5.6 KiB
GitLab Secure [ULTIMATE]
Check your application for security vulnerabilities that may lead to unauthorized access, data leaks, and denial of services. GitLab will perform static and dynamic tests on the code of your application, looking for known flaws and report them in the merge request so you can fix them before merging. Security teams can use dashboards to get a high-level view on projects and groups, and start remediation processes when needed.
Security scanning tools
GitLab can scan and report any vulnerabilities found in your project.
| Secure scanning tools | Description |
|---|---|
| Container Scanning [ULTIMATE] | Scan Docker containers for known vulnerabilities. |
| Dependency Scanning [ULTIMATE] | Analyze your dependencies for known vulnerabilities. |
| Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) [ULTIMATE] | Analyze running web applications for known vulnerabilities. |
| License Management [ULTIMATE] | Search your project's dependencies for their licenses. |
| Security Dashboard [ULTIMATE] | View vulnerabilities in all your projects and groups. |
| Static Application Security Testing (SAST) [ULTIMATE] | Analyze source code for known vulnerabilities. |
Interacting with the vulnerabilities
Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 10.8.
CAUTION: Warning: This feature is currently Alpha and while you can start using it, it may receive important changes in the future.
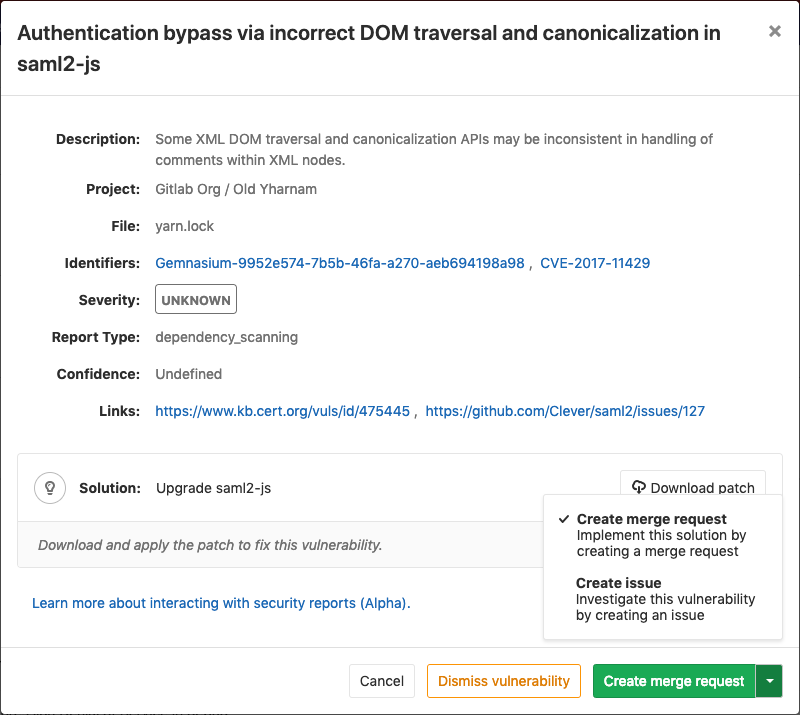
Each security vulnerability in the merge request report or the Security Dashboard is actionable. Clicking on an entry, a detailed information will pop up with different possible options:
- Dismiss vulnerability: Dismissing a vulnerability
will place a
strikethroughstyling on it. - Create issue: The new issue will have the title and description pre-populated with the information from the vulnerability report and will be created as confidential by default.
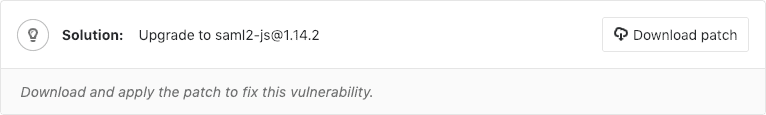
- Solution: For some vulnerabilities (Dependency Scanning and Container Scanning) a solution is provided for how to fix the vulnerability.
Dismissing a vulnerability
You can dismiss vulnerabilities by clicking the Dismiss vulnerability button. This will dismiss the vulnerability and re-render it to reflect its dismissed state. If you wish to undo this dismissal, you can click the Undo dismiss button.
Creating an issue for a vulnerability
You can create an issue for a vulnerability by selecting the Create issue button from within the vulnerability modal or using the action buttons to the right of a vulnerability row when in the group security dashboard.
This will create a confidential issue on the project this vulnerability came from and pre-fill it with some useful information taken from the vulnerability report. Once the issue is created, you will be redirected to it so you can edit, assign, or comment on it.
Upon returning to the group security dashboard, you'll see that the vulnerability will now have an associated issue next to the name.
Solutions for vulnerabilities
Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 11.7.
CAUTION: Warning: Automatic Patch creation is only available for a subset of Dependency Scanning. At the moment only Node.JS projects managed with yarn are supported.
Some vulnerabilities can be fixed by applying the solution that GitLab automatically generates.
Manually applying the suggested patch
Some vulnerabilities can be fixed by applying a patch that is automatically generated by GitLab. To apply the fix:
- Click on the vulnerability.
- Download and review the patch file
remediation.patch. - Ensure your local project has the same commit checked out that was used to generate the patch.
- Run
git apply remediation.patch. - Verify and commit the changes to your branch.
Creating a merge request from a vulnerability
Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 11.9.
In certain cases, GitLab will allow you to create a merge request that will automatically remediate the vulnerability. Any vulnerability that has a solution can have a merge request created to automatically solve the issue.
If this action is available there will be a Create merge request button in the vulnerability modal. Clicking on this button will create a merge request to apply the solution onto the source branch.