24 KiB
Exploring GitLab Pages
Notes:
- This feature was introduced in GitLab EE 8.3.
- Custom CNAMEs with TLS support were introduced in GitLab EE 8.5.
- GitLab Pages was ported to Community Edition in GitLab 8.17.
- This document is about the user guide. To learn how to enable GitLab Pages across your GitLab instance, visit the administrator documentation.
With GitLab Pages you can host for free your static websites on GitLab. Combined with the power of GitLab CI and the help of GitLab Runner you can deploy static pages for your individual projects, your user or your group.
Read GitLab Pages on GitLab.com for specific information, if you are using GitLab.com to host your website.
Getting started with GitLab Pages domains
Note: In the rest of this document we will assume that the general domain name that is used for GitLab Pages is
example.io.
In general there are two types of pages one might create:
- Pages per user (
username.example.io) or per group (groupname.example.io) - Pages per project (
username.example.io/projectnameorgroupname.example.io/projectname)
In GitLab, usernames and groupnames are unique and we often refer to them as namespaces. There can be only one namespace in a GitLab instance. Below you can see the connection between the type of GitLab Pages, what the project name that is created on GitLab looks like and the website URL it will be ultimately be served on.
| Type of GitLab Pages | The name of the project created in GitLab | Website URL |
|---|---|---|
| User pages | username.example.io |
http(s)://username.example.io |
| Group pages | groupname.example.io |
http(s)://groupname.example.io |
| Project pages owned by a user | projectname |
http(s)://username.example.io/projectname |
| Project pages owned by a group | projectname |
http(s)://groupname.example.io/projectname |
| Project pages owned by a subgroup | subgroup/projectname |
http(s)://groupname.example.io/subgroup/projectname |
Warning: There are some known limitations regarding namespaces served under the general domain name and HTTPS. Make sure to read that section.
GitLab Pages requirements
In brief, this is what you need to upload your website in GitLab Pages:
- Find out the general domain name that is used for GitLab Pages (ask your administrator). This is very important, so you should first make sure you get that right.
- Create a project
- Push a
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile in the root directory of your repository with a specific job namedpages - Set up a GitLab Runner to build your website
Note: If shared runners are enabled by your GitLab administrator, you should be able to use them instead of bringing your own.
User or group Pages
For user and group pages, the name of the project should be specific to the
username or groupname and the general domain name that is used for GitLab Pages.
Head over your GitLab instance that supports GitLab Pages and create a
repository named username.example.io, where username is your username on
GitLab. If the first part of the project name doesn't match exactly your
username, it won’t work, so make sure to get it right.
To create a group page, the steps are the same like when creating a website for users. Just make sure that you are creating the project within the group's namespace.
After you push some static content to your repository and GitLab Runner uploads
the artifacts to GitLab CI, you will be able to access your website under
http(s)://username.example.io. Keep reading to find out how.
Note: If your username/groupname contains a dot, for example
foo.bar, you will not be able to use the wildcard domain HTTPS, read more at limitations.
Project Pages
GitLab Pages for projects can be created by both user and group accounts. The steps to create a project page for a user or a group are identical:
- Create a new project
- Push a
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile in the root directory of your repository with a specific job namedpages. - Set up a GitLab Runner to build your website
A user's project will be served under http(s)://username.example.io/projectname
whereas a group's project under http(s)://groupname.example.io/projectname.
For practical examples for group and project Pages, read through the guide GitLab Pages from A to Z: Part 1 - Static sites and GitLab Pages domains.
Quick Start
Read through GitLab Pages Quick Start Guide or watch the video tutorial on how to publish a website with GitLab Pages on GitLab.com from a forked project.
See also All you Need to Know About GitLab Pages for a list with all the resources we have for GitLab Pages.
Explore the contents of .gitlab-ci.yml
The key thing about GitLab Pages is the .gitlab-ci.yml file, something that
gives you absolute control over the build process. You can actually watch your
website being built live by following the CI job traces.
For a simplified user guide on setting up GitLab CI/CD for Pages, read through
the article GitLab Pages from A to Z: Part 4 - Creating and Tweaking .gitlab-ci.yml for GitLab Pages
Note: Before reading this section, make sure you familiarize yourself with GitLab CI and the specific syntax of
.gitlab-ci.ymlby following our quick start guide.
