28 KiB
| table_display_block | type |
|---|---|
| true | reference |
GitLab CI/CD environment variables
After a brief overview over the use of environment variables, this document teaches you how to use GitLab CI/CD's variables, presents the full reference for predefined variables, and dives into more advanced applications.
Overview
An environment variable is a dynamic-named value that can affect the way running processes will behave on an operating system.
They are part of the environment in which a process runs.
For example, a running process can query the value of the
TEMP environment variable to discover a suitable location
to store temporary files, or to define a URL for a database
that can be reused in different scripts.
Variables are useful for customizing your jobs in GitLab CI/CD's pipelines. Using variables means no hardcoded values.
Predefined environment variables
GitLab CI/CD has a default set of predefined variables which can be used without any specification needed. You can call issues numbers, user names, branch names, pipeline and commit IDs, and much more.
Predefined environment variables are the ones that GitLab provides out of the box for the local environment of the Runner.
GitLab reads the .gitlab-ci.yml file, sends the information
to the Runner (which runs the script commands), under which
the variables are exposed.
For example, two jobs under the same pipeline can share the same
CI_PIPELINE_ID variable, but each one has its own CI_JOB_ID
variable.
NOTE: Note: Find here the full predefined variables reference table.
Custom environment variables
When your use case requires a specific variable, you can
set them up easily from the UI
or directly in the .gitlab-ci.yml file and reuse them as you wish.
That can be very powerful as it can be used for scripting without the need to specify the value itself.
Variable types
Introduced in GitLab 11.11.
There are two types of variables supported by GitLab:
- "Variable": the Runner will create an environment variable named same as the variable key and set its value to the variable value.
- "File": the Runner will write the variable value to a temporary file and set the path to this file as the value of an environment variable named same as the variable key.
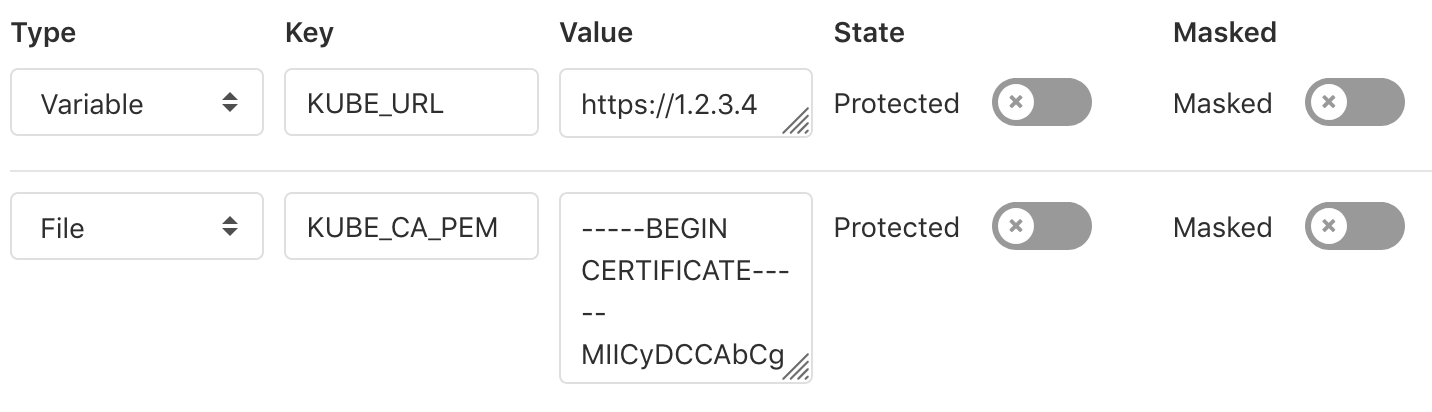
Many tools (like AWS CLI and kubectl) provide the ability to customise configuration using files by either providing the file path as a command line argument or an environment variable. Prior to the introduction of variable types, the common pattern was to use the value of a CI variable, save it in a file, and then use the newly created file in your script:
# Save the content of variable in a file
echo "$KUBE_CA_PEM" > "$(pwd)/kube.ca.pem"
# Use the newly created file
kubectl config set-cluster e2e --server="$KUBE_URL" --certificate-authority="$(pwd)/kube.ca.pem"
This can be simplified by creating a variable of type "File" and using it directly. For example, let's say we have the following variables.
We can then call them from .gitlab-ci.yml like this:
kubectl config set-cluster e2e --server="$KUBE_URL" --certificate-authority="$KUBE_CA_PEM"
Variable types can be set via the UI or the API, but not in .gitlab-ci.yml.
Masked variables
Introduced in GitLab 11.10
Variables can be created as masked variables. This means that the value of the variable will be hidden in job logs, though it must match certain requirements to do so:
-
The value must be in a single line.
-
The value must only consist of characters from the Base64 alphabet (RFC4648).
In GitLab 12.2 and newer,
@and:are also valid values. -
The value must be at least 8 characters long.
-
The value must not use variables.
If the value does not meet the requirements above, then the CI variable will fail to save. In order to save, either alter the value to meet the masking requirements or disable Masked for the variable.
Getting started
To get started with environment variables in the scope of GitLab CI/CD, let's go over a few examples.
