15 KiB
| stage | group | info | type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create | Code Review | To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/product/ux/technical-writing/#assignments | index, reference |
Review a merge request (FREE)
- Introduced in GitLab 13.5.
- Feature flag removed in GitLab 13.9.
Merge requests are the primary method of making changes to files in a GitLab project. Create and submit a merge request to propose changes. Your team leaves comments on your merge request, and makes code suggestions you can accept from the user interface. When your work is reviewed, your team members can choose to accept or reject it.
You can review merge requests from the GitLab interface. If you install the GitLab Workflow VS Code extension, you can also review merge requests in Visual Studio Code.
Suggested reviewers (ULTIMATE SAAS)
Introduced in GitLab 15.4.
GitLab can recommend reviewers with Suggested Reviewers. Using the changes in a merge request and a project's contribution graph, machine learning powered suggestions appear in the reviewer section of the right merge request sidebar.
This feature is currently in Open Beta behind a feature flag.
Learn more about how suggested reviewers works and data privacy.
Enable suggested reviewers
Project Maintainers or Owners can enable suggested reviewers by visiting the project settings.
Enabling suggested reviewers will trigger GitLab to create an ML model for your project that will be used to generate reviewers. The larger your project, the longer this can take, but usually, the model will be ready to generate suggestions within a few hours.
No action is required once the feature is enabled. Once the model is ready, recommendations will populate the Reviewer dropdown in the right-hand sidebar of a merge request with new commits.
Review a merge request
- Introduced in GitLab 11.4.
- Moved from GitLab Premium to GitLab Free in 13.1.
When you review a merge request, you can create comments that are visible only to you. When you're ready, you can publish them together in a single action. To start your review:
- Go to the merge request you want to review, and select the Changes tab. To learn more about navigating the diffs displayed in this tab, read Changes tab in merge requests.
- Select the {comment} comment icon in the gutter to expand the diff lines and display a comment box. In GitLab version 13.2 and later, you can select multiple lines.
- In the text area, write your first comment, then select Start a review below your comment.
- Continue adding comments to lines of code. After each comment, select Add to review. Comments made as part of a review are visible only to you until you submit your review.
- Optional. You can use quick actions inside review comments. The comment shows the actions to perform after publication, but does not perform them until you submit your review.
- When your review is complete, you can submit the review. Your comments are now visible, and any quick actions included in your comments are performed.
In GitLab 13.10 and later, if you approve a merge request and are shown in the reviewer list, a green check mark {check-circle-filled} displays next to your name.
Submit a review
You can submit your completed review in multiple ways:
-
Use the
/submit_reviewquick action in the text of a non-review comment. -
Select Finish review, then select Submit review at the bottom of the modal window. In the modal window, you can supply a Summary comment, approve the merge request, and include quick actions:
When you submit your review, GitLab:
- Publishes the comments in your review.
- Sends a single email to every notifiable user of the merge request, with your review comments attached. Replying to this email creates a new comment on the merge request.
- Perform any quick actions you added to your review comments.
- Optional. Approves the merge request.
Resolve or unresolve thread with a comment
Review comments can also resolve or unresolve resolvable threads. To resolve or unresolve a thread when replying to a comment:
- In the comment text area, write your comment.
- Select or clear Resolve thread.
- Select Add comment now or Add to review.
Pending comments display information about the action to be taken when the comment is published:
- {check-circle-filled} Thread will be resolved.
- {check-circle} Thread stays unresolved.
Add a new comment
Introduced in GitLab 13.10.
If you have a review in progress, you can also add a comment from the Overview tab by selecting Add to review:
Approval Rule information for Reviewers (PREMIUM)
- Introduced in GitLab 13.8.
- Feature flag
reviewer_approval_rulesremoved in GitLab 13.9.
When editing the Reviewers field in a new or existing merge request, GitLab
displays the name of the matching approval rule
below the name of each suggested reviewer. Code Owners are displayed as Codeowner without group detail.
