8.7 KiB
| type | stage | group | info |
|---|---|---|---|
| reference, howto | Manage | Authentication and Authorization | To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/product/ux/technical-writing/#assignments |
SAML Group Sync (PREMIUM)
Introduced for self-managed instances in GitLab 15.1.
WARNING:
Adding or changing Group Sync configuration can remove users from the mapped GitLab group.
Removal happens if there is any mismatch between the group names and the list of groups in the SAML response.
Before making changes, ensure either the SAML response includes the groups attribute
and the AttributeValue value matches the SAML Group Name in GitLab,
or that all groups are removed from GitLab to disable Group Sync.
For a demo of Group Sync using Azure, see Demo: SAML Group Sync.
Configure SAML Group Sync
NOTE: You must include the SAML configuration block on all Sidekiq nodes in addition to Rails application nodes if you:
- Use SAML Group Sync.
- Have multiple GitLab nodes, for example in a distributed or highly available architecture.
NOTE:
SAML Group Sync is only supported for the SAML provider named saml.
As a result, SAML Group Sync only supports a single SAML provider. For more information, see issue 386605.
WARNING: To prevent users being accidentally removed from the GitLab group, follow these instructions closely before enabling Group Sync in GitLab.
To configure SAML Group Sync for self-managed GitLab instances:
-
Configure the SAML OmniAuth Provider.
-
Ensure your SAML identity provider sends an attribute statement with the same name as the value of the
groups_attributesetting. See the following attribute statement example for reference:gitlab_rails['omniauth_providers'] = [ { name: "saml", label: "Provider name", # optional label for login button, defaults to "Saml", groups_attribute: 'Groups', args: { assertion_consumer_service_url: "https://gitlab.example.com/users/auth/saml/callback", idp_cert_fingerprint: "43:51:43:a1:b5:fc:8b:b7:0a:3a:a9:b1:0f:66:73:a8", idp_sso_target_url: "https://login.example.com/idp", issuer: "https://gitlab.example.com", name_identifier_format: "urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent" } } ]
To configure SAML Group Sync for GitLab.com instances:
- See SAML SSO for GitLab.com groups.
- Ensure your SAML identity provider sends an attribute statement named
Groupsorgroups.
NOTE:
The value for Groups or groups in the SAML response may be either the group name or an ID.
For example, Azure AD sends the Azure Group Object ID instead of the name. Use the ID value when configuring SAML Group Links.
<saml:AttributeStatement>
<saml:Attribute Name="Groups">
<saml:AttributeValue xsi:type="xs:string">Developers</saml:AttributeValue>
<saml:AttributeValue xsi:type="xs:string">Product Managers</saml:AttributeValue>
</saml:Attribute>
</saml:AttributeStatement>
Other attribute names such as http://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/claims/groups
are not accepted as a source of groups.
See examples
for configuring the required attribute name in the SAML identity provider's settings.
Configure SAML Group Links
When SAML is enabled, users with the Maintainer or Owner role see a new menu item in group Settings > SAML Group Links. You can configure one or more SAML Group Links to map a SAML identity provider group name to a GitLab role. This can be done for a top-level group or any subgroup.
To link the SAML groups:
- In SAML Group Name, enter the value of the relevant
saml:AttributeValue. The value entered here must exactly match the value sent in the SAML response. For some IdPs, this may be a group ID or object ID (Azure AD) instead of a friendly group name. - Choose the role in Access Level.
- Select Save.
- Repeat to add additional group links if required.
If a user is a member of multiple SAML groups mapped to the same GitLab group, the user gets the highest role from the groups. For example, if one group is linked as Guest and another Maintainer, a user in both groups gets the Maintainer role.
Users granted:
- A higher role with Group Sync are displayed as having direct membership of the group.
- A lower or the same role with Group Sync are displayed as having inherited membership of the group.
Automatic member removal
After a group sync, users who are not members of a mapped SAML group are removed from the group. On GitLab.com, users in the top-level group are assigned the default membership role instead of being removed.
For example, in the following diagram:
- Alex Garcia signs into GitLab and is removed from GitLab Group C because they don't belong to SAML Group C.
- Sidney Jones belongs to SAML Group C, but is not added to GitLab Group C because they have not yet signed in.