Using predefined environment variables
To get started, choose one of the existing
predefined variables
to be output by the Runner. For example, let's say that you want
a given job you're running through your script to output the
stage that job is running for. In your .gitlab-ci.yml file,
call the variable from your script according to the syntaxes available. To
output the job stage, use the predefined variable CI_JOB_STAGE:
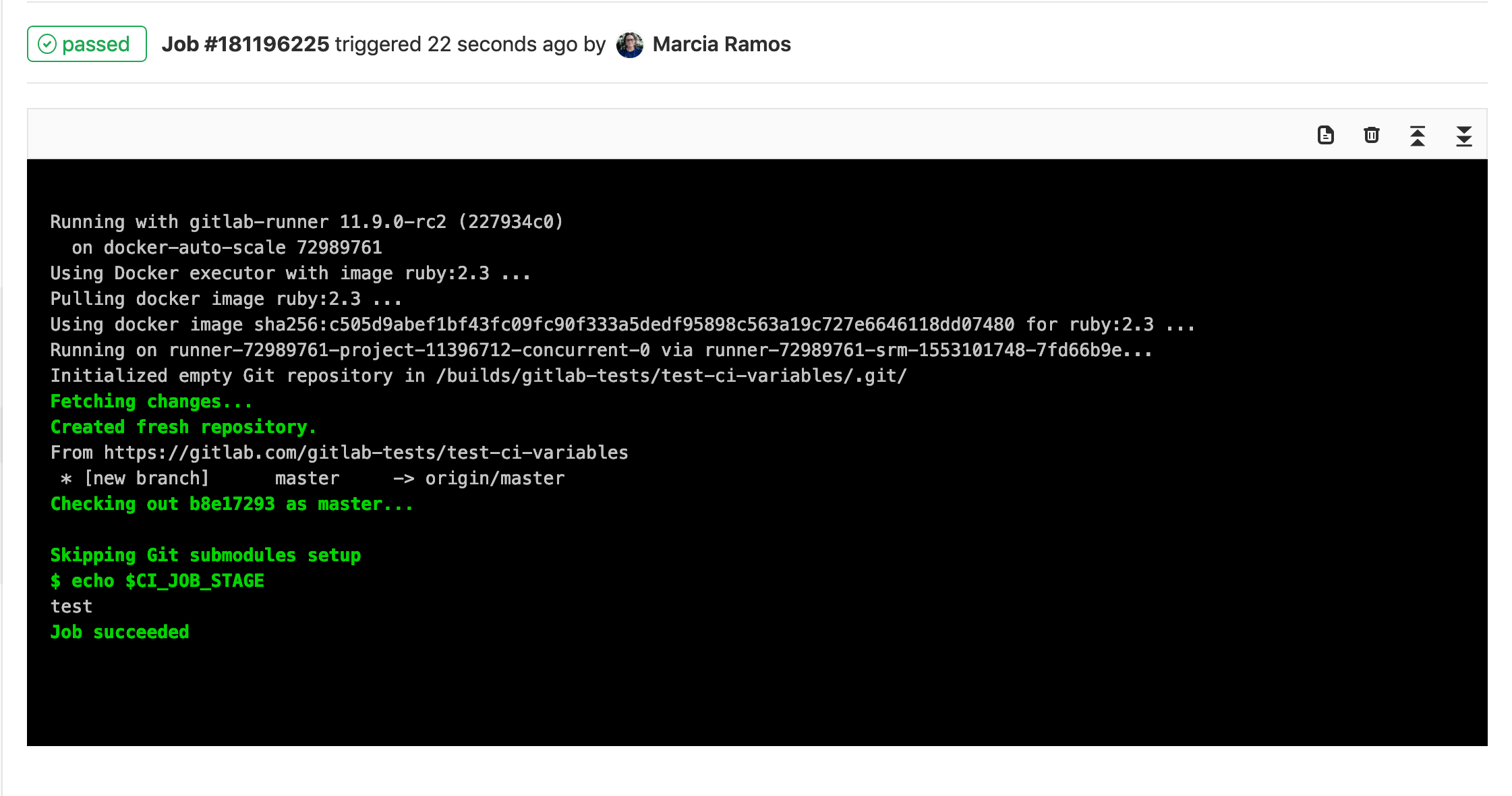
test_variable:
stage: test
script:
- echo $CI_JOB_STAGE
For this case, the Runner will output the stage for the
job test_variable, which is test:
As another example, let's say you're using your own GitLab
instance you want to know what domain your GitLab Pages are
served under. You can easily call it with the predefined
variable $CI_PAGES_DOMAIN in your script:
pages:
script:
- ...
- echo $CI_PAGES_DOMAIN
For GitLab.com users, the output will be gitlab.io. For your
private instance, the output will be whatever your sysadmin has
defined.
Creating a custom environment variable
Assume you have something you want to repeat through your scripts
in GitLab CI/CD's configuration file. To keep this example simple,
let's say you want to output HELLO WORLD for a TEST variable.
You can either set the variable directly in the .gitlab-ci.yml
file or through the UI.
Via .gitlab-ci.yml
To create a new custom env_var variable via .gitlab-ci.yml, define their variable/value pair under
variables:
variables:
TEST: "HELLO WORLD"
For a deeper look into them, see .gitlab-ci.yml defined variables.