This example shows reviewers and approval rules when creating a new merge request:
This example shows reviewers and approval rules in a merge request sidebar:
Request a new review
Introduced in GitLab 13.9.
After a reviewer completes their merge request reviews, the author of the merge request can request a new review from the reviewer:
- If the right sidebar in the merge request is collapsed, select the {chevron-double-lg-left} Expand Sidebar icon to expand it.
- In the Reviewers section, select the Re-request a review icon ({redo}) next to the reviewer's name.
GitLab creates a new to-do item for the reviewer, and sends them a notification email.
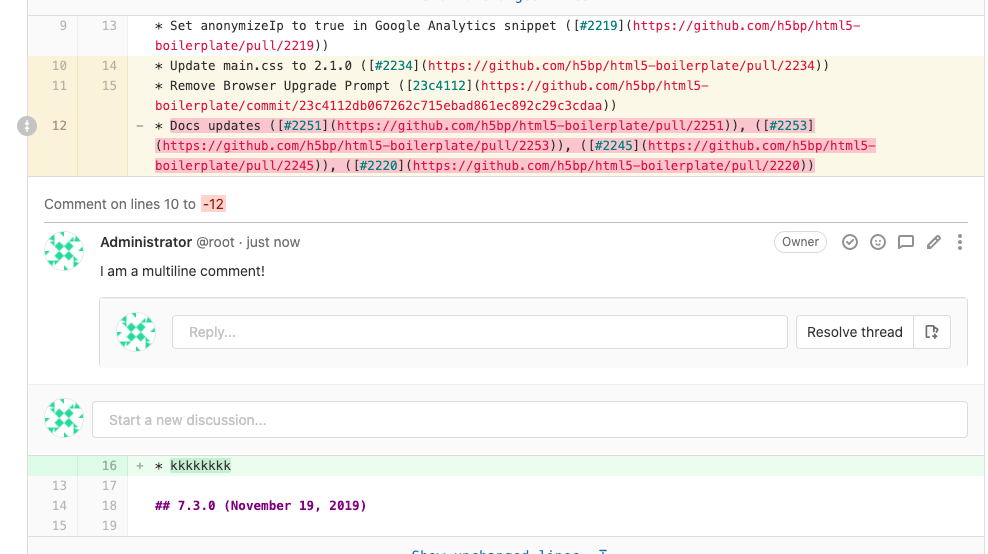
Comment on multiple lines
- Introduced in GitLab 13.2.
- Added click-and-drag features in GitLab 13.8.
- Feature flag removed in GitLab 13.9.
When commenting on a diff, you can select which lines of code your comment refers to by either:
- Dragging the {comment} comment icon in the gutter to highlight lines in the diff. GitLab expands the diff lines and displays a comment box.
- After starting a comment by selecting the {comment} comment icon in the gutter, select the first line number your comment refers to in the Commenting on lines select box. New comments default to single-line comments, unless you select a different starting line.
Multiline comments display the comment's line numbers above the body of the comment:
Bulk edit merge requests at the project level
Users with at least the Developer role can manage merge requests.
When bulk-editing merge requests in a project, you can edit the following attributes:
- Status (open/closed)
- Assignee
- Milestone
- Labels
- Subscriptions
To update multiple project merge requests at the same time:
- In a project, go to Merge requests.
- Select Edit merge requests. A sidebar on the right-hand side of your screen appears with editable fields.
- Select the checkboxes next to each merge request you want to edit.
- Select the appropriate fields and their values from the sidebar.
- Select Update all.
Bulk edit merge requests at the group level (PREMIUM)
Introduced in GitLab 12.2.
Users with at least the Developer role can manage merge requests.
When bulk editing merge requests in a group, you can edit the following attributes:
- Milestone
- Labels
To update multiple group merge requests at the same time:
- In a group, go to Merge requests.
- Select Edit merge requests. A sidebar on the right-hand side of your screen appears with editable fields.
- Select the checkboxes next to each merge request you want to edit.
- Select the appropriate fields and their values from the sidebar.
- Select Update all.
