3.1 KiB
| type |
|---|
| reference, howto |
Standalone Vulnerability pages
Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 13.0.
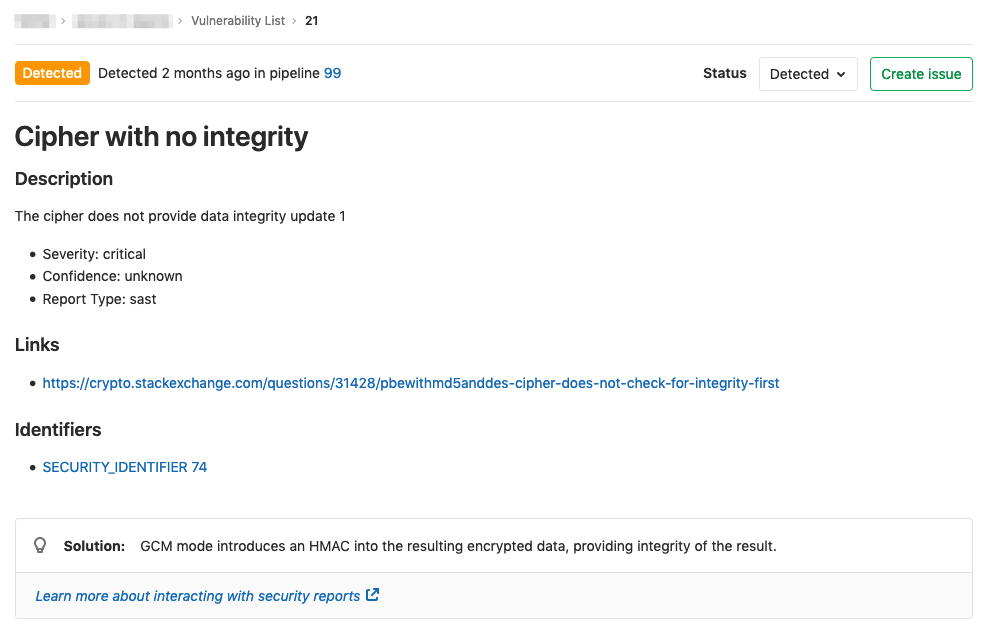
Each security vulnerability in the Vulnerability List has its own standalone page.
On the standalone vulnerability page, you can interact with the vulnerability in several different ways:
- Change the Vulnerability Status - You can change the status of a vulnerability to Detected, Confirmed, Dismissed, or Resolved.
- Create issue - Create a new issue with the title and description prepopulated with information from the vulnerability report. By default, such issues are confidential.
- Solution - For some vulnerabilities, a solution is provided for how to fix the vulnerability.
Changing vulnerability status
You can switch the status of a vulnerability using the Status dropdown to one of the following values:
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| Detected | The default state for a newly discovered vulnerability |
| Confirmed | A user has seen this vulnerability and confirmed it to be real |
| Dismissed | A user has seen this vulnerability and dismissed it |
| Resolved | The vulnerability has been fixed and is no longer in the codebase |
Creating an issue for a vulnerability
You can create an issue for a vulnerability by selecting the Create issue button.
This creates a confidential issue in the project the vulnerability came from, and prepopulates it with useful information from the vulnerability report. After the issue is created, GitLab redirects you to the issue page so you can edit, assign, or comment on the issue.
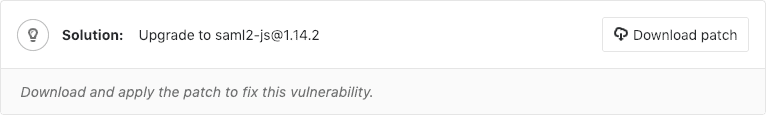
Automatic remediation solutions for vulnerabilities
You can fix some vulnerabilities by applying the solution that GitLab automatically generates for you. GitLab supports the following scanners:
- Dependency Scanning: Automatic Patch creation
is only available for Node.js projects managed with
yarn. - Container Scanning.
Manually applying a suggested patch
To apply a patch automatically generated by GitLab to fix a vulnerability:
- Open the issue created in Create issue.
- In the Issue description, scroll to Solution and download the linked patch file.
- Ensure your local project has the same commit checked out that was used to generate the patch.
- Run
git apply remediation.patchto apply the patch. - Verify and commit the changes to your branch.