Via the UI
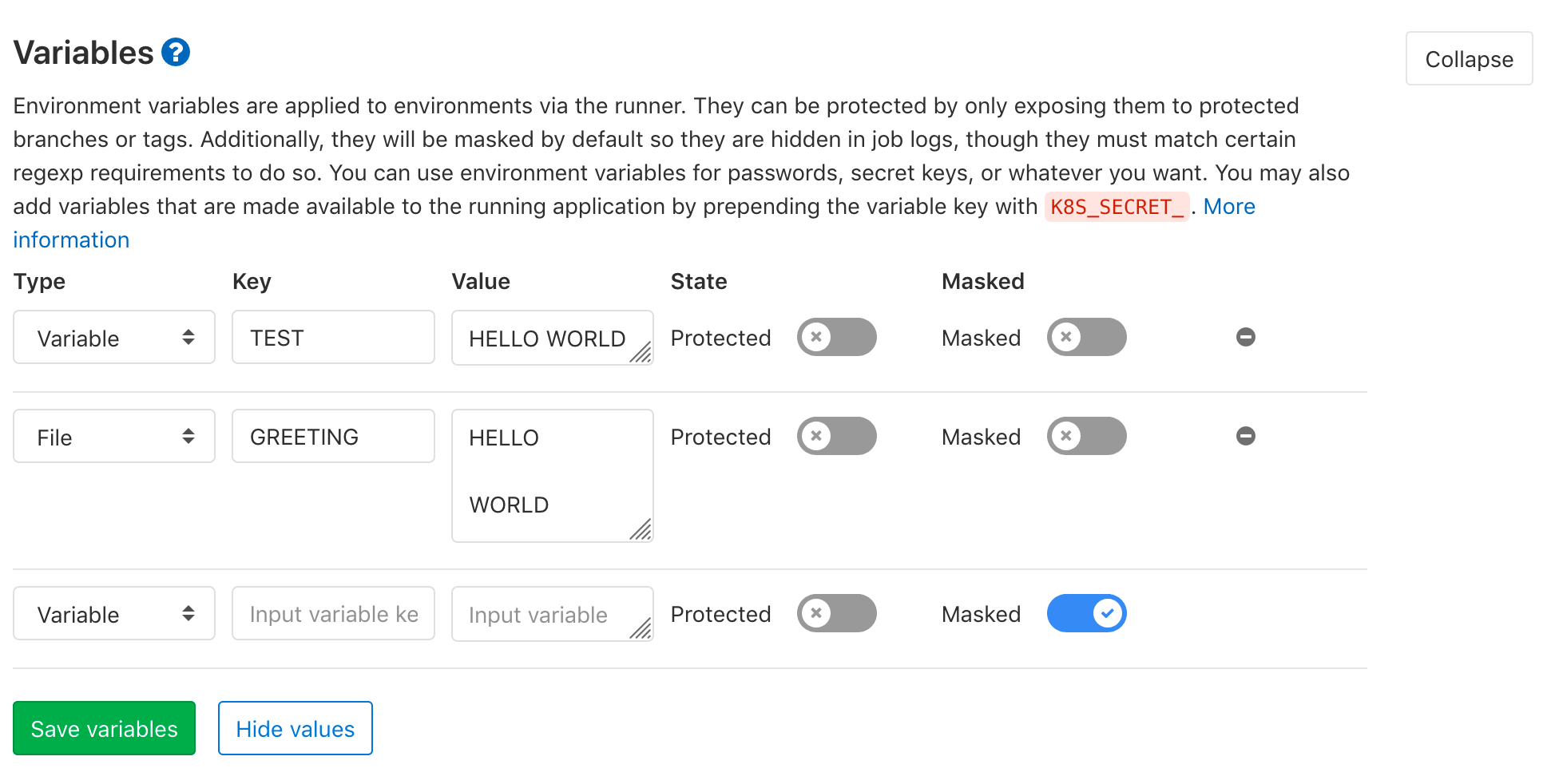
From the UI, navigate to your project's Settings > CI/CD and expand Variables. Create a new variable by choosing its type, naming it in the field Input variable key, and defining its value in the Input variable value field:
You'll also see the option to mask and/or protect your variables.
