* Fully automate dev setup with Gitpod This commit implements a fully-automated development setup using Gitpod.io, an online IDE for GitHub and GitLab that enables Dev-Environments-As-Code. This makes it easy for anyone to get a ready-to-code workspace for any branch, issue or pull request almost instantly with a single click. Signed-off-by: justaugustus <foo@agst.us> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .github | ||
| api | ||
| cmd/dex | ||
| connector | ||
| Documentation | ||
| examples | ||
| pkg | ||
| scripts | ||
| server | ||
| storage | ||
| version | ||
| web | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .editorconfig | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitpod.yml | ||
| .golangci.yml | ||
| ADOPTERS.md | ||
| code-of-conduct.md | ||
| DCO | ||
| docker-compose.yaml | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| go.mod | ||
| go.sum | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| MAINTAINERS | ||
| Makefile | ||
| NOTICE | ||
| README.md | ||
dex - A federated OpenID Connect provider
Dex is an identity service that uses OpenID Connect to drive authentication for other apps.
Dex acts as a portal to other identity providers through "connectors." This lets dex defer authentication to LDAP servers, SAML providers, or established identity providers like GitHub, Google, and Active Directory. Clients write their authentication logic once to talk to dex, then dex handles the protocols for a given backend.
ID Tokens
ID Tokens are an OAuth2 extension introduced by OpenID Connect and dex's primary feature. ID Tokens are JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) signed by dex and returned as part of the OAuth2 response that attest to the end user's identity. An example JWT might look like:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IjlkNDQ3NDFmNzczYjkzOGNmNjVkZDMyNjY4NWI4NjE4MGMzMjRkOTkifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJodHRwOi8vMTI3LjAuMC4xOjU1NTYvZGV4Iiwic3ViIjoiQ2djeU16UXlOelE1RWdabmFYUm9kV0kiLCJhdWQiOiJleGFtcGxlLWFwcCIsImV4cCI6MTQ5Mjg4MjA0MiwiaWF0IjoxNDkyNzk1NjQyLCJhdF9oYXNoIjoiYmk5NmdPWFpTaHZsV1l0YWw5RXFpdyIsImVtYWlsIjoiZXJpYy5jaGlhbmdAY29yZW9zLmNvbSIsImVtYWlsX3ZlcmlmaWVkIjp0cnVlLCJncm91cHMiOlsiYWRtaW5zIiwiZGV2ZWxvcGVycyJdLCJuYW1lIjoiRXJpYyBDaGlhbmcifQ.OhROPq_0eP-zsQRjg87KZ4wGkjiQGnTi5QuG877AdJDb3R2ZCOk2Vkf5SdP8cPyb3VMqL32G4hLDayniiv8f1_ZXAde0sKrayfQ10XAXFgZl_P1yilkLdknxn6nbhDRVllpWcB12ki9vmAxklAr0B1C4kr5nI3-BZLrFcUR5sQbxwJj4oW1OuG6jJCNGHXGNTBTNEaM28eD-9nhfBeuBTzzO7BKwPsojjj4C9ogU4JQhGvm_l4yfVi0boSx8c0FX3JsiB0yLa1ZdJVWVl9m90XmbWRSD85pNDQHcWZP9hR6CMgbvGkZsgjG32qeRwUL_eNkNowSBNWLrGNPoON1gMg
ID Tokens contains standard claims assert which client app logged the user in, when the token expires, and the identity of the user.
{
"iss": "http://127.0.0.1:5556/dex",
"sub": "CgcyMzQyNzQ5EgZnaXRodWI",
"aud": "example-app",
"exp": 1492882042,
"iat": 1492795642,
"at_hash": "bi96gOXZShvlWYtal9Eqiw",
"email": "jane.doe@coreos.com",
"email_verified": true,
"groups": [
"admins",
"developers"
],
"name": "Jane Doe"
}
Because these tokens are signed by dex and contain standard-based claims other services can consume them as service-to-service credentials. Systems that can already consume OpenID Connect ID Tokens issued by dex include:
For details on how to request or validate an ID Token, see "Writing apps that use dex".
