9.8 KiB
| stage | group | info |
|---|---|---|
| Create | Source Code | To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/engineering/ux/technical-writing/#assignments |
Code Owners (PREMIUM)
Moved to GitLab Premium in 13.9.
Code Owners define who owns specific files or directories in a repository.
- The users you define as Code Owners are displayed in the UI when you browse directories.
- You can set your merge requests so they must be approved by Code Owners before merge.
- You can protect a branch and allow only Code Owners to approve changes to the branch.
If you don't want to use Code Owners for approvals, you can configure rules instead.
Set up Code Owners
You can use Code Owners to specify users or shared groups that are responsible for specific files and directories in a repository.
To set up Code Owners:
-
Choose the location where you want to specify Code Owners:
- In the root directory of the repository
- In the
.gitlab/directory - In the
docs/directory
-
In that location, create a file named
CODEOWNERS. -
In the file, enter text that follows one of these patterns:
# Code Owners for a file filename @username1 @username2 # Code Owners for a directory directoryname/ @username1 @username2 # All group members as Code Owners for a file filename @groupname # All group members as Code Owners for a directory directoryname/ @groupname
The Code Owners are now displayed in the UI. They apply to the current branch only.
Next steps:
Groups as Code Owners
- Introduced in GitLab 12.1.
- Group and subgroup hierarchy support was introduced in GitLab 13.0.
You can use members of groups and subgroups as Code Owners for a project.
For example, if you have these groups:
- Group X (
group-x) with Project A in it. - Subgroup Y (
group-x/subgroup-y), which belongs to Group X, with Project B in it.
The eligible Code Owners:
- For Project A are the members of Group X only, because Project A doesn't belong to Subgroup Y.
- For Project B are the members of both Group X and Subgroup Y.
You can invite Subgroup Y to Project A so that their members also become eligible Code Owners.
If you do not invite Subgroup Y to Project A, but make them Code Owners, their approval of the merge request becomes optional.
Inviting Subgroup Y to a parent group of Project A is not supported. To set Subgroup Y as Code Owners, add this group directly to the project itself.
Add a group as a Code Owner
To set a group as a Code Owner:
In the CODEOWNERS file, enter text that follows one of these patterns:
# All group members as Code Owners for a file
file.md @group-x
# All subgroup members as Code Owners for a file
file.md @group-x/subgroup-y
# All group and subgroup members as Code Owners for a file
file.md @group-x @group-x/subgroup-y
When a file matches multiple CODEOWNERS entries
When a file matches multiple entries in the CODEOWNERS file,
the users from last pattern matching the file are used.
For example, in the following CODEOWNERS file:
README.md @user1
# This line would also match the file README.md
*.md @user2
The Code Owner for README.md would be @user2.
If you use sections, the last user for each section is used.
Only one CODEOWNERS pattern can match per file path.
Organize Code Owners by putting them into sections
- Introduced in GitLab Premium 13.2 behind a feature flag, enabled by default.
- Feature flag removed in GitLab 13.4.
You can organize Code Owners by putting them into named sections.
You can use sections for shared directories, so that multiple teams can be reviewers.
To add a section to the CODEOWNERS file, enter a section name in brackets,
followed by the files or directories, and users, groups, or subgroups:
[README Owners]
README.md @user1 @user2
internal/README.md @user2
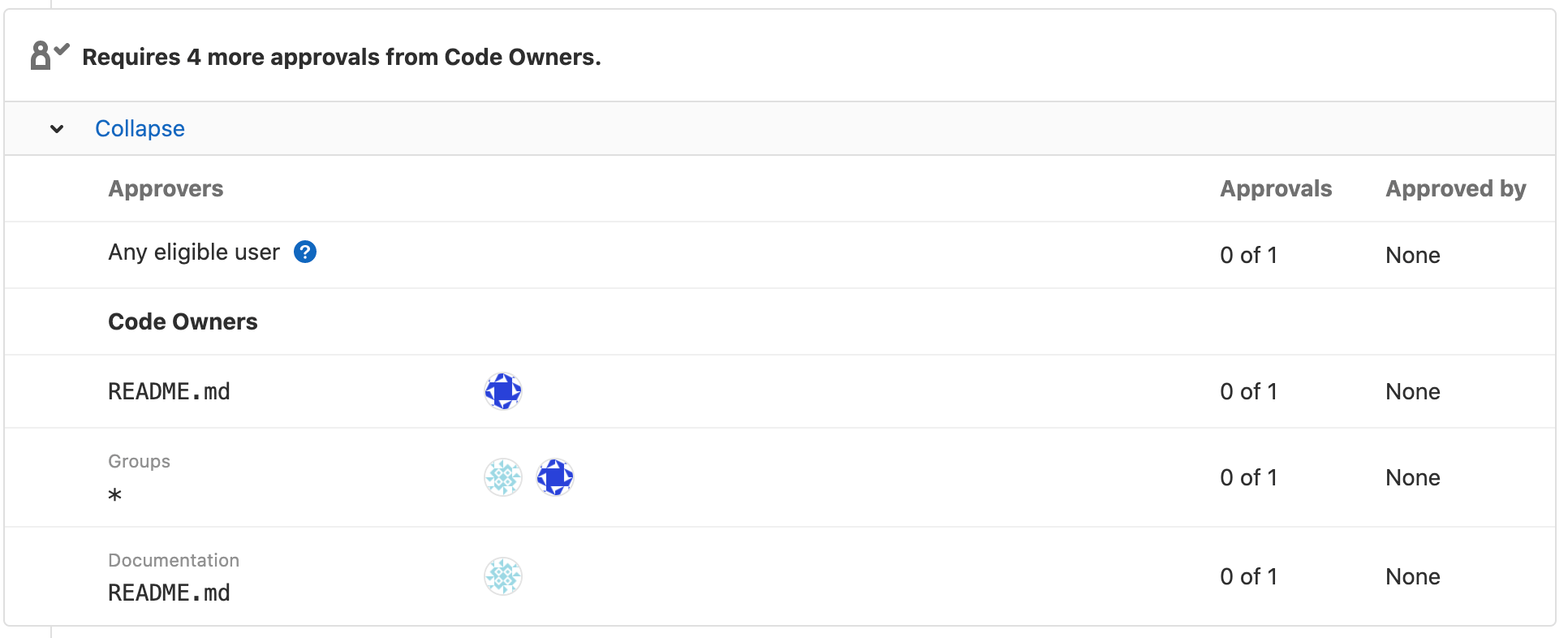
Each Code Owner in the merge request widget is listed under a label. The following image shows a Groups and Documentation section:
Sections with duplicate names
If multiple sections have the same name, they are combined. Also, section headings are not case-sensitive. For example:
[Documentation]
ee/docs/ @docs
docs/ @docs
[Database]
README.md @database
model/db/ @database
[DOCUMENTATION]
README.md @docs