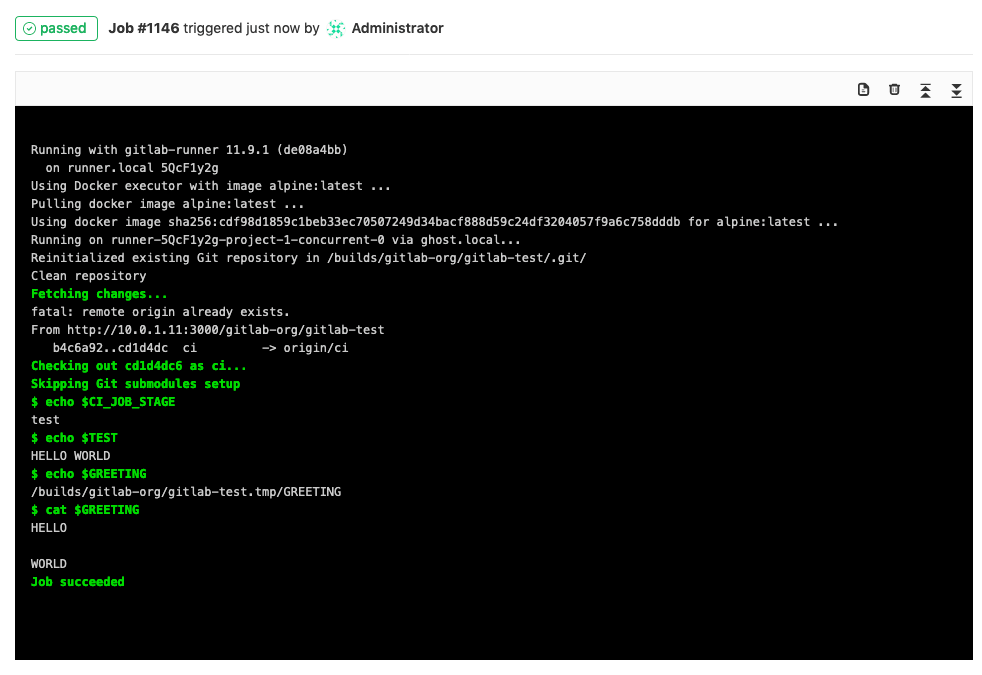
Once you've set the variables, call them from the .gitlab-ci.yml file:
test_variable:
stage: test
script:
- echo $CI_JOB_STAGE # calls a predefined variable
- echo $TEST # calls a custom variable of type `env_var`
- echo $GREETING # calls a custom variable of type `file` that contains the path to the temp file
- cat $GREETING # the temp file itself contains the variable value
The output will be:
Syntax of environment variables in job scripts
All variables are set as environment variables in the build environment, and
they are accessible with normal methods that are used to access such variables.
In most cases bash or sh is used to execute the job script.
To access environment variables, use the syntax for your Runner's shell.
| Shell | Usage |
|---|---|
| bash/sh | $variable |
| windows batch | %variable% |
| PowerShell | $env:variable |
To access environment variables in bash, prefix the variable name with ($):
job_name:
script:
- echo $CI_JOB_ID
To access environment variables in Windows Batch, surround the variable
with (%):
job_name:
script:
- echo %CI_JOB_ID%
To access environment variables in a Windows PowerShell environment, prefix
the variable name with ($env:):
job_name:
script:
- echo $env:CI_JOB_ID
You can also list all environment variables with the export command,
but be aware that this will also expose the values of all the variables
you set, in the job log:
job_name:
script:
- export
Example values:
export CI_JOB_ID="50"
export CI_COMMIT_SHA="1ecfd275763eff1d6b4844ea3168962458c9f27a"
export CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA="1ecfd275"
export CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME="master"
export CI_REPOSITORY_URL="https://gitlab-ci-token:abcde-1234ABCD5678ef@example.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss.git"
export CI_COMMIT_TAG="1.0.0"
export CI_JOB_NAME="spec:other"
export CI_JOB_STAGE="test"
export CI_JOB_MANUAL="true"
export CI_JOB_TRIGGERED="true"
export CI_JOB_TOKEN="abcde-1234ABCD5678ef"
export CI_PIPELINE_ID="1000"
export CI_PIPELINE_IID="10"
export CI_PAGES_DOMAIN="gitlab.io"
export CI_PAGES_URL="https://gitlab-org.gitlab.io/gitlab-ce"
export CI_PROJECT_ID="34"
export CI_PROJECT_DIR="/builds/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss"
export CI_PROJECT_NAME="gitlab-ce"
export CI_PROJECT_NAMESPACE="gitlab-org"
export CI_PROJECT_PATH="gitlab-org/gitlab-ce"
export CI_PROJECT_URL="https://example.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss"
export CI_REGISTRY="registry.example.com"
export CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE="registry.example.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss"
export CI_RUNNER_ID="10"
export CI_RUNNER_DESCRIPTION="my runner"
export CI_RUNNER_TAGS="docker, linux"
export CI_SERVER="yes"
export CI_SERVER_HOST="example.com"
export CI_SERVER_NAME="GitLab"
export CI_SERVER_REVISION="70606bf"
export CI_SERVER_VERSION="8.9.0"
export CI_SERVER_VERSION_MAJOR="8"
export CI_SERVER_VERSION_MINOR="9"
export CI_SERVER_VERSION_PATCH="0"
export GITLAB_USER_ID="42"
export GITLAB_USER_EMAIL="user@example.com"
export CI_REGISTRY_USER="gitlab-ci-token"
export CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD="longalfanumstring"
.gitlab-ci.yml defined variables
NOTE: Note: This feature requires GitLab Runner 0.5.0 or higher and GitLab 7.14 or higher.
GitLab CI allows you to add to .gitlab-ci.yml variables that are set in the
build environment. The variables are hence saved in the repository, and they
are meant to store non-sensitive project configuration. For example, RAILS_ENV or
DATABASE_URL.
For example, if you set the variable below globally (not inside a job), it will be used in all executed commands and scripts:
variables:
DATABASE_URL: "postgres://postgres@postgres/my_database"
The YAML-defined variables are also set to all created service containers, thus allowing to fine tune them.
Variables can be defined at a global level, but also at a job level. To turn off global defined variables in your job, define an empty hash:
job_name:
variables: {}
You are able to use other variables inside your variable definition (or escape them with $$):
variables:
LS_CMD: 'ls $FLAGS $$TMP_DIR'
FLAGS: '-al'
script:
- 'eval $LS_CMD' # will execute 'ls -al $TMP_DIR'
Group-level environment variables
Introduced in GitLab 9.4.