Associated features
These features are associated with merge requests:
- Cherry-pick changes: Cherry-pick any commit in the UI by selecting the Cherry-pick button in a merged merge requests or a commit.
- Fast-forward merge requests: For a linear Git history and a way to accept merge requests without creating merge commits
- Find the merge request that introduced a change: When viewing the commit details page, GitLab links to the merge requests containing that commit.
- Merge requests versions: Select and compare the different versions of merge request diffs
- Resolve conflicts: GitLab can provide the option to resolve certain merge request conflicts in the GitLab UI.
- Revert changes: Revert changes from any commit from a merge request.
- Keyboard shortcuts: Access and modify specific parts of a merge request with keyboard commands.
Troubleshooting
Sometimes things don't go as expected in a merge request. Here are some troubleshooting steps.
Merge request cannot retrieve the pipeline status
This can occur if Sidekiq doesn't pick up the changes fast enough.
Sidekiq
Sidekiq didn't process the CI state change fast enough. Wait a few seconds and the status should update automatically.
Bug
Merge request pipeline statuses can't be retrieved when the following occurs:
- A merge request is created
- The merge request is closed
- Changes are made in the project
- The merge request is reopened
To enable the pipeline status to be properly retrieved, close and reopen the merge request again.
Tips
Here are some tips to help you be more efficient with merge requests in the command line.
Copy the branch name for local checkout
Introduced in GitLab 13.4.
The merge request sidebar contains the branch reference for the source branch used to contribute changes for this merge request.
To copy the branch reference into your clipboard, select the Copy branch name button
({copy-to-clipboard}) in the right sidebar. Use it to check out the branch locally
from the command line by running git checkout <branch-name>.
Checkout merge requests locally through the head ref
A merge request contains all the history from a repository, plus the additional commits added to the branch associated with the merge request. Here's a few ways to check out a merge request locally.
You can check out a merge request locally even if the source project is a fork (even a private fork) of the target project.
This relies on the merge request head ref (refs/merge-requests/:iid/head)
that is available for each merge request. It allows checking out a merge
request by using its ID instead of its branch.
Introduced in GitLab
13.4, 14 days after a merge request gets closed or merged, the merge request
head ref is deleted. This means that the merge request isn't available
for local checkout from the merge request head ref anymore. The merge request
can still be re-opened. If the merge request's branch
exists, you can still check out the branch, as it isn't affected.
Checkout locally by adding a Git alias
Add the following alias to your ~/.gitconfig:
[alias]
mr = !sh -c 'git fetch $1 merge-requests/$2/head:mr-$1-$2 && git checkout mr-$1-$2' -
Now you can check out a particular merge request from any repository and any
remote. For example, to check out the merge request with ID 5 as shown in GitLab
from the origin remote, do:
git mr origin 5
This fetches the merge request into a local mr-origin-5 branch and check
it out.
Checkout locally by modifying .git/config for a given repository
Locate the section for your GitLab remote in the .git/config file. It looks
like this:
[remote "origin"]
url = https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss.git
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*
You can open the file with:
git config -e
Now add the following line to the above section:
fetch = +refs/merge-requests/*/head:refs/remotes/origin/merge-requests/*
In the end, it should look like this:
[remote "origin"]
url = https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss.git
fetch = +refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*
fetch = +refs/merge-requests/*/head:refs/remotes/origin/merge-requests/*
Now you can fetch all the merge requests:
git fetch origin
...
From https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss.git
* [new ref] refs/merge-requests/1/head -> origin/merge-requests/1
* [new ref] refs/merge-requests/2/head -> origin/merge-requests/2
...
And to check out a particular merge request:
git checkout origin/merge-requests/1
All the above can be done with the git-mr script.
Cached merge request count
- Introduced in GitLab 13.11.
- Feature flag removed in GitLab 14.0.
In a group, the sidebar displays the total count of open merge requests. This value is cached if it's greater than than 1000. The cached value is rounded to thousands (or millions) and updated every 24 hours.