20 KiB
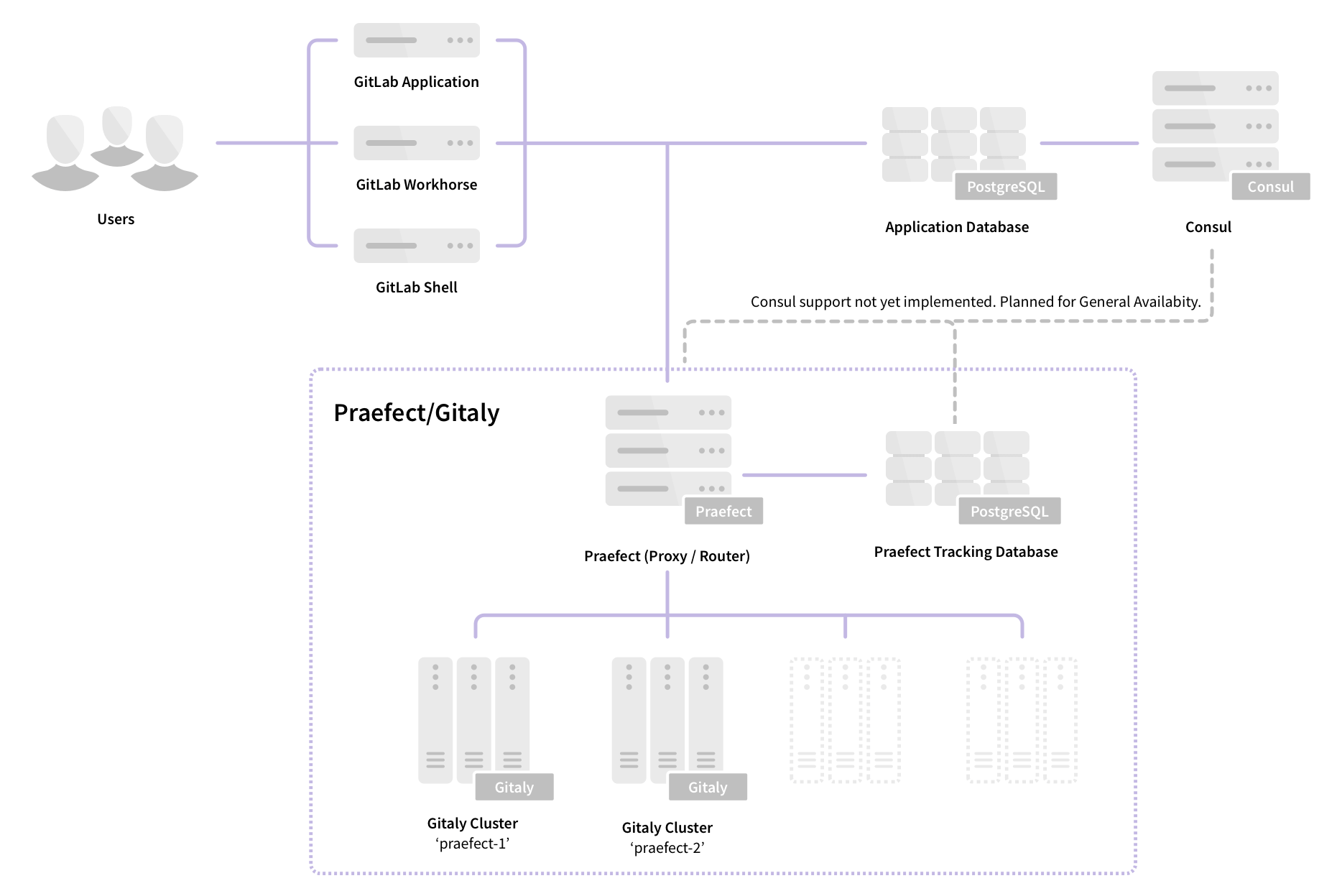
Praefect: High Availability
NOTE: Note: Praefect is an experimental service, and data loss is likely.
Praefect is an optional reverse-proxy for Gitaly to manage a cluster of Gitaly nodes for high availability. Initially, high availability be implemented through asynchronous replication. If a Gitaly node becomes unavailable, it will be possible to fail over to a warm Gitaly replica.
The first minimal version will support:
- Eventual consistency of the secondary replicas.
- Automatic fail over from the primary to the secondary.