GitLab CI/CD allows you to define per-project or per-group variables
that are set in the pipeline environment. Group-level variables are stored out of
the repository (not in .gitlab-ci.yml) and are securely passed to GitLab Runner
making them available during a pipeline run. It's the recommended method to
use for storing things like passwords, SSH keys, and credentials.
Group-level variables can be added by:
- Navigating to your group's Settings > CI/CD page.
- Inputing variable types, keys, and values in the Variables section. Any variables of subgroups will be inherited recursively.
Once you set them, they will be available for all subsequent pipelines.
Priority of environment variables
Variables of different types can take precedence over other variables, depending on where they are defined.
The order of precedence for variables is (from highest to lowest):
- Trigger variables or scheduled pipeline variables.
- Project-level variables or protected variables.
- Group-level variables or protected variables.
- YAML-defined job-level variables.
- YAML-defined global variables.
- Deployment variables.
- Predefined environment variables.
For example, if you define:
API_TOKEN=secureas a project variable.API_TOKEN=yamlin your.gitlab-ci.yml.
API_TOKEN will take the value secure as the project
variables take precedence over those defined in .gitlab-ci.yml.
Unsupported variables
There are cases where some variables cannot be used in the context of a
.gitlab-ci.yml definition (for example under script). Read more about which variables are not supported.
Where variables can be used
Click here for a section that describes where and how the different types of variables can be used.
Advanced use
Protected environment variables
Introduced in GitLab 9.3.
Variables can be protected. Whenever a variable is protected, it would only be securely passed to pipelines running on the protected branches or protected tags. The other pipelines would not get any protected variables.
Protected variables can be added by going to your project's Settings > CI/CD, then finding the section called Variables, and check "Protected".
Once you set them, they will be available for all subsequent pipelines.
Limiting environment scopes of environment variables
You can limit the environment scope of a variable by defining which environments it can be available for.
To learn more about about scoping environments, see Scoping environments with specs.
Deployment environment variables
Introduced in GitLab 8.15.
Project services that are responsible for deployment configuration may define their own variables that are set in the build environment. These variables are only defined for deployment jobs. Please consult the documentation of the project services that you are using to learn which variables they define.
An example project service that defines deployment variables is the Kubernetes integration.
Auto DevOps environment variables
Introduced in GitLab 11.7.
You can configure Auto DevOps to
pass CI variables to the running application by prefixing the key of the
variable with K8S_SECRET_.
These prefixed variables will then be available as environment variables on the running application container.
CAUTION: Caution: Variables with multiline values are not currently supported due to limitations with the current Auto DevOps scripting environment.
Environment variables triggered manually
Introduced in GitLab 10.8.
Manually triggered pipelines allow you to override the value of a current variable.
For instance, suppose you added a
custom variable $TEST
as exemplified above and you want to override it in a manual pipeline.
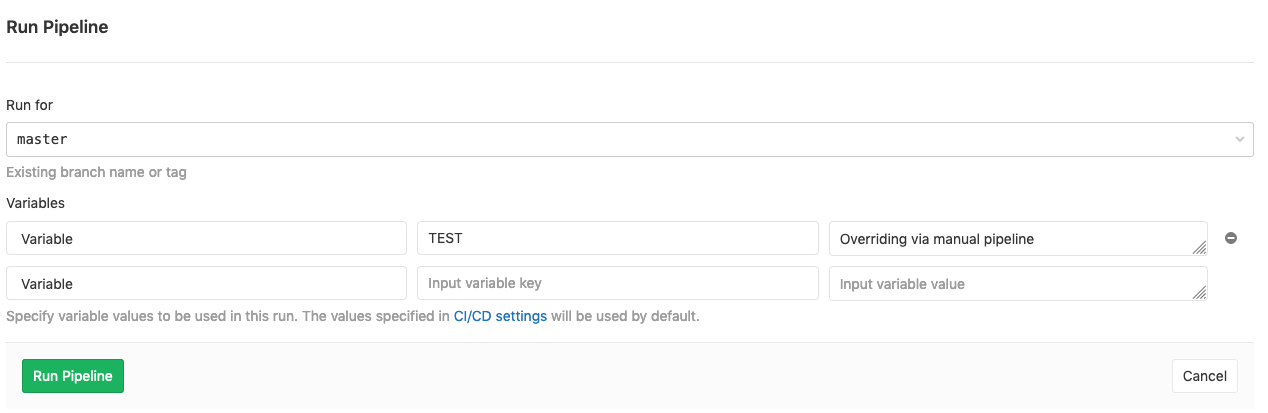
Navigate to your project's CI/CD > Pipelines and click Run pipeline.