To make use of GitLab Pages, the contents of .gitlab-ci.yml must follow the
rules below:
- A special job named
pagesmust be defined - Any static content which will be served by GitLab Pages must be placed under
a
public/directory artifactswith a path to thepublic/directory must be defined
In its simplest form, .gitlab-ci.yml looks like:
pages:
script:
- my_commands
artifacts:
paths:
- public
When the Runner reaches to build the pages job, it executes whatever is
defined in the script parameter and if the job completes with a non-zero
exit status, it then uploads the public/ directory to GitLab Pages.
The public/ directory should contain all the static content of your website.
Depending on how you plan to publish your website, the steps defined in the
script parameter may differ.
Be aware that Pages are by default branch/tag agnostic and their deployment
relies solely on what you specify in .gitlab-ci.yml. If you don't limit the
pages job with the only parameter,
whenever a new commit is pushed to whatever branch or tag, the Pages will be
overwritten. In the example below, we limit the Pages to be deployed whenever
a commit is pushed only on the master branch:
pages:
script:
- my_commands
artifacts:
paths:
- public
only:
- master
We then tell the Runner to treat the public/ directory as artifacts and
upload it to GitLab. And since all these parameters were all under a pages
job, the contents of the public directory will be served by GitLab Pages.
How .gitlab-ci.yml looks like when the static content is in your repository
Supposed your repository contained the following files:
├── index.html
├── css
│ └── main.css
└── js
└── main.js
Then the .gitlab-ci.yml example below simply moves all files from the root
directory of the project to the public/ directory. The .public workaround
is so cp doesn't also copy public/ to itself in an infinite loop:
pages:
script:
- mkdir .public
- cp -r * .public
- mv .public public
artifacts:
paths:
- public
only:
- master
How .gitlab-ci.yml looks like when using a static generator
In general, GitLab Pages support any kind of static site generator,
since .gitlab-ci.yml can be configured to run any possible command.
In the root directory of your Git repository, place the source files of your
favorite static generator. Then provide a .gitlab-ci.yml file which is
specific to your static generator.
The example below, uses Jekyll to build the static site:
image: ruby:2.1 # the script will run in Ruby 2.1 using the Docker image ruby:2.1
pages: # the build job must be named pages
script:
- gem install jekyll # we install jekyll
- jekyll build -d public/ # we tell jekyll to build the site for us
artifacts:
paths:
- public # this is where the site will live and the Runner uploads it in GitLab
only:
- master # this script is only affecting the master branch
Here, we used the Docker executor and in the first line we specified the base image against which our jobs will run.
You have to make sure that the generated static files are ultimately placed
under the public directory, that's why in the script section we run the
jekyll command that jobs the website and puts all content in the public/
directory. Depending on the static generator of your choice, this command will
differ. Search in the documentation of the static generator you will use if
there is an option to explicitly set the output directory. If there is not
such an option, you can always add one more line under script to rename the
resulting directory in public/.
We then tell the Runner to treat the public/ directory as artifacts and
upload it to GitLab.
See the jekyll example project to better understand how this works.
For a list of Pages projects, see the example projects to get you started.
How to set up GitLab Pages in a repository where there's also actual code
Remember that GitLab Pages are by default branch/tag agnostic and their
deployment relies solely on what you specify in .gitlab-ci.yml. You can limit
the pages job with the only parameter,
whenever a new commit is pushed to a branch that will be used specifically for
your pages.
That way, you can have your project's code in the master branch and use an
orphan branch (let's name it pages) that will host your static generator site.
You can create a new empty branch like this:
git checkout --orphan pages
The first commit made on this new branch will have no parents and it will be
the root of a new history totally disconnected from all the other branches and
commits. Push the source files of your static generator in the pages branch.
Below is a copy of .gitlab-ci.yml where the most significant line is the last
one, specifying to execute everything in the pages branch:
image: ruby:2.1
pages:
script:
- gem install jekyll
- jekyll build -d public/
artifacts:
paths:
- public
only:
- pages
See an example that has different files in the master branch
and the source files for Jekyll are in a pages branch which
also includes .gitlab-ci.yml.
Next steps
So you have successfully deployed your website, congratulations! Let's check what more you can do with GitLab Pages.
Example projects
Below is a list of example projects for GitLab Pages with a plain HTML website or various static site generators. Contributions are very welcome.
