7.4 KiB
Prometheus integration
Introduced in GitLab 9.0.
GitLab offers powerful integration with Prometheus for monitoring key metrics of your apps, directly within GitLab. Metrics for each environment are retrieved from Prometheus, and then displayed within the GitLab interface.
There are two ways to set up Prometheus integration, depending on where your apps are running:
- For deployments on Kubernetes, GitLab can automatically deploy and manage Prometheus.
- For other deployment targets, simply specify the Prometheus server.
Once enabled, GitLab will automatically detect metrics from known services in the metric library.
Enabling Prometheus Integration
Managed Prometheus on Kubernetes
Note
: Introduced in GitLab 10.5
GitLab can seamlessly deploy and manage Prometheus on a connected Kubernetes cluster, making monitoring of your apps easy.
Requirements
- A connected Kubernetes cluster
- Helm Tiller installed by GitLab
Getting started
Once you have a connected Kubernetes cluster with Helm installed, deploying a managed Prometheus is as easy as a single click.
- Go to the Operations > Kubernetes page to view your connected clusters
- Select the cluster you would like to deploy Prometheus to
- Click the Install button to deploy Prometheus to the cluster
About managed Prometheus deployments
Prometheus is deployed into the gitlab-managed-apps namespace, using the official Helm chart. Prometheus is only accessible within the cluster, with GitLab communicating through the Kubernetes API.
The Prometheus server will automatically detect and monitor nodes, pods, and endpoints. To configure a resource to be monitored by Prometheus, simply set the following Kubernetes annotations:
prometheus.io/scrapetotrueto enable monitoring of the resource.prometheus.io/portto define the port of the metrics endpoint.prometheus.io/pathto define the path of the metrics endpoint. Defaults to/metrics.
CPU and Memory consumption is monitored, but requires naming conventions in order to determine the environment. If you are using Auto DevOps, this is handled automatically.
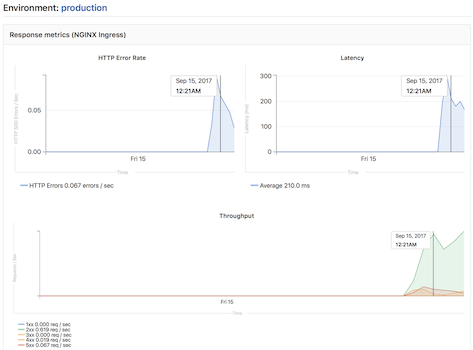
The NGINX Ingress that is deployed by GitLab to clusters, is automatically annotated for monitoring providing key response metrics: latency, throughput, and error rates.
Manual configuration of Prometheus
Requirements
Integration with Prometheus requires the following:
- GitLab 9.0 or higher
- Prometheus must be configured to collect one of the supported metrics
- Each metric must be have a label to indicate the environment
- GitLab must have network connectivity to the Prometheus server
Getting started
Installing and configuring Prometheus to monitor applications is fairly straight forward.
- Install Prometheus
- Set up one of the supported monitoring targets
- Configure the Prometheus server to collect their metrics
Configuration in GitLab
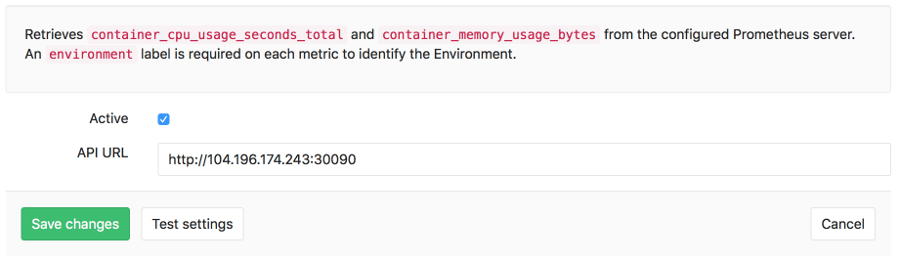
The actual configuration of Prometheus integration within GitLab is very simple. All you will need is the DNS or IP address of the Prometheus server you'd like to integrate with.
- Navigate to the Integrations page
- Click the Prometheus service
- Provide the base URL of the your server, for example
http://prometheus.example.com/. The Test Settings button can be used to confirm connectivity from GitLab to the Prometheus server.
Monitoring CI/CD Environments
Once configured, GitLab will attempt to retrieve performance metrics for any environment which has had a successful deployment.
GitLab will automatically scan the Prometheus server for metrics from known servers like Kubernetes and NGINX, and attempt to identify individual environment. The supported metrics and scan process is detailed in our Prometheus Metrics Library documentation.
You can view the performance dashboard for an environment by clicking on the monitoring button.
Determining the performance impact of a merge
Introduced in GitLab 9.2. GitLab 9.3 added the numeric comparison of the 30 minute averages. Requires Kubernetes metrics
Developers can view the performance impact of their changes within the merge request workflow. When a source branch has been deployed to an environment, a sparkline and numeric comparison of the average memory consumption will appear. On the sparkline, a dot indicates when the current changes were deployed, with up to 30 minutes of performance data displayed before and after. The comparison shows the difference between the 30 minute average before and after the deployment. This information is updated after each commit has been deployed.
Once merged and the target branch has been redeployed, the metrics will switch to show the new environments this revision has been deployed to.
Performance data will be available for the duration it is persisted on the Prometheus server.
Troubleshooting
If the "No data found" screen continues to appear, it could be due to:
- No successful deployments have occurred to this environment.
- Prometheus does not have performance data for this environment, or the metrics
are not labeled correctly. To test this, connect to the Prometheus server and
run a query, replacing
$CI_ENVIRONMENT_SLUGwith the name of your environment.