Choose the branch you want to run the pipeline for, then add a new variable through the UI:
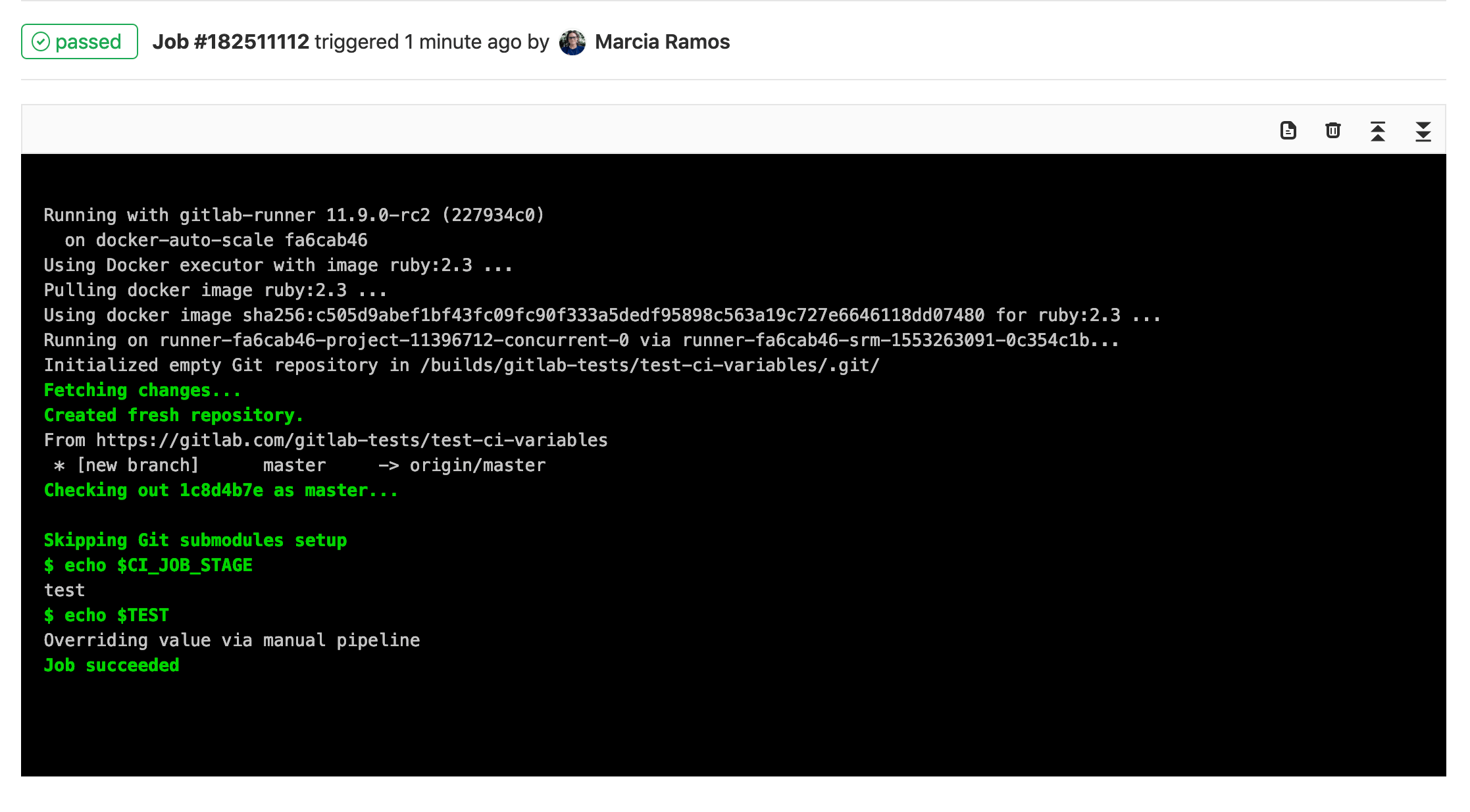
The Runner will override the value previously set and use the custom value you set for this specific pipeline:
Environment variables expressions
Introduced in GitLab 10.7.
It is possible to use variables expressions with only / except policies in
.gitlab-ci.yml. By using this approach you can limit what jobs are going to
be created within a pipeline after pushing a code to GitLab.
This is particularly useful in combination with variables and triggered pipeline variables.
deploy:
script: cap staging deploy
environment: staging
only:
variables:
- $RELEASE == "staging"
- $STAGING
Each expression provided is going to be evaluated before creating a pipeline.
If any of the conditions in variables evaluates to truth when using only,
a new job is going to be created. If any of the expressions evaluates to truth
when except is being used, a job is not going to be created.
This follows usual rules for only / except policies.
Supported syntax
Below you can find supported syntax reference:
-
Equality matching using a string
Examples:
$VARIABLE == "some value"$VARIABLE != "some value"(introduced in GitLab 11.11)
You can use equality operator
==or!=to compare a variable content to a string. We support both, double quotes and single quotes to define a string value, so both$VARIABLE == "some value"and$VARIABLE == 'some value'are supported."some value" == $VARIABLEis correct too. -
Checking for an undefined value
Examples:
$VARIABLE == null$VARIABLE != null(introduced in GitLab 11.11)
It sometimes happens that you want to check whether a variable is defined or not. To do that, you can compare a variable to
nullkeyword, like$VARIABLE == null. This expression is going to evaluate to truth if variable is not defined when==is used, or to falsey if!=is used. -
Checking for an empty variable
Examples:
$VARIABLE == ""$VARIABLE != ""(introduced in GitLab 11.11)
If you want to check whether a variable is defined, but is empty, you can simply compare it against an empty string, like
$VAR == ''or non-empty string$VARIABLE != "". -
Comparing two variables
Examples:
$VARIABLE_1 == $VARIABLE_2$VARIABLE_1 != $VARIABLE_2(introduced in GitLab 11.11)
It is possible to compare two variables. This is going to compare values of these variables.