Visit the GitLab Pages group for a full list of example projects: https://gitlab.com/groups/pages.
Serving compressed assets
Most modern browsers support downloading files in a compressed format. This speeds up downloads by reducing the size of files.
Before serving an uncompressed file, Pages will check whether the same file
exists with a .gz extension. If it does, and the browser supports receiving
compressed files, it will serve that version instead of the uncompressed one.
To take advantage of this feature, the artifact you upload to the Pages should have this structure:
public/
├─┬ index.html
│ └ index.html.gz
│
├── css/
│ └─┬ main.css
│ └ main.css.gz
│
└── js/
└─┬ main.js
└ main.js.gz
This can be achieved by including a script: command like this in your
.gitlab-ci.yml pages job:
pages:
# Other directives
script:
- # build the public/ directory first
- find public -type f -iregex '.*\.\(htm\|html\|txt\|text\|js\|css\)$' -execdir gzip -f --keep {} \;
By pre-compressing the files and including both versions in the artifact, Pages can serve requests for both compressed and uncompressed content without needing to compress files on-demand.
Resolving ambiguous URLs
Introduced in GitLab 11.8
GitLab Pages makes assumptions about which files to serve when receiving a request for a URL that does not include an extension.
Consider a Pages site deployed with the following files:
public/
├─┬ index.html
│ ├ data.html
│ └ info.html
│
├── data/
│ └── index.html
├── info/
│ └── details.html
└── other/
└── index.html
Pages supports reaching each of these files through several different URLs. In
particular, it will always look for an index.html file if the URL only
specifies the directory. If the URL references a file that doesn't exist, but
adding .html to the URL leads to a file that does exist, it will be served
instead. Here are some examples of what will happen given the above Pages site:
| URL path | HTTP response | File served |
|---|---|---|
/ |
200 OK |
public/index.html |
/index.html |
200 OK |
public/index.html |
/index |
200 OK |
public/index.html |
/data |
200 OK |
public/data/index.html |
/data/ |
200 OK |
public/data/index.html |
/data.html |
200 OK |
public/data.html |
/info |
200 OK |
public/info.html |
/info/ |
200 OK |
public/info.html |
/info.html |
200 OK |
public/info.html |
/info/details |
200 OK |
public/info/details.html |
/info/details.html |
200 OK |
public/info/details.html |
/other |
302 Found |
public/other/index.html |
/other/ |
200 OK |
public/other/index.html |
/other/index |
200 OK |
public/other/index.html |
/other/index.html |
200 OK |
public/other/index.html |
NOTE: Note:
When public/data/index.html exists, it takes priority over the public/data.html
file for both the /data and /data/ URL paths.
Add a custom domain to your Pages website
For a complete guide on Pages domains, read through the article GitLab Pages from A to Z: Part 3 - Setting Up Custom Domains - DNS Records and SSL/TLS Certificates
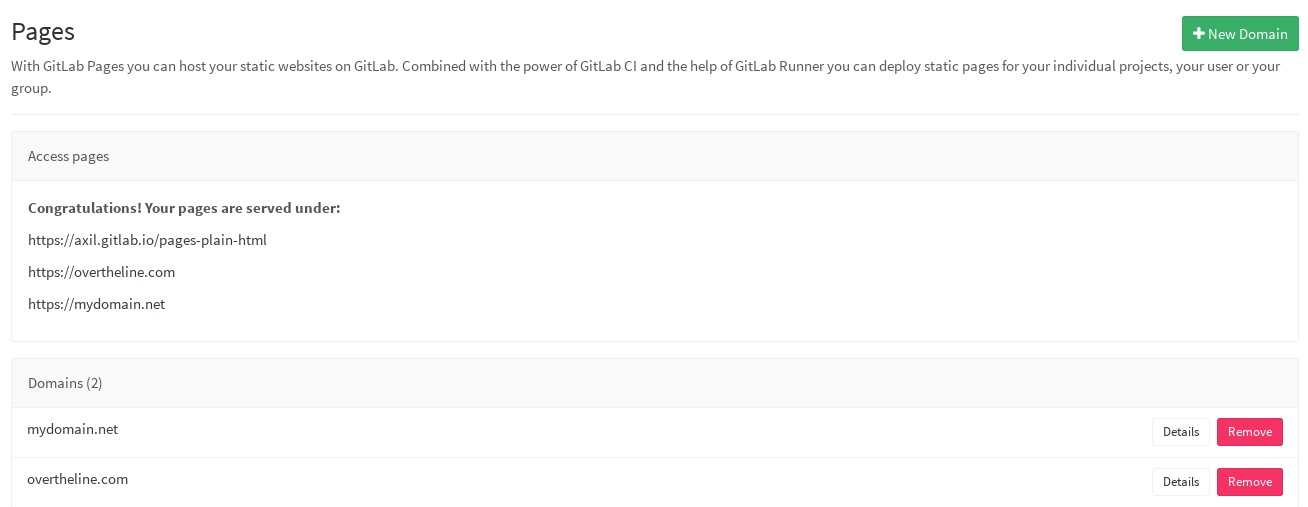
If this setting is enabled by your GitLab administrator, you should be able to see the New Domain button when visiting your project's settings through the gear icon in the top right and then navigating to Pages.
