4.7 KiB
| stage | group | info |
|---|---|---|
| Create | Ecosystem | To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/engineering/ux/technical-writing/#assignments |
Integrate your GitLab server with Bitbucket Cloud
NOTE: Starting from GitLab 11.4, OmniAuth is enabled by default. If you're using an earlier version, you must explicitly enable it.
You can set up Bitbucket.org as an OAuth2 provider so that you can use your Bitbucket.org account credentials to sign into GitLab or import your projects from Bitbucket.org.
- To use Bitbucket.org as an OmniAuth provider, follow the Bitbucket OmniAuth provider section.
- To import projects from Bitbucket, follow both the Bitbucket OmniAuth provider and Bitbucket project import sections.
Bitbucket OmniAuth provider
To enable the Bitbucket OmniAuth provider you must register your application with Bitbucket.org. Bitbucket generates an application ID and secret key for you to use.
-
Sign in to Bitbucket.org.
-
Navigate to your individual user settings (Bitbucket settings) or a team's settings (Manage team), depending on how you want the application registered. It does not matter if the application is registered as an individual or a team, that is entirely up to you.
-
In the left menu under Access Management, select OAuth.
-
Select Add consumer.
-
Provide the required details:
- Name: This can be anything. Consider something like
<Organization>'s GitLabor<Your Name>'s GitLabor something else descriptive. - Application description: (Optional) Fill this in if you wish.
- Callback URL: (Required in GitLab versions 8.15 and greater)
The URL to your GitLab installation, such as
https://gitlab.example.com/users/auth. Be sure to append/users/authto the end of the callback URL to prevent an OAuth2 convert redirect vulnerability. Leaving this field empty results in anInvalid redirect_urimessage. - URL: The URL to your GitLab installation, such as
https://gitlab.example.com.
- Name: This can be anything. Consider something like
-
Grant at least the following permissions:
Account: Email, Read Projects: Read Repositories: Read Pull Requests: Read Issues: Read Wiki: Read and Write -
Select Save.
-
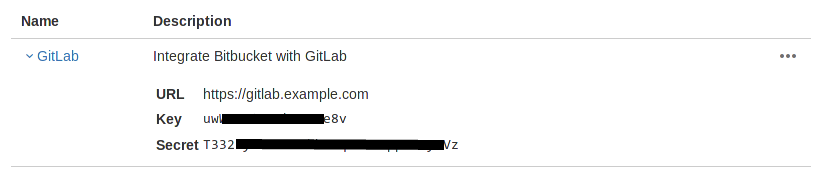
Select your newly created OAuth consumer, and you should now see a Key and Secret in the list of OAuth consumers. Keep this page open as you continue the configuration.
-
On your GitLab server, open the configuration file:
# For Omnibus packages sudo editor /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb # For installations from source sudo -u git -H editor /home/git/gitlab/config/gitlab.yml -
Add the Bitbucket provider configuration:
For Omnibus packages:
gitlab_rails['omniauth_providers'] = [ { "name" => "bitbucket", "app_id" => "BITBUCKET_APP_KEY", "app_secret" => "BITBUCKET_APP_SECRET", "url" => "https://bitbucket.org/" } ]For installations from source:
omniauth: enabled: true providers: - { name: 'bitbucket', app_id: 'BITBUCKET_APP_KEY', app_secret: 'BITBUCKET_APP_SECRET', url: 'https://bitbucket.org/' }
Where
BITBUCKET_APP_KEYis the Key andBITBUCKET_APP_SECRETthe Secret from the Bitbucket application page. -
Save the configuration file.
-
For the changes to take effect, reconfigure GitLab if you installed via Omnibus GitLab, or restart if installed from source.
On the sign-in page there should now be a Bitbucket icon below the regular sign-in form. Click the icon to begin the authentication process. Bitbucket asks the user to sign in and authorize the GitLab application. If successful, the user is returned to GitLab and signed in.
Bitbucket project import
After the above configuration is set up, you can use Bitbucket to sign into GitLab and start importing your projects.
If you want to import projects from Bitbucket, but don't want to enable signing in, you can disable Sign-Ins in the admin panel.