and authorize the GitLab application. If everything goes well the user will be returned to GitLab and will be signed in.
GitHub Enterprise with self-signed Certificate
If you are attempting to import projects from GitHub Enterprise with a self-signed
certificate and the imports are failing, you will need to disable SSL verification.
It should be disabled by adding verify_ssl to false in the provider configuration
and changing the global Git sslVerify option to false in the GitLab server.
For omnibus package:
gitlab_rails['omniauth_providers'] = [
{
"name" => "github",
"app_id" => "YOUR_APP_ID",
"app_secret" => "YOUR_APP_SECRET",
"url" => "https://github.example.com/",
"verify_ssl" => false,
"args" => { "scope" => "user:email" }
}
]
You will also need to disable Git SSL verification on the server hosting GitLab.
omnibus_gitconfig['system'] = { "http" => ["sslVerify = false"] }
For installation from source:
- { name: 'github', app_id: 'YOUR_APP_ID',
app_secret: 'YOUR_APP_SECRET',
url: "https://github.example.com/",
verify_ssl: false,
args: { scope: 'user:email' } }
You will also need to disable Git SSL verification on the server hosting GitLab.
$ git config --global http.sslVerify false
For the changes to take effect, reconfigure GitLab if you installed via Omnibus, or restart GitLab if you installed from source.