-
Variable presence check
Example:
$STAGINGIf you only want to create a job when there is some variable present, which means that it is defined and non-empty, you can simply use variable name as an expression, like
$STAGING. If$STAGINGvariable is defined, and is non empty, expression will evaluate to truth.$STAGINGvalue needs to a string, with length higher than zero. Variable that contains only whitespace characters is not an empty variable. -
Pattern matching (introduced in GitLab 11.0)
Examples:
$VARIABLE =~ /^content.*/$VARIABLE_1 !~ /^content.*/(introduced in GitLab 11.11)
It is possible perform pattern matching against a variable and regular expression. Expression like this evaluates to truth if matches are found when using
=~. It evaluates to truth if matches are not found when!~is used.Pattern matching is case-sensitive by default. Use
iflag modifier, like/pattern/ito make a pattern case-insensitive. -
Conjunction / Disjunction (introduced in GitLab 12.0)
Examples:
$VARIABLE1 =~ /^content.*/ && $VARIABLE2 == "something"$VARIABLE1 =~ /^content.*/ && $VARIABLE2 =~ /thing$/ && $VARIABLE3$VARIABLE1 =~ /^content.*/ || $VARIABLE2 =~ /thing$/ && $VARIABLE3
It is possible to join multiple conditions using
&&or||. Any of the otherwise supported syntax may be used in a conjunctive or disjunctive statement. Precedence of operators follows standard Ruby 2.5 operation precedence.
Debug tracing
Introduced in GitLab Runner 1.7.
CAUTION: Warning: Enabling debug tracing can have severe security implications. The output will contain the content of all your variables and any other secrets! The output will be uploaded to the GitLab server and made visible in job traces!
By default, GitLab Runner hides most of the details of what it is doing when processing a job. This behavior keeps job traces short, and prevents secrets from being leaked into the trace unless your script writes them to the screen.
If a job isn't working as expected, this can make the problem difficult to
investigate; in these cases, you can enable debug tracing in .gitlab-ci.yml.
Available on GitLab Runner v1.7+, this feature enables the shell's execution
trace, resulting in a verbose job trace listing all commands that were run,
variables that were set, etc.
Before enabling this, you should ensure jobs are visible to team members only. You should also erase all generated job traces before making them visible again.
To enable debug traces, set the CI_DEBUG_TRACE variable to true:
job_name:
variables:
CI_DEBUG_TRACE: "true"
Example truncated output with debug trace set to true:
...
export CI_SERVER_TLS_CA_FILE="/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.tmp/CI_SERVER_TLS_CA_FILE"
if [[ -d "/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace/.git" ]]; then
echo $'\''\x1b[32;1mFetching changes...\x1b[0;m'\''
$'\''cd'\'' "/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace"
$'\''git'\'' "config" "fetch.recurseSubmodules" "false"
$'\''rm'\'' "-f" ".git/index.lock"
$'\''git'\'' "clean" "-ffdx"
$'\''git'\'' "reset" "--hard"
$'\''git'\'' "remote" "set-url" "origin" "https://gitlab-ci-token:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx@example.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.git"
$'\''git'\'' "fetch" "origin" "--prune" "+refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*" "+refs/tags/*:refs/tags/*"
else
$'\''mkdir'\'' "-p" "/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.tmp/git-template"
$'\''rm'\'' "-r" "-f" "/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace"
$'\''git'\'' "config" "-f" "/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.tmp/git-template/config" "fetch.recurseSubmodules" "false"
echo $'\''\x1b[32;1mCloning repository...\x1b[0;m'\''
$'\''git'\'' "clone" "--no-checkout" "https://gitlab-ci-token:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx@example.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.git" "/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace" "--template" "/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.tmp/git-template"
$'\''cd'\'' "/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace"
fi
echo $'\''\x1b[32;1mChecking out dd648b2e as master...\x1b[0;m'\''
$'\''git'\'' "checkout" "-f" "-q" "dd648b2e48ce6518303b0bb580b2ee32fadaf045"
'
+++ hostname
++ echo 'Running on runner-8a2f473d-project-1796893-concurrent-0 via runner-8a2f473d-machine-1480971377-317a7d0f-digital-ocean-4gb...'
Running on runner-8a2f473d-project-1796893-concurrent-0 via runner-8a2f473d-machine-1480971377-317a7d0f-digital-ocean-4gb...