This code results in three entries under the Documentation section header, and two entries under Database. The entries defined under the sections Documentation and DOCUMENTATION are combined, using the case of the first section.
Make a Code Owners section optional
Introduced in GitLab Premium 13.8.
You can designate optional sections in your Code Owners file. Prepend the
section name with the caret ^ character to treat the entire section as optional.
Optional sections enable you to designate responsible parties for various parts
of your codebase, but not require approval from them. This approach provides
a more relaxed policy for parts of your project that are frequently updated,
but don't require stringent reviews.
In this example, the [Go] section is optional:
[Documentation]
*.md @root
[Ruby]
*.rb @root
^[Go]
*.go @root
The optional Code Owners section displays in merge requests under the Approval Rules area:
If a section is duplicated in the file, and one of them is marked as optional and the other isn't, the section is required.
Optional sections in the CODEOWNERS file are treated as optional only
when changes are submitted by using merge requests. If a change is submitted directly
to the protected branch, approval from Code Owners is still required, even if the
section is marked as optional.
Allowed to Push
The Code Owner approval and protected branch features do not apply to users who are Allowed to push.
Example CODEOWNERS file
# This is an example of a CODEOWNERS file.
# Lines that start with `#` are ignored.
# app/ @commented-rule
# Specify a default Code Owner by using a wildcard:
* @default-codeowner
# Specify multiple Code Owners by using a tab or space:
* @multiple @code @owners
# Rules defined later in the file take precedence over the rules
# defined before.
# For example, for all files with a filename ending in `.rb`:
*.rb @ruby-owner
# Files with a `#` can still be accessed by escaping the pound sign:
\#file_with_pound.rb @owner-file-with-pound
# Specify multiple Code Owners separated by spaces or tabs.
# In the following case the CODEOWNERS file from the root of the repo
# has 3 Code Owners (@multiple @code @owners):
CODEOWNERS @multiple @code @owners
# You can use both usernames or email addresses to match
# users. Everything else is ignored. For example, this code
# specifies the `@legal` and a user with email `janedoe@gitlab.com` as the
# owner for the LICENSE file:
LICENSE @legal this_does_not_match janedoe@gitlab.com
# Use group names to match groups, and nested groups to specify
# them as owners for a file:
README @group @group/with-nested/subgroup
# End a path in a `/` to specify the Code Owners for every file
# nested in that directory, on any level:
/docs/ @all-docs
# End a path in `/*` to specify Code Owners for every file in
# a directory, but not nested deeper. This code matches
# `docs/index.md` but not `docs/projects/index.md`:
/docs/* @root-docs
# This code makes matches a `lib` directory nested anywhere in the repository:
lib/ @lib-owner
# This code match only a `config` directory in the root of the repository:
/config/ @config-owner
# If the path contains spaces, escape them like this:
path\ with\ spaces/ @space-owner
# Code Owners section:
[Documentation]
ee/docs @docs
docs @docs
[Database]
README.md @database
model/db @database
# This section is combined with the previously defined [Documentation] section:
[DOCUMENTATION]
README.md @docs
Troubleshooting
Approvals shown as optional
A Code Owner approval rule is optional if these conditions are not met:
- The user or group are not a member of the project or parent group.
- Code Owner approval on a protected branch has not been set up.
- The section is marked as optional.
Approvals do not show
Code Owner approval rules only update when the merge request is created.
If you update the CODEOWNERS file, close the merge request and create a new one.
User not shown as possible approver
A user might not show as an approver on the Code Owner merge request approval rules.
This result occurs when a rule prevents the specific user from approving the merge request. Check the project merge request approval setting.