Kubernetes + dex
Dex's main production use is as an auth-N addon in CoreOS's enterprise Kubernetes solution, Tectonic. Dex runs natively on top of any Kubernetes cluster using Third Party Resources and can drive API server authentication through the OpenID Connect plugin. Clients, such as the Tectonic Console and kubectl, can act on behalf users who can login to the cluster through any identity provider dex supports.
More docs for running dex as a Kubernetes authenticator can be found here.
Connectors
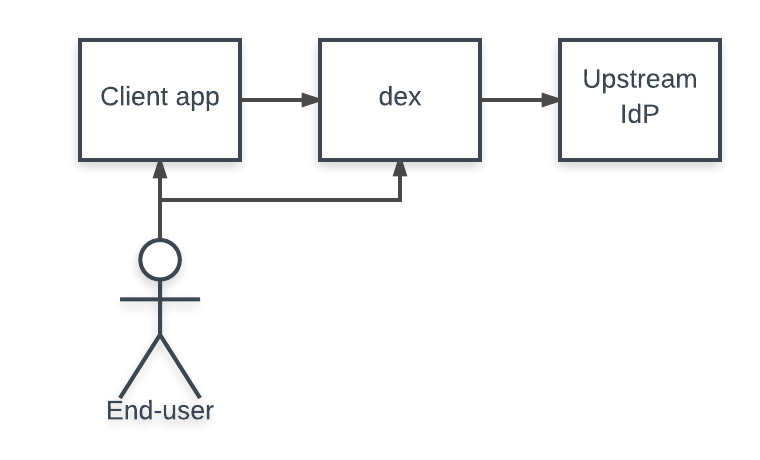
When a user logs in through dex, the user's identity is usually stored in another user-management system: a LDAP directory, a GitHub org, etc. Dex acts as a shim between a client app and the upstream identity provider. The client only needs to understand OpenID Connect to query dex, while dex implements an array of protocols for querying other user-management systems.
A "connector" is a strategy used by dex for authenticating a user against another identity provider. Dex implements connectors that target specific platforms such as GitHub, LinkedIn, and Microsoft as well as established protocols like LDAP and SAML.
Depending on the connectors limitations in protocols can prevent dex from issuing refresh tokens or returning group membership claims. For example, because SAML doesn't provide a non-interactive way to refresh assertions, if a user logs in through the SAML connector dex won't issue a refresh token to its client. Refresh token support is required for clients that require offline access, such as kubectl.
Dex implements the following connectors:
| Name | supports refresh tokens | supports groups claim | supports preferred_username claim | status | notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDAP | yes | yes | yes | stable | |
| GitHub | yes | yes | yes | stable | |
| SAML 2.0 | no | yes | no | stable | |
| GitLab | yes | yes | yes | beta | |
| OpenID Connect | yes | yes | yes | beta | Includes Salesforce, Azure, etc. |
| yes | yes | yes | alpha | ||
| yes | no | no | beta | ||
| Microsoft | yes | yes | no | beta | |
| AuthProxy | no | no | no | alpha | Authentication proxies such as Apache2 mod_auth, etc. |
| Bitbucket Cloud | yes | yes | no | alpha | |
| OpenShift | no | yes | no | stable | |
| Atlassian Crowd | yes | yes | yes * | beta | preferred_username claim must be configured through config |
| Gitea | yes | no | yes | alpha |
Stable, beta, and alpha are defined as:
- Stable: well tested, in active use, and will not change in backward incompatible ways.
- Beta: tested and unlikely to change in backward incompatible ways.
- Alpha: may be untested by core maintainers and is subject to change in backward incompatible ways.
All changes or deprecations of connector features will be announced in the release notes.
Documentation
- Getting started
- Intro to OpenID Connect
- Writing apps that use dex
- What's new in v2
- Custom scopes, claims, and client features
- Storage options
- gRPC API
- Using Kubernetes with dex
- Client libraries
Reporting a security vulnerability
Due to their public nature, GitHub and mailing lists are NOT appropriate places for reporting vulnerabilities. Please refer to CoreOS's security disclosure process when reporting issues that may be security related.
Getting help
- For feature requests and bugs, file an issue.
- For general discussion about both using and developing dex, you can join the #dexidp channel on the Kubernetes Slack, or join the dex-dev mailing list.