- Reporting of possible data loss if replication queue is non empty.
Follow the HA Gitaly epic for updates and roadmap.
Requirements for configuring Gitaly for High Availability
NOTE: Note: this reference architecture is not highly available because Praefect is a single point of failure.
The minimal alpha reference architecture additionally requires:
- 1 Praefect node
- 1 PostgreSQL server (PostgreSQL 9.6 or newer)
- 3 Gitaly nodes (1 primary, 2 secondary)
See the design document for implementation details.
Setup Instructions
If you installed GitLab using the Omnibus package (highly recommended), follow the steps below:
- Preparation
- Configuring the Praefect database
- Configuring the Praefect proxy/router
- Configuring each Gitaly node (once for each Gitaly node)
- Updating the GitLab server configuration
Preparation
Before beginning, you should already have a working GitLab instance. Learn how to install GitLab.
Provision a PostgreSQL server (PostgreSQL 9.6 or newer). Configuration through the GitLab Omnibus distribution is not yet supported. Follow this issue for updates.
Prepare all your new nodes by installing GitLab.
- 1 Praefect node (minimal storage required)
- 3 Gitaly nodes (high CPU, high memory, fast storage)
You will need the IP/host address for each node.
POSTGRESQL_SERVER_ADDRESS: the IP/host address of the PostgreSQL serverPRAEFECT_SERVER_ADDRESS: the IP/host address of the Praefect serverGITALY_SERVER_ADDRESS: the IP/host address of each Gitaly node
Secrets
The communication between components is secured with different secrets, which are described below. Before you begin, generate a unique secret for each, and make note of it. This will make it easy to replace these placeholder tokens with secure tokens as you complete the setup process.
GITLAB_SHELL_SECRET_TOKEN: this is used by Git hooks to make callback HTTP API requests to GitLab when accepting a Git push. This secret is shared with GitLab Shell for legacy reasons.PRAEFECT_EXTERNAL_TOKEN: repositories hosted on your Praefect cluster can only be accessed by Gitaly clients that carry this token.PRAEFECT_INTERNAL_TOKEN: this token is used for replication traffic inside your Praefect cluster. This is distinct fromPRAEFECT_EXTERNAL_TOKENbecause Gitaly clients must not be able to access internal nodes of the Praefect cluster directly; that could lead to data loss.PRAEFECT_SQL_PASSWORD: this password is used by Praefect to connect to PostgreSQL.GRAFANA_PASSWORD: this password is used to access theadminaccount in the Grafana dashboards.
We will note in the instructions below where these secrets are required.
PostgreSQL
NOTE: Note: don't reuse the GitLab application database for the Praefect database.
To complete this section you will need:
- 1 Praefect node
- 1 PostgreSQL server (PostgreSQL 9.6 or newer)
- An SQL user with permissions to create databases
During this section, we will configure the PostgreSQL server, from the Praefect
node, using psql which is installed by GitLab Omnibus.
-
SSH into the Praefect node and login as root:
sudo -i -
Connect to the PostgreSQL server with administrative access. This is likely the
postgresuser. The databasetemplate1is used because it is created by default on all PostgreSQL servers./opt/gitlab/embedded/bin/psql -U postgres -d template1 -h POSTGRESQL_SERVER_ADDRESSCreate a new user
praefectwhich will be used by Praefect. ReplacePRAEFECT_SQL_PASSWORDwith the strong password you generated in the preparation step.CREATE ROLE praefect WITH LOGIN CREATEDB PASSWORD 'PRAEFECT_SQL_PASSWORD'; -
Reconnect to the PostgreSQL server, this time as the
praefectuser:/opt/gitlab/embedded/bin/psql -U praefect -d template1 -h POSTGRESQL_SERVER_ADDRESSCreate a new database
praefect_production. By creating the database while connected as thepraefectuser, we are confident they have access.CREATE DATABASE praefect_production WITH ENCODING=UTF8;
The database used by Praefect is now configured.
Praefect
To complete this section you will need:
- Configured PostgreSQL server, including:
- IP/host address (
POSTGRESQL_SERVER_ADDRESS) - password (
PRAEFECT_SQL_PASSWORD)
- IP/host address (
Praefect should be run on a dedicated node. Do not run Praefect on the application server, or a Gitaly node.