graph TB
subgraph SAML users
SAMLUserA[Sidney Jones]
SAMLUserB[Zhang Wei]
SAMLUserC[Alex Garcia]
SAMLUserD[Charlie Smith]
end
subgraph SAML groups
SAMLGroupA["Group A"] --> SAMLGroupB["Group B"]
SAMLGroupA --> SAMLGroupC["Group C"]
SAMLGroupA --> SAMLGroupD["Group D"]
end
SAMLGroupB --> |Member|SAMLUserA
SAMLGroupB --> |Member|SAMLUserB
SAMLGroupC --> |Member|SAMLUserA
SAMLGroupC --> |Member|SAMLUserB
SAMLGroupD --> |Member|SAMLUserD
SAMLGroupD --> |Member|SAMLUserC
graph TB
subgraph GitLab users
GitLabUserA[Sidney Jones]
GitLabUserB[Zhang Wei]
GitLabUserC[Alex Garcia]
GitLabUserD[Charlie Smith]
end
subgraph GitLab groups
GitLabGroupA["Group A (SAML configured)"] --> GitLabGroupB["Group B (SAML Group Link not configured)"]
GitLabGroupA --> GitLabGroupC["Group C (SAML Group Link configured)"]
GitLabGroupA --> GitLabGroupD["Group D (SAML Group Link configured)"]
end
GitLabGroupB --> |Member|GitLabUserA
GitLabGroupC --> |Member|GitLabUserB
GitLabGroupC --> |Member|GitLabUserC
GitLabGroupD --> |Member|GitLabUserC
GitLabGroupD --> |Member|GitLabUserD
graph TB
subgraph GitLab users
GitLabUserA[Sidney Jones]
GitLabUserB[Zhang Wei]
GitLabUserC[Alex Garcia]
GitLabUserD[Charlie Smith]
end
subgraph GitLab groups after Alex Garcia signs in
GitLabGroupA[Group A]
GitLabGroupA["Group A (SAML configured)"] --> GitLabGroupB["Group B (SAML Group Link not configured)"]
GitLabGroupA --> GitLabGroupC["Group C (SAML Group Link configured)"]
GitLabGroupA --> GitLabGroupD["Group D (SAML Group Link configured)"]
end
GitLabGroupB --> |Member|GitLabUserA
GitLabGroupC --> |Member|GitLabUserB
GitLabGroupD --> |Member|GitLabUserC
GitLabGroupD --> |Member|GitLabUserD
User that belongs to many SAML groups automatically removed from GitLab group
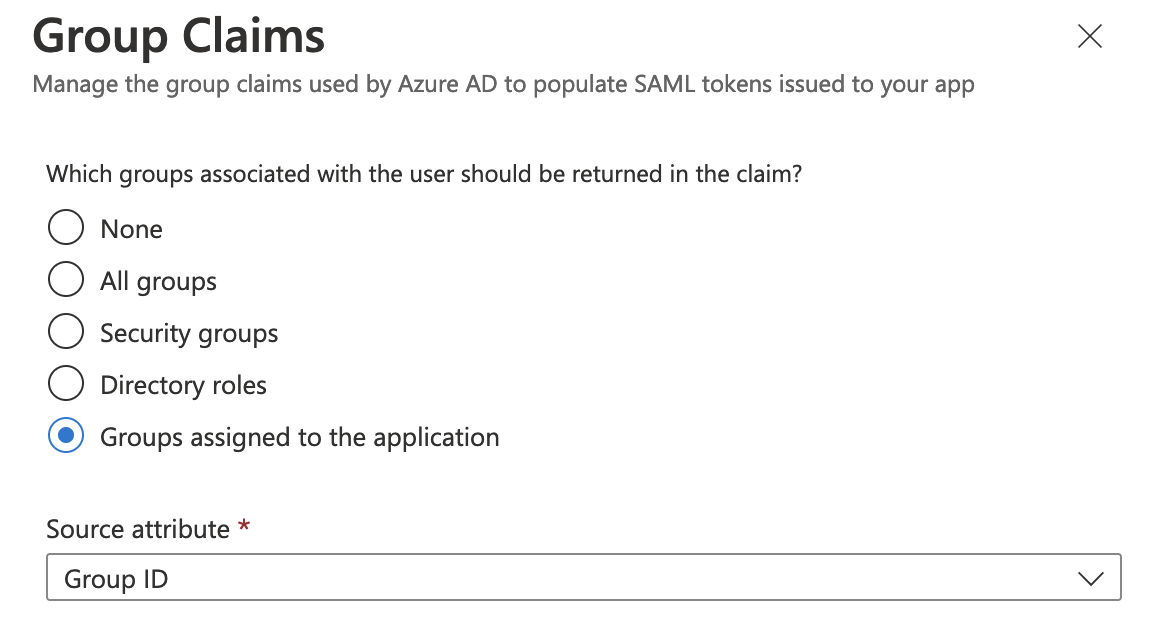
When using Azure AD as the SAML identity provider, users that belong to many SAML groups can be automatically removed from your GitLab group. Users are removed from GitLab groups if the group claim is missing from the user's SAML assertion.
Because of a known issue with Azure AD, if a user belongs to more than 150 SAML groups, the group claim is not sent in the user's SAML assertion.
With an Azure AD premium subscription, you can allow up to 500 group IDs to be sent in a SAML token using the Azure AD documentation configuration steps.
Otherwise, you can work around this issue by changing the group claims to use the Groups assigned to the application option instead.
Use the API
Introduced in GitLab 15.3.
You can use the GitLab API to list, add, and delete SAML group links.