++ export CI=true
++ CI=true
++ export CI_API_V4_URL=https://example.com:3000/api/v4
++ CI_API_V4_URL=https://example.com:3000/api/v4
++ export CI_DEBUG_TRACE=false
++ CI_DEBUG_TRACE=false
++ export CI_COMMIT_SHA=dd648b2e48ce6518303b0bb580b2ee32fadaf045
++ CI_COMMIT_SHA=dd648b2e48ce6518303b0bb580b2ee32fadaf045
++ export CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA=dd648b2e
++ CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA=dd648b2e
++ export CI_COMMIT_BEFORE_SHA=dd648b2e48ce6518303b0bb580b2ee32fadaf045
++ CI_COMMIT_BEFORE_SHA=dd648b2e48ce6518303b0bb580b2ee32fadaf045
++ export CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME=master
++ CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME=master
++ export CI_JOB_ID=7046507
++ CI_JOB_ID=7046507
++ export CI_REPOSITORY_URL=https://gitlab-ci-token:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx@example.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.git
++ CI_REPOSITORY_URL=https://gitlab-ci-token:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx@example.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.git
++ export CI_JOB_TOKEN=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
++ CI_JOB_TOKEN=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
++ export CI_PROJECT_ID=1796893
++ CI_PROJECT_ID=1796893
++ export CI_PROJECT_DIR=/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace
++ CI_PROJECT_DIR=/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace
++ export CI_SERVER=yes
++ CI_SERVER=yes
++ export 'CI_SERVER_HOST=example.com'
++ CI_SERVER_HOST='example.com'
++ export 'CI_SERVER_NAME=GitLab CI'
++ CI_SERVER_NAME='GitLab CI'
++ export CI_SERVER_VERSION=
++ CI_SERVER_VERSION=
++ export CI_SERVER_VERSION_MAJOR=
++ CI_SERVER_VERSION_MAJOR=
++ export CI_SERVER_VERSION_MINOR=
++ CI_SERVER_VERSION_MINOR=
++ export CI_SERVER_VERSION_PATCH=
++ CI_SERVER_VERSION_PATCH=
++ export CI_SERVER_REVISION=
++ CI_SERVER_REVISION=
++ export GITLAB_CI=true
++ GITLAB_CI=true
++ export CI=true
++ CI=true
++ export CI_API_V4_URL=https://example.com:3000/api/v4
++ CI_API_V4_URL=https://example.com:3000/api/v4
++ export GITLAB_CI=true
++ GITLAB_CI=true
++ export CI_JOB_ID=7046507
++ CI_JOB_ID=7046507
++ export CI_JOB_TOKEN=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
++ CI_JOB_TOKEN=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
++ export CI_COMMIT_REF=dd648b2e48ce6518303b0bb580b2ee32fadaf045
++ CI_COMMIT_REF=dd648b2e48ce6518303b0bb580b2ee32fadaf045
++ export CI_COMMIT_BEFORE_SHA=dd648b2e48ce6518303b0bb580b2ee32fadaf045
++ CI_COMMIT_BEFORE_SHA=dd648b2e48ce6518303b0bb580b2ee32fadaf045
++ export CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME=master
++ CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME=master
++ export CI_COMMIT_NAME=debug_trace
++ CI_JOB_NAME=debug_trace
++ export CI_JOB_STAGE=test
++ CI_JOB_STAGE=test
++ export CI_SERVER_HOST=example.com
++ CI_SERVER_HOST=example.com
++ export CI_SERVER_NAME=GitLab
++ CI_SERVER_NAME=GitLab
++ export CI_SERVER_VERSION=8.14.3-ee
++ CI_SERVER_VERSION=8.14.3-ee
++ export CI_SERVER_REVISION=82823
++ CI_SERVER_REVISION=82823
++ export CI_PAGES_DOMAIN=gitlab.io
++ CI_PAGES_DOMAIN=gitlab.io
++ export CI_PAGES_URL=https://gitlab-examples.gitlab.io/ci-debug-trace
++ CI_PAGES_URL=https://gitlab-examples.gitlab.io/ci-debug-trace
++ export CI_PROJECT_ID=17893
++ CI_PROJECT_ID=17893
++ export CI_PROJECT_NAME=ci-debug-trace
++ CI_PROJECT_NAME=ci-debug-trace
++ export CI_PROJECT_PATH=gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace
++ CI_PROJECT_PATH=gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace
++ export CI_PROJECT_NAMESPACE=gitlab-examples
++ CI_PROJECT_NAMESPACE=gitlab-examples
++ export CI_PROJECT_URL=https://example.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace
++ CI_PROJECT_URL=https://example.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace
++ export CI_PIPELINE_ID=52666
++ CI_PIPELINE_ID=52666
++ export CI_PIPELINE_IID=123
++ CI_PIPELINE_IID=123
++ export CI_RUNNER_ID=1337
++ CI_RUNNER_ID=1337
++ export CI_RUNNER_DESCRIPTION=shared-runners-manager-1.example.com
++ CI_RUNNER_DESCRIPTION=shared-runners-manager-1.example.com
++ export 'CI_RUNNER_TAGS=shared, docker, linux, ruby, mysql, postgres, mongo'
++ CI_RUNNER_TAGS='shared, docker, linux, ruby, mysql, postgres, mongo'
++ export CI_REGISTRY=registry.example.com
++ CI_REGISTRY=registry.example.com
++ export CI_DEBUG_TRACE=true
++ CI_DEBUG_TRACE=true
++ export GITLAB_USER_ID=42
++ GITLAB_USER_ID=42
++ export GITLAB_USER_EMAIL=user@example.com
++ GITLAB_USER_EMAIL=user@example.com
++ export VERY_SECURE_VARIABLE=imaverysecurevariable
++ VERY_SECURE_VARIABLE=imaverysecurevariable
++ mkdir -p /builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.tmp
++ echo -n '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIFQzCCBCugAwIBAgIRAL/ElDjuf15xwja1ZnCocWAwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQELBQAw'
...