-
SSH into the Praefect node and login as root:
sudo -i -
Disable all other services by editing
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb:# Disable all other services on the Praefect node postgresql['enable'] = false redis['enable'] = false nginx['enable'] = false prometheus['enable'] = false grafana['enable'] = false unicorn['enable'] = false sidekiq['enable'] = false gitlab_workhorse['enable'] = false gitaly['enable'] = false # Enable only the Praefect service praefect['enable'] = true # Prevent database connections during 'gitlab-ctl reconfigure' gitlab_rails['rake_cache_clear'] = false gitlab_rails['auto_migrate'] = false -
Configure Praefect to listen on network interfaces by editing
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb:# Make Praefect accept connections on all network interfaces. # Use firewalls to restrict access to this address/port. praefect['listen_addr'] = '0.0.0.0:2305' # Enable Prometheus metrics access to Praefect. You must use firewalls # to restrict access to this address/port. praefect['prometheus_listen_addr'] = '0.0.0.0:9652' -
Configure a strong
auth_tokenfor Praefect by editing/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb. This will be needed by clients outside the cluster (like GitLab Shell) to communicate with the Praefect cluster :praefect['auth_token'] = 'PRAEFECT_EXTERNAL_TOKEN' -
Configure Praefect to connect to the PostgreSQL database by editing
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb.You will need to replace
POSTGRESQL_SERVER_ADDRESSwith the IP/host address of the database, andPRAEFECT_SQL_PASSWORDwith the strong password set above.praefect['database_host'] = 'POSTGRESQL_SERVER_ADDRESS' praefect['database_port'] = 5432 praefect['database_user'] = 'praefect' praefect['database_password'] = 'PRAEFECT_SQL_PASSWORD' praefect['database_dbname'] = 'praefect_production'If you want to use a TLS client certificate, the options below can be used:
# Connect to PostreSQL using a TLS client certificate # praefect['database_sslcert'] = '/path/to/client-cert' # praefect['database_sslkey'] = '/path/to/client-key' # Trust a custom certificate authority # praefect['database_sslrootcert'] = '/path/to/rootcert'By default Praefect will refuse to make an unencrypted connection to PostgreSQL. You can override this by uncommenting the following line:
# praefect['database_sslmode'] = 'disable' -
Configure the Praefect cluster to connect to each Gitaly node in the cluster by editing
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb.In the example below we have configured one cluster named
praefect. This cluster has three Gitaly nodesgitaly-1,gitaly-2, andgitaly-3, which will be replicas of each other.Replace
PRAEFECT_INTERNAL_TOKENwith a strong secret, which will be used by Praefect when communicating with Gitaly nodes in the cluster. This token is distinct from thePRAEFECT_EXTERNAL_TOKEN.Replace
GITALY_HOSTwith the IP/host address of the each Gitaly node.More Gitaly nodes can be added to the cluster to increase the number of replicas. More clusters can also be added for very large GitLab instances.
NOTE: Note: The
gitaly-1node is currently denoted the primary. This can be used to manually fail from one node to another. This will be removed in the future to allow for automatic failover.# Name of storage hash must match storage name in git_data_dirs on GitLab # server ('praefect') and in git_data_dirs on Gitaly nodes ('gitaly-1') praefect['virtual_storages'] = { 'praefect' => { 'gitaly-1' => { 'address' => 'tcp://GITALY_HOST:8075', 'token' => 'PRAEFECT_INTERNAL_TOKEN', 'primary' => true }, 'gitaly-2' => { 'address' => 'tcp://GITALY_HOST:8075', 'token' => 'PRAEFECT_INTERNAL_TOKEN' }, 'gitaly-3' => { 'address' => 'tcp://GITALY_HOST:8075', 'token' => 'PRAEFECT_INTERNAL_TOKEN' } } } -
Save the changes to
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband reconfigure Praefect:gitlab-ctl reconfigure -
Verify that Praefect can reach PostgreSQL:
sudo -u git /opt/gitlab/embedded/bin/praefect -config /var/opt/gitlab/praefect/config.toml sql-pingIf the check fails, make sure you have followed the steps correctly. If you edit
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb, remember to runsudo gitlab-ctl reconfigureagain before trying thesql-pingcommand.
Gitaly
NOTE: Note: Complete these steps for each Gitaly node.