You can add multiple domains pointing to your website hosted under GitLab. Once the domain is added, you can see it listed under the Domains section.
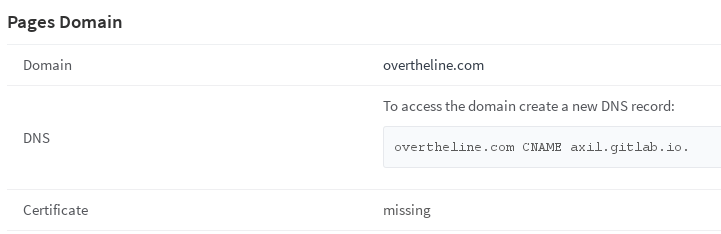
As a last step, you need to configure your DNS and add a CNAME pointing to your user/group page. Click on the Details button of a domain for further instructions.
Note: Currently there is support only for custom domains on per-project basis. That means that if you add a custom domain (
example.com) for your user website (username.example.io), a project that is served underusername.example.io/foo, will not be accessible underexample.com/foo.
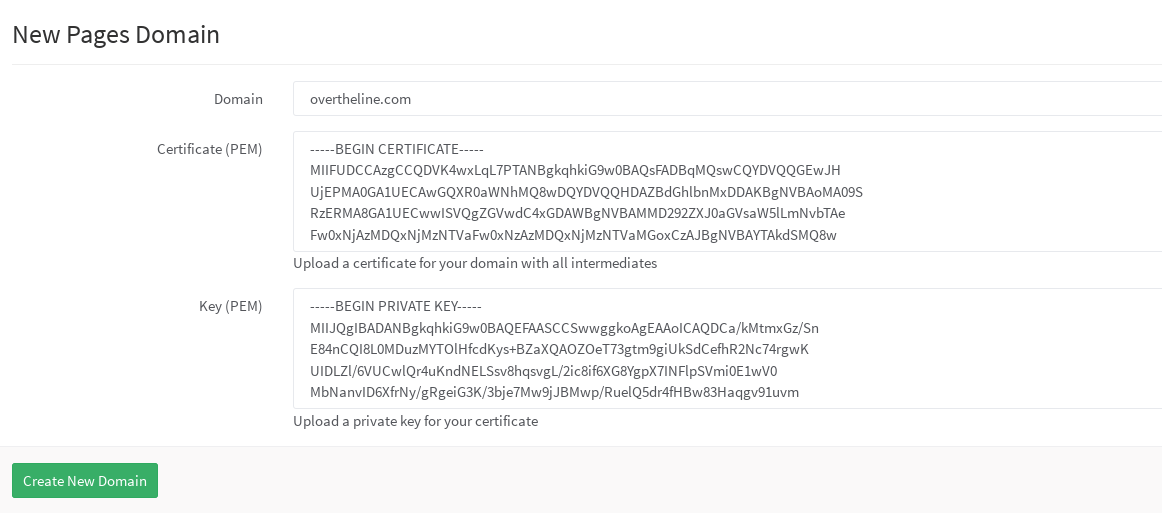
Secure your custom domain website with TLS
When you add a new custom domain, you also have the chance to add a TLS certificate. If this setting is enabled by your GitLab administrator, you should be able to see the option to upload the public certificate and the private key when adding a new domain.