To complete this section you will need:
- Configured Praefect node
- 3 (or more) servers, with GitLab installed, to be configured as Gitaly nodes. These should be dedicated nodes, do not run other services on these nodes.
Every Gitaly server assigned to the Praefect cluster needs to be configured. The configuration is the same as a normal standalone Gitaly server, except:
- the storage names are exposed to Praefect, not GitLab
- the secret token is shared with Praefect, not GitLab
The configuration of all Gitaly nodes in the Praefect cluster can be identical, because we rely on Praefect to route operations correctly.
Particular attention should be shown to:
- the
gitaly['auth_token']configured in this section must match thetokenvalue underpraefect['virtual_storages']on the Praefect node. This was set in the previous section. This document uses the placeholderPRAEFECT_INTERNAL_TOKENthroughout. - the storage names in
git_data_dirsconfigured in this section must match the storage names underpraefect['virtual_storages']on the Praefect node. This was set in the previous section. This document usesgitaly-1,gitaly-2, andgitaly-3as Gitaly storage names.
For more information on Gitaly server configuration, see our Gitaly documentation.
-
SSH into the Gitaly node and login as root:
sudo -i -
Disable all other services by editing
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb:# Disable all other services on the Praefect node postgresql['enable'] = false redis['enable'] = false nginx['enable'] = false prometheus['enable'] = false grafana['enable'] = false unicorn['enable'] = false sidekiq['enable'] = false gitlab_workhorse['enable'] = false prometheus_monitoring['enable'] = false # Enable only the Praefect service gitaly['enable'] = true # Prevent database connections during 'gitlab-ctl reconfigure' gitlab_rails['rake_cache_clear'] = false gitlab_rails['auto_migrate'] = false -
Configure Gitaly to listen on network interfaces by editing
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb:# Make Gitaly accept connections on all network interfaces. # Use firewalls to restrict access to this address/port. gitaly['listen_addr'] = '0.0.0.0:8075' # Enable Prometheus metrics access to Gitaly. You must use firewalls # to restrict access to this address/port. gitaly['prometheus_listen_addr'] = '0.0.0.0:9236' -
Configure a strong
auth_tokenfor Gitaly by editing/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb. This will be needed by clients to communicate with this Gitaly nodes. Typically, this token will be the same for all Gitaly nodes.gitaly['auth_token'] = 'PRAEFECT_INTERNAL_TOKEN' -
Configure the GitLab Shell
secret_token, andinternal_api_urlwhich are needed forgit pushoperations.If you have already configured Gitaly on its own server
gitlab_shell['secret_token'] = 'GITLAB_SHELL_SECRET_TOKEN' # Configure the gitlab-shell API callback URL. Without this, `git push` will # fail. This can be your front door GitLab URL or an internal load balancer. # Examples: 'https://example.gitlab.com', 'http://1.2.3.4' gitlab_rails['internal_api_url'] = 'GITLAB_SERVER_URL' -
Configure the storage location for Git data by setting
git_data_dirsin/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb. Each Gitaly node should have a unique storage name (eggitaly-1).Instead of configuring
git_data_dirsuniquely for each Gitaly node, it is often easier to have include the configuration for all Gitaly nodes on every Gitaly node. This is supported because the Praefectvirtual_storagesconfiguration maps each storage name (eggitaly-1) to a specific node, and requests are routed accordingly. This means every Gitaly node in your fleet can share the same configuration.# You can include the data dirs for all nodes in the same config, because # Praefect will only route requests according to the addresses provided in the # prior step. git_data_dirs({ "gitaly-1" => { "path" => "/var/opt/gitlab/git-data" }, "gitaly-2" => { "path" => "/var/opt/gitlab/git-data" }, "gitaly-3" => { "path" => "/var/opt/gitlab/git-data" } }) -
Save the changes to
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband reconfigure Gitaly:gitlab-ctl reconfigure -
To ensure that Gitaly has updated its Prometheus listen address, restart Gitaly:
gitlab-ctl restart gitaly
Complete these steps for each Gitaly node!
After all Gitaly nodes are configured, you can run the Praefect connection checker to verify Praefect can connect to all Gitaly servers in the Praefect config.
-
SSH into the Praefect node and run the Praefect connection checker:
sudo /opt/gitlab/embedded/bin/praefect -config /var/opt/gitlab/praefect/config.toml dial-nodes
GitLab
To complete this section you will need:
The Praefect cluster needs to be exposed as a storage location to the GitLab
application. This is done by updating the git_data_dirs.