For a complete guide on Pages domains, read through the article GitLab Pages from A to Z: Part 3 - Setting Up Custom Domains - DNS Records and SSL/TLS Certificates
Custom error codes pages
You can provide your own 403 and 404 error pages by creating the 403.html and
404.html files respectively in the root directory of the public/ directory
that will be included in the artifacts. Usually this is the root directory of
your project, but that may differ depending on your static generator
configuration.
If the case of 404.html, there are different scenarios. For example:
- If you use project Pages (served under
/projectname/) and try to access/projectname/non/existing_file, GitLab Pages will try to serve first/projectname/404.html, and then/404.html. - If you use user/group Pages (served under
/) and try to access/non/existing_fileGitLab Pages will try to serve/404.html. - If you use a custom domain and try to access
/non/existing_file, GitLab Pages will try to serve only/404.html.
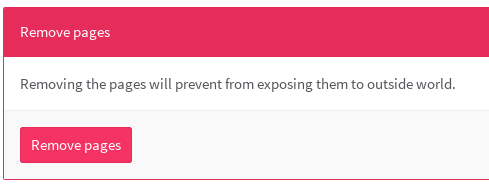
Remove the contents of your pages
If you ever feel the need to purge your Pages content, you can do so by going to your project's settings through the gear icon in the top right, and then navigating to Pages. Hit the Remove pages button and your Pages website will be deleted. Simple as that.
GitLab Pages on GitLab.com
If you are using GitLab.com to host your website, then:
- The general domain name for GitLab Pages on GitLab.com is
gitlab.io. - Custom domains and TLS support are enabled.
- Shared runners are enabled by default, provided for free and can be used to build your website. If you want you can still bring your own Runner.
The rest of the guide still applies.
See also: GitLab Pages from A to Z: Part 1 - Static sites and GitLab Pages domains.
GitLab Pages access control [CORE ONLY]
Introduced in GitLab 11.5.
NOTE: Note: GitLab Pages access control is not activated on GitLab.com. You can check its progress on the infrastructure issue tracker.
You can enable Pages access control on your project, so that only members of your project (at least Guest) can access your website:
-
Navigate to your project's Settings > General > Permissions.
-
Toggle the Pages button to enable the access control.
NOTE: Note: If you don't see the toggle button, that means that it's not enabled. Ask your administrator to enable it.
-
The Pages access control dropdown allows you to set who can view pages hosted with GitLab Pages, depending on your project's visibility:
- If your project is private:
- Only project members: Only project members will be able to browse the website.
- Everyone: Everyone, both logged into and logged out of GitLab, will be able to browse the website, no matter their project membership.
- If your project is internal:
- Only project members: Only project members will be able to browse the website.
- Everyone with access: Everyone logged into GitLab will be able to browse the website, no matter their project membership.
- Everyone: Everyone, both logged into and logged out of GitLab, will be able to browse the website, no matter their project membership.
- If your project is public:
- Only project members: Only project members will be able to browse the website.
- Everyone with access: Everyone, both logged into and logged out of GitLab, will be able to browse the website, no matter their project membership.
- If your project is private:
-
Click Save changes.
The next time someone tries to access your website and the access control is enabled, they will be presented with a page to sign into GitLab and verify they can access the website.
Limitations
When using Pages under the general domain of a GitLab instance (*.example.io),
you cannot use HTTPS with sub-subdomains. That means that if your
username/groupname contains a dot, for example foo.bar, the domain
https://foo.bar.example.io will not work. This is a limitation of the
HTTP Over TLS protocol. HTTP pages will continue to work provided you
don't redirect HTTP to HTTPS.
GitLab Pages does not support group websites for subgroups. You can only create the highest-level group website.
Redirects in GitLab Pages
Since you cannot use any custom server configuration files, like .htaccess or
any .conf file, if you want to redirect a page to another
location, you can use the HTTP meta refresh tag.
Some static site generators provide plugins for that functionality so that you don't have to create and edit HTML files manually. For example, Jekyll has the redirect-from plugin.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I download my generated pages?
Sure. All you need to do is download the artifacts archive from the job page.
Can I use GitLab Pages if my project is private?
Yes. GitLab Pages doesn't care whether you set your project's visibility level to private, internal or public.
Do I need to create a user/group website before creating a project website?
No, you don't. You can create your project first and it will be accessed under
http(s)://namespace.example.io/projectname.
Known issues
For a list of known issues, visit GitLab's public issue tracker.