Particular attention should be shown to:
- the storage name added to
git_data_dirsin this section must match the storage name underpraefect['virtual_storages']on the Praefect node. This was set in the Praefect section of this guide. This document usespraefectas the Praefect storage name.
-
SSH into the GitLab node and login as root:
sudo -i -
Add the Praefect cluster as a storage location by editing
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb.You will need to replace:
PRAEFECT_HOSTwith the IP address or hostname of the Praefect nodePRAEFECT_EXTERNAL_TOKENwith the real secret
git_data_dirs({ "default" => { "path" => "/var/opt/gitlab/git-data" }, "praefect" => { "gitaly_address" => "tcp://PRAEFECT_HOST:2305", "gitaly_token" => 'PRAEFECT_EXTERNAL_TOKEN' } }) -
Configure the
gitlab_shell['secret_token']so that callbacks from Gitaly nodes during agit pushare properly authenticated by editing/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb:You will need to replace
GITLAB_SHELL_SECRET_TOKENwith the real secret.gitlab_shell['secret_token'] = 'GITLAB_SHELL_SECRET_TOKEN' -
Configure the
external_urlso that files could be served by GitLab by proper endpoint access by editing/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb:You will need to replace
GITLAB_SERVER_URLwith the real URL on which current GitLab instance is serving:external_url 'GITLAB_SERVER_URL' -
Add Prometheus monitoring settings by editing
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb.You will need to replace:
PRAEFECT_HOSTwith the IP address or hostname of the Praefect nodeGITALY_HOSTwith the IP address or hostname of each Gitaly node
prometheus['scrape_configs'] = [ { 'job_name' => 'praefect', 'static_configs' => [ 'targets' => [ 'PRAEFECT_HOST:9652' # praefect ] ] }, { 'job_name' => 'praefect-gitaly', 'static_configs' => [ 'targets' => [ 'GITALY_HOST:9236', # gitaly-1 'GITALY_HOST:9236', # gitaly-2 'GITALY_HOST:9236', # gitaly-3 ] ] } ] grafana['disable_login_form'] = false -
Save the changes to
/etc/gitlab/gitlab.rband reconfigure GitLab:gitlab-ctl reconfigure -
Verify that GitLab can reach Praefect:
gitlab-rake gitlab:gitaly:check -
Set the Grafana admin password. This command will prompt you to enter a new password:
gitlab-ctl set-grafana-password -
Update the Repository storage settings from Admin Area > Settings > Repository > Repository storage to make the newly configured Praefect cluster the storage location for new Git repositories.
- Deselect the default storage location
- Select the praefect storage location
-
Verify everything is still working by creating a new project. Check the "Initialize repository with a README" box so that there is content in the repository that viewed. If the project is created, and you can see the README file, it works!
-
Inspect metrics by browsing to
/-/grafanaon your GitLab server. Log in withadmin/GRAFANA_PASSWORD. Go to 'Explore' and querygitlab_build_infoto verify that you are getting metrics from all your machines.
Congratulations! You have configured a highly available Praefect cluster.
Migrating existing repositories to Praefect
If your GitLab instance already has repositories, these won't be migrated automatically.
Repositories may be moved from one storage location using the Repository API:
curl --request PUT \
--header "PRIVATE-TOKEN: <your_access_token>" \
--data "repository_storage=praefect" \
https://example.gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/123
Debugging Praefect
If you receive an error, check /var/log/gitlab/gitlab-rails/production.log.
Here are common errors and potential causes:
- 500 response code
- ActionView::Template::Error (7:permission denied)
praefect['auth_token']andgitlab_rails['gitaly_token']do not match on the GitLab server.
- Unable to save project. Error: 7:permission denied
- Secret token in
praefect['storage_nodes']on GitLab server does not match the value ingitaly['auth_token']on one or more Gitaly servers.
- Secret token in
- ActionView::Template::Error (7:permission denied)
- 503 response code
- GRPC::Unavailable (14:failed to connect to all addresses)
- GitLab was unable to reach Praefect.
- GRPC::Unavailable (14:all SubCons are in TransientFailure...)
- Praefect cannot reach one or more of its child Gitaly nodes. Try running the Praefect connection checker to diagnose.
- GRPC::Unavailable (14:failed to